Abstract
Background:
Despite widespread human exposure to biphenol A (BPA), limited studies exist on the association of BPA with adverse health outcomes in young children. This study aims to investigate the effect of prenatal exposure to BPA on toll-like receptor–induced cytokine responses in neonates and its association with infectious diseases later in life.
Methods:
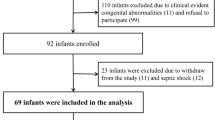
Cord bloods were collected from 275 full-term neonates. Production of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 were evaluated after stimulating mononuclear cells with toll-like receptor ligands (TLR1-4 and 7–8). Serum BPA concentrations were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Bacteria from nasopharyngeal specimens were identified with multiplex PCR and culture method.
Result:
Result showed significant association between cord BPA concentration and TLR3- and TLR4-stimulated TNF-α response (P = 0.001) and that of TLR78-stimulated IL-6 response (P = 0.03). Clinical analysis did not show prenatal BPA exposure to be correlated with infection or bacterial colonization during the first year of life.
Conclusion:
This is the first cohort study that indicated prenatal BPA exposure to play a part in TLR-related innate immune response of neonatal infants. However, despite an altered immune homeostasis, result did not show such exposure to be associated with increased risk of infection during early infancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Teeguarden JG, Hanson-Drury S. A systematic review of bisphenol A “low dose” studies in the context of human exposure: a case for establishing standards for reporting “low-dose” effects of chemicals. Food Chem Toxicol 2013;63:938–48.
Weisglas-Kuperus N, Patandin S, Berbers GA, et al. Immunologic effects of background exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and dioxins in Dutch preschool children. Environ Health Perspect 2000;108:1203–7.
Jusko TA, De Roos AJ, Schwartz SM, et al. Maternal and early postnatal polychlorinated biphenyl exposure in relation to total serum immunoglobulin concentrations in 6-month-old infants. J Immunotoxicol 2011;8:95–100.
Lee MH, Chung SW, Kang BY, et al. Enhanced interleukin-4 production in CD4+ T cells and elevated immunoglobulin E levels in antigen-primed mice by bisphenol A and nonylphenol, endocrine disruptors: involvement of nuclear factor-AT and Ca2+. Immunology 2003;109:76–86.
O’Brien E, Dolinoy DC, Mancuso P. Perinatal bisphenol A exposures increase production of pro-inflammatory mediators in bone marrow-derived mast cells of adult mice. J Immunotoxicol 2014;11:205–12.
Holladay SD, Xiao S, Diao H, et al. Perinatal bisphenol A exposure in C57B6/129svj male mice: potential altered cytokine/chemokine production in adulthood. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2010;7:2845–52.
Liao SL, Yeh KW, Lai SH, Lee WI, Huang JL. Maturation of Toll-like receptor 1-4 responsiveness during early life. Early Hum Dev 2013;89:473–8.
Shen CM, Lin SC, Niu DM, Kou YR. Development of monocyte Toll-like receptor 2 and Toll-like receptor 4 in preterm newborns during the first few months of life. Pediatr Res 2013;73:685–91.
Förster-Waldl E, Sadeghi K, Tamandl D, et al. Monocyte toll-like receptor 4 expression and LPS-induced cytokine production increase during gestational aging. Pediatr Res 2005;58:121–4.
Kosarac I, Kubwabo C, Lalonde K, Foster W. A novel method for the quantitative determination of free and conjugated bisphenol A in human maternal and umbilical cord blood serum using a two-step solid phase extraction and gas chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2012;898:90–4.
Kuroda N, Kinoshita Y, Sun Y, et al. Measurement of bisphenol A levels in human blood serum and ascitic fluid by HPLC using a fluorescent labeling reagent. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2003;30:1743–9.
Aris A. Estimation of bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations in pregnant women, fetuses and nonpregnant women in Eastern Townships of Canada. Reprod Toxicol 2014;45:8–13.
Tsai MH, Huang SH, Chen CL, et al. Pathogenic bacterial nasopharyngeal colonization and its impact on respiratory diseases in the first year of life: the PATCH Birth Cohort Study. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2015;34:652–8.
Følsgaard NV, Schjørring S, Chawes BL, et al. Pathogenic bacteria colonizing the airways in asymptomatic neonates stimulates topical inflammatory mediator release. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013;187:589–95.
Byun JA, Heo Y, Kim YO, Pyo MY. Bisphenol A-induced downregulation of murine macrophage activities in vitro and ex vivo. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2005;19:19–24.
Tian X, Takamoto M, Sugane K. Bisphenol A promotes IL-4 production by Th2 cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2003;132:240–7.
Guo H, Liu T, Uemura Y, et al. Bisphenol A in combination with TNF-alpha selectively induces Th2 cell-promoting dendritic cells in vitro with an estrogen-like activity. Cell Mol Immunol 2010;7:227–34.
Yan H, Takamoto M, Sugane K. Exposure to bisphenol A prenatally or in adulthood promotes T(H)2 cytokine production associated with reduction of CD4CD25 regulatory T cells. Environ Health Perspect 2008;116:514–9.
