Abstract
Background:
Earlier studies on seasonality in growth reported the largest height gains during spring and largest body weight gains during autumn. We examined seasonality in height, body weight, BMI, fat mass index (FMI), and fat-free mass index (FFMI) among contemporary Danish 8–11-y olds.
Methods:
A total of 760 children from the OPUS School Meal Study provided >2,200 measurements on height, body weight, and composition between September and June. Average velocities were calculated using change-score analyses based on 3-mo intervals. As a complementary analysis, point velocities derived from estimated growth curves were fitted using semiparametric regression that included covariate adjustment and allowed flexible modeling of the time trend.
Results:
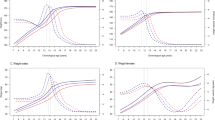
Average velocities showed the following trends: height was higher than the average (6.10 cm/y) in January–April. Body weight was below the average (4.02 kg/y) in August–January and above in January–May; BMI (average: 0.49 kg/ m2/y) and FFMI (average: 0.17 kg/m2/y) showed similar trends. In contrast, FMI was above the average (0.38 kg/m2/y) in November–March. Similar trends were seen for point velocities.
Conclusion:
Our findings suggest seasonality in growth and body composition of Danish children. We recovered the well-known height velocity peak during spring time, but unlike earlier studies, we found coincident peaks in body weight, BMI, and FFMI velocities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Malling-Hansen R. Periods in Growth of Children and in the Heat of the Sun: Empirical Findings. Copenhagen, Denmark: Hoffenberg & Traps Etablissement, 1886.
Bransby ER. The seasonal growth of children. Med Off 1945;73:149, 157, 165.
Marshall WA. Evaluation of growth rate in height over periods of less than one year. Arch Dis Child 1971;46:414–20.
Orr JB, Clark ML. A report on seasonal variation in the growth of school-children. Lancet 1930;216:365–7.
Reynolds EL, Sontag LW. Seasonal variations in weight, height and appearance of ossification centres. J Pediatr 1944;24:524.
Takahashi E. Growth and environmental factors in Japan. Hum Biol 1966;38:112–30.
Emerson H. Seasonal variation in growth of school children. JAMA 1927;89:1326–31.
Porter TW. The seasonal variation in the growth of Boston school children. Am J Phys 1920;52:121–31.
Kondo S, Takahashi E, Kato K, Takahashi S, Ikeda M. Secular trends in height and weight of Japanese pupils. Tohoku J Exp Med 1978;126:203–13.
Ikeda M, Watanabe T. Constant growth of primary school children throughout four seasons of year. Tohoku J Exp Med 1985;145:413–8.
Gelander L, Karlberg J, Albertsson-Wikland K. Seasonality in lower leg length velocity in prepubertal children. Acta Paediatr 1994;83:1249–54.
Tillmann V, Thalange NK, Foster PJ, Gill MS, Price DA, Clayton PE. The relationship between stature, growth, and short-term changes in height and weight in normal prepubertal children. Pediatr Res 1998;44:882–6.
Gelander L, Blum WF, Larsson L, Rosberg S, Albertsson-Wikland K. Monthly measurements of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 in healthy prepubertal children: characterization and relationship with growth: the 1-year growth study. Pediatr Res 1999;45:377–83.
Land C, Blum WF, Stabrey A, Schoenau E. Seasonality of growth response to GH therapy in prepubertal children with idiopathic growth hormone deficiency. Eur J Endocrinol 2005;152:727–33.
Shulman DI, Frane J, Lippe B. Is there “seasonal” variation in height velocity in children treated with growth hormone? Data from the National Cooperative Growth Study. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 2013;2013:2.
Baranowski T, O’Connor T, Johnston C, et al. School year versus summer differences in child weight gain: a narrative review. Child Obes 2014;10:18–24.
Rodriguez AX, Olvera N, Leung P, O’Connor DP, Smith DW. Association between the summer season and body fatness and aerobic fitness among Hispanic children. J Sch Health 2014;84:233–8.
