Abstract
Background:
Few studies have addressed the growing concerns of chronic kidney diseases in children with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate long-term kidney dysfunction and determine if urinary angiotensinogen (AGT) was suitable as a novel early biomarker for kidney dysfunction in IUGR offspring.
Methods:
Pregnant rats underwent bilateral uterine artery ligation, and as a control group, sham surgeries were performed.
Results:
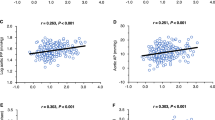
The birth weight was reduced, the urinary AGT to creatinine ratio was significantly higher at week 20, and urinary protein levels were significantly higher at week 32 in IUGR rats than in control rats. On the other hand, the histological findings at week 32 revealed long-term kidney dysfunction, more severe glomerulosclerosis, and greater glomerular diameters in IUGR rats. Moreover, AGT mRNA expression and immunohistological staining were significantly increased in IUGR rats; this suggests that the intrarenal renin–angiotensin system (RAS) contributes to renal dysfunction of IUGR offspring.
Conclusion:
Urinary AGT elevation prior to urinary protein levels suggests that AGT is an early biomarker. At week 32, kidney dysfunction was severe in IUGR rats and intrarenal RAS appeared to be one of the causes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA. Living with the past: evolution, development, and patterns of disease. Science 2004;305:1733–6.
Luyckx VA, Brenner BM. Low birth weight, nephron number, and kidney disease. Kidney Int 2005;68:S68–77.
Lim K, Lombardo P, Schneider-Kolsky M, Hilliard L, Denton KM, Black MJ. Induction of hyperglycemia in adult intrauterine growth-restricted rats: effects on renal function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2011;301:F288–94.
Shen Q, Xu H, Wei LM, Chen J, Liu HM, Guo W. A comparative proteomic study of nephrogenesis in intrauterine growth restriction. Pediatr Nephrol 2010;25:1063–72.
Shen Q, Xu H, Wei LM, Chen J, Liu HM. Intrauterine growth restriction and postnatal high-protein diet affect the kidneys in adult rats. Nutrition 2011;27:364–71.
Neitzke U, Harder T, Plagemann A. Intrauterine growth restriction and developmental programming of the metabolic syndrome: a critical appraisal. Microcirculation 2011;18:304–11.
Kusuda S, Fujimura M, Uchiyama A, Totsu S, Matsunami K ; Neonatal Research Network, Japan. Trends in morbidity and mortality among very-low-birth-weight infants from 2003 to 2008 in Japan. Pediatr Res 2012;72:531–8.
Carmody JB, Charlton JR. Short-term gestation, long-term risk: prematurity and chronic kidney disease. Pediatrics 2013;131:1168–79.
Taranta-Janusz K, Wasilewska A, Dębek W, Fiłonowicz R, Michaluk-Skutnik J. Urinary angiotensinogen as a novel marker of obstructive nephropathy in children. Acta Paediatr 2013;102:e429–33.
Saito T, Urushihara M, Kotani Y, Kagami S, Kobori H. Increased urinary angiotensinogen is precedent to increased urinary albumin in patients with type 1 diabetes. Am J Med Sci 2009;338:478–80.
Kobori H, Katsurada A, Ozawa Y, et al. Enhanced intrarenal oxidative stress and angiotensinogen in IgA nephropathy patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007;358:156–63.
Konishi Y, Nishiyama A, Morikawa T, et al. Relationship between urinary angiotensinogen and salt sensitivity of blood pressure in patients with IgA nephropathy. Hypertension 2011;58:205–11.
Nishizaki N, Hirano D, Nishizaki Y, et al. Increased urinary angiotensinogen is an effective marker of chronic renal impairment in very low birth weight children. Clin Exp Nephrol 2014;18:642–8.
Woods LL, Ingelfinger JR, Nyengaard JR, Rasch R. Maternal protein restriction suppresses the newborn renin-angiotensin system and programs adult hypertension in rats. Pediatr Res 2001;49:460–7.
Kamiyama M, Zsombok A, Kobori H. Urinary angiotensinogen as a novel early biomarker of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activation in experimental type 1 diabetes. J Pharmacol Sci 2012;119:314–23.
Urushihara M, Kobori H. Angiotensinogen expression is enhanced in the progression of glomerular disease. Int J Clin Med 2011;2:378–87.
Dillion JJ. Angiotensinogen-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensinogen receptor blockers for IgA nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 2004;24:218–24.
Fujihara CK, Malheiros DM, Zatz R, Noronha IL. Mycophenolate mofetil attenuates renal injury in the rat remnant kidney. Kidney Int 1998;54:1510–9.
Fujihara CK, Velho M, Malheiros DM, Zatz R. An extremely high dose of losartan affords superior renoprotection in the remnant model. Kidney Int 2005;67:1913–24.
Kobori H, Ozawa Y, Suzaki Y, Nishiyama A. Enhanced intrarenal angiotensinogen contributes to early renal injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:2073–80.
Hodgin JB, Rasoulpour M, Markowitz GS, D’Agati VD. Very low birth weight is a risk factor for secondary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2009;4:71–6.
Brenner BM, Lawler EV, Mackenzie HS. The hyperfiltration theory: a paradigm shift in nephrology. Kidney Int 1996;49:1774–7.
Lane PH, Steffes MW, Mauer SM. Estimation of glomerular volume: a comparison of four methods. Kidney Int 1992;41:1085–9.
Yoshida Y, Fogo A, Ichikawa I. Glomerular hemodynamic changes vs. hypertrophy in experimental glomerular sclerosis. Kidney Int 1989;35:654–60.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Yumiko Sakurai, of the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, Juntendo University; Tomomi Ikeda; and Takako Ikegami of the Division of Molecular and Biochemical Research, Biomedical Research Center, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine; Yuuko Kojima and Shinji Nakamura, of the Division of Biomedical Imaging Research, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, for their extended technical support; and Takeshi Asakura and Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review for detailed and precise advice related to the writing of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murano, Y., Nishizaki, N., Endo, A. et al. Evaluation of kidney dysfunction and angiotensinogen as an early novel biomarker of intrauterine growth restricted offspring rats. Pediatr Res 78, 678–682 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.153
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.153
This article is cited by
-
Role of renal sympathetic nerve activity in prenatal programming of hypertension
Pediatric Nephrology (2018)