Chao TC, Van Alten PJ, Greager JA, Walter RJ. Steroid sex hormones regulate the release of tumor necrosis factor by macrophages. Cell Immunol 1995;160:43–9.
Liu Y, Mei C, Liu H, et al. Modulation of cytokine expression in human macrophages by endocrine-disrupting chemical bisphenol-A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014;451:592–8.
Zhu J, Jiang L, Liu Y, et al. MAPK and NF-κB pathways are involved in bisphenol A-induced TNF-α and IL-6 production in BV2 microglial cells. Inflammation 2015;38:637–48.
Roy A, Bauer SM, Lawrence BP. Developmental exposure to bisphenol A modulates innate but not adaptive immune responses to influenza A virus infection. PLoS One 2012;7:e38448.
Sugita-Konishi Y, Shimura S, Nishikawa T, Sunaga F, Naito H, Suzuki Y. Effect of Bisphenol A on non-specific immunodefenses against non-pathogenic Escherichia coli. Toxicol Lett 2003;136:217–27.
Calippe B, Douin-Echinard V, Delpy L, et al. 17Beta-estradiol promotes TLR4-triggered proinflammatory mediator production through direct estrogen receptor alpha signaling in macrophages in vivo. J Immunol 2010;185:1169–76.
Lee J, Lee SJ, Lim KT. CTB glycoprotein (75kDa) inhibits IgE releasing, TNF-α and IL-6 expressed by bisphenol A in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol 2012;50:2109–17.
Braun JM, Hauser R. Bisphenol A and children’s health. Curr Opin Pediatr 2011;23:233–9.
Rogers JA, Metz L, Yong VW. Review: endocrine disrupting chemicals and immune responses: a focus on bisphenol-A and its potential mechanisms. Mol Immunol 2013;53:421–30.
Goto M, Takano-Ishikawa Y, Ono H, Yoshida M, Yamaki K, Shinmoto H. Orally administered bisphenol A disturbed antigen specific immunoresponses in the naïve condition. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2007;71:2136–43.
Sawai C, Anderson K, Walser-Kuntz D. Effect of bisphenol A on murine immune function: modulation of interferon-gamma, IgG2a, and disease symptoms in NZB X NZW F1 mice. Environ Health Perspect 2003;111:1883–7.
Lawrence BP. Environmental toxins as modulators of antiviral immune responses. Viral Immunol 2007;20:231–42.
Ménard S, Guzylack-Piriou L, Lencina C, et al. Perinatal exposure to a low dose of bisphenol A impaired systemic cellular immune response and predisposes young rats to intestinal parasitic infection. PLoS One 2014;9:e112752.
Gascon M, Casas M, Morales E, et al. Prenatal exposure to bisphenol A and phthalates and childhood respiratory tract infections and allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;135:370–8.
Kishi R, Kobayashi S, Ikeno T, et al.; Members of the Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Ten years of progress in the Hokkaido birth cohort study on environment and children’s health: cohort profile–updated 2013. Environ Health Prev Med 2013;18:429–50.
Teeguarden J, Hanson-Drury S, Fisher JW, Doerge DR. Are typical human serum BPA concentrations measurable and sufficient to be estrogenic in the general population? Food Chem Toxicol 2013;62:949–63.
Vandenberg LN, Chahoud I, Heindel JJ, Padmanabhan V, Paumgartten FJ, Schoenfelder G. Urinary, circulating, and tissue biomonitoring studies indicate widespread exposure to bisphenol A. Cien Saude Colet 2012;17:407–34.
Vandenberg LN, Hauser R, Marcus M, Olea N, Welshons WV. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod Toxicol 2007;24:139–77.
Ikezuki Y, Tsutsumi O, Takai Y, Kamei Y, Taketani Y. Determination of bisphenol A concentrations in human biological fluids reveals significant early prenatal exposure. Hum Reprod 2002;17:2839–41.
Balows A. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 5th edn. Washington, DC: American society for microbiology, 1991.
Hendolin PH, Paulin L, Ylikoski J. Clinically applicable multiplex PCR for four middle ear pathogens. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38:125–32.
Schwalbe R, Steele-Moore L, Goodwin AC. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Protocols. Florida: Taylor & Francis Group; CRC Press, 2007.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the families for their participation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, SL., Tsai, MH., Lai, SH. et al. Prenatal exposure to bisphenol-A is associated with Toll-like receptor–induced cytokine suppression in neonates. Pediatr Res 79, 438–444 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.234
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.234
This article is cited by
-
Sex-dependent dysregulation of human neutrophil responses by bisphenol A
Environmental Health (2021)
-
Effect of bisphenol A on human neutrophils immunophenotype
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Infant anemia is associated with reduced TLR-stimulated cytokine responses and increased nasopharyngeal colonization with Moxarella catarrhalis
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Environmental Mechanisms of Neurodevelopmental Toxicity
Current Environmental Health Reports (2018)
-
Caesarean Section is associated with reduced perinatal cytokine response, increased risk of bacterial colonization in the airway, and infantile wheezing
Scientific Reports (2017)