Luboshitzky R, Yanai D, Shen-Orr Z, Israeli E, Herer P, Lavie P. Daily and seasonal variations in the concentration of melatonin in the human pineal gland. Brain Res Bull 1998;47:271–6.
Valcavi R, Zini M, Maestroni GJ, Conti A, Portioli I. Melatonin stimulates growth hormone secretion through pathways other than the growth hormone-releasing hormone. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1993;39:193–9.
Cahill S, Tuplin E, Holahan MR. Circannual changes in stress and feeding hormones and their effect on food-seeking behaviors. Front Neurosci 2013;7:140.
Gracia-Marco L, Ortega FB, Ruiz JR, et al.; Helena Study Group. Seasonal variation in physical activity and sedentary time in different European regions. The HELENA study. J Sports Sci 2013;31:1831–40.
Hjorth MF, Chaput JP, Michaelsen K, Astrup A, Tetens I, Sjödin A. Seasonal variation in objectively measured physical activity, sedentary time, cardio-respiratory fitness and sleep duration among 8-11 year-old Danish children: a repeated-measures study. BMC Public Health 2013;13:808.
Damsgaard CT, Dalskov SM, Petersen RA, et al. Design of the OPUS School Meal Study: a randomised controlled trial assessing the impact of serving school meals based on the New Nordic Diet. Scand J Public Health 2012;40:693–703.
Damsgaard CT, Dalskov SM, Laursen RP, et al. Provision of healthy school meals does not affect the metabolic syndrome score in 8-11-year-old children, but reduces cardiometabolic risk markers despite increasing waist circumference. Br J Nutr 2014;112:1826–36.
Morris NM, Udry JR. Validation of a self-administered instrument to assess stage of adolescent development. J Youth Adolesc 1980;9:271–80.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 2000;320:1240–3.
Cole TJ, Flegal KM, Nicholls D, Jackson AA. Body mass index cut offs to define thinness in children and adolescents: international survey. BMJ 2007;335:194.
VanItallie TB, Yang MU, Heymsfield SB, Funk RC, Boileau RA. Height-normalized indices of the body’s fat-free mass and fat mass: potentially useful indicators of nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr 1990;52:953–9.
Margulies L, Horlick M, Thornton JC, Wang J, Ioannidou E, Heymsfield SB. Reproducibility of pediatric whole body bone and body composition measures by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry using the GE Lunar Prodigy. J Clin Densitom 2005;8:298–304.
Fan J, Zhang J-T. Two-step estimation of functional linear models with applications to longitudinal data. J R Soc Statist Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 2000;62:303–322.
Shi M, Weiss RE, Taylor JMG. An analysis of paediatric CD4 counts for acquired immune deficiency syndrome using flexible random curves. J R Soc Statist Soc Ser C Appl Stat 1996;45:151–63.
Wu H, Zhang J-T. Local polynomial mixed-effects models for longitudinal data. J Am Statist Assoc 2002;97:883–97.
Laursen RP, Dalskov SM, Damsgaard CT, Ritz C. Back-transformation of treatment differences–an approximate method. Eur J Clin Nutr 2014;68:277–80.
Silverman BW. The Kernel Method for Univariate Data. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis. 1st ed. London: Chapman and Hall, 1986:34–74.
Loader C. Local Regression and Likelihood. New York: Springer, 1999:101–5.
Hothorn T, Bretz F, Westfall P. Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom J 2008;50:346–63.
Acknowledgements
We thank the children and their parents for their participation and the schools for their cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalskov, SM., Ritz, C., Larnkjær, A. et al. Seasonal variations in growth and body composition of 8–11-y-old Danish children . Pediatr Res 79, 358–363 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.206
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.206
This article is cited by
-
Association between time of assessment within a school year and physical fitness of primary school children
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Evaluating the seasonality of growth in infants using a mobile phone application
npj Digital Medicine (2020)