Abstract
Background:
Bacterial contact in utero modulates fetal and neonatal immune responses. Maternal probiotic supplementation reduces the risk of immune-mediated disease in the infant. We investigated the immunomodulatory properties of live Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and its SpaC pilus adhesin in human fetal intestinal models.
Methods:
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α mRNA expression was measured by qPCR in a human fetal intestinal organ culture model exposed to live L. rhamnosus GG and proinflammatory stimuli. Binding of recombinant SpaC pilus protein to intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) was assessed in human fetal intestinal organ culture and the human fetal intestinal epithelial cell line H4 by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence, respectively. TLR-related gene expression in fetal ileal organ culture after exposure to recombinant SpaC was assessed by qPCR.
Results:
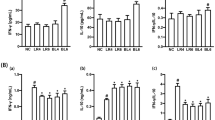
Live L. rhamnosus GG significantly attenuates pathogen-induced TNF-α mRNA expression in the human fetal gut. Recombinant SpaC protein was found to adhere to the fetal gut and to modulate varying levels of TLR-related gene expression.
Conclusion:
The human fetal gut is responsive to luminal microbes. L. rhamnosus GG significantly attenuates fetal intestinal inflammatory responses to pathogenic bacteria. The L. rhamnosus GG pilus adhesin SpaC binds to immature human IECs and directly modulates IEC innate immune gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Rautava S, Luoto R, Salminen S, Isolauri E . Microbial contact during pregnancy, intestinal colonization and human disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:565–76.
Goldenberg RL, Culhane JF, Iams JD, Romero R . Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet 2008;371:75–84.
Steel JH, Malatos S, Kennea N, et al. Bacteria and inflammatory cells in fetal membranes do not always cause preterm labor. Pediatr Res 2005;57:404–11.
Satokari R, Grönroos T, Laitinen K, Salminen S, Isolauri E . Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus DNA in the human placenta. Lett Appl Microbiol 2009;48:8–12.
Rautava S, Collado MC, Salminen S, Isolauri E . Probiotics modulate host-microbe interaction in the placenta and fetal gut: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neonatology 2012;102:178–84.
Mshvildadze M, Neu J, Shuster J, Theriaque D, Li N, Mai V . Intestinal microbial ecology in premature infants assessed with non-culture-based techniques. J Pediatr 2010;156:20–5.
Fichorova RN, Onderdonk AB, Yamamoto H, et al.; Extremely Low Gestation Age Newborns (ELGAN) Study Investigators. Maternal microbe-specific modulation of inflammatory response in extremely low-gestational-age newborns. MBio 2011;2:e00280–10.
Isolauri E, Rautava S, Salminen S . Probiotics in the development and treatment of allergic disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2012;41:747–62.
Rautava S, Kainonen E, Salminen S, Isolauri E . Maternal probiotic supplementation during pregnancy and breast-feeding reduces the risk of eczema in the infant. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;130:1355–60.
von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Satokari R, et al. Mucosal adhesion properties of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG SpaCBA and SpaFED pilin subunits. Appl Environ Microbiol 2010;76:2049–57.
Tripathi P, Beaussart A, Alsteens D, et al. Adhesion and nanomechanics of pili from the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. ACS Nano 2013;7:3685–97.
Kankainen M, Paulin L, Tynkkynen S, et al. Comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals pili containing a human- mucus binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009;106:17193–8.
Reunanen J, von Ossowski I, Hendrickx AP, Palva A, de Vos WM . Characterization of the SpaCBA pilus fibers in the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Appl Environ Microbiol 2012;78:2337–44.
Lebeer S, Claes I, Tytgat HL, et al. Functional analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG pili in relation to adhesion and immunomodulatory interactions with intestinal epithelial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 2012;78:185–93.
von Ossowski I, Pietilä TE, Rintahaka J, et al. Using recombinant Lactococci as an approach to dissect the immunomodulating capacity of surface piliation in probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. PLoS ONE 2013;8:e64416.
Bermudez-Brito M, Muñoz-Quezada S, Gomez-Llorente C, et al. Human intestinal dendritic cells decrease cytokine release against Salmonella infection in the presence of Lactobacillus paracasei upon TLR activation. PLoS ONE 2012;7:e43197.
Ganguli K, Meng D, Rautava S, Lu L, Walker WA, Nanthakumar N . Probiotics prevent necrotizing enterocolitis by modulating enterocyte genes that regulate innate immune-mediated inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2013;304:G132–41.
DiGiulio DB . Diversity of microbes in amniotic fluid. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;17:2–11.
Onderdonk AB, Delaney ML, DuBois AM, Allred EN, Leviton A . Detection of bacteria in placental tissues obtained from extremely low gestational age neonates. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008;198:110 e1–7.
Koren O, Goodrich JK, Cullender TC, et al. Host remodeling of the gut microbiome and metabolic changes during pregnancy. Cell 2012;150:470–80.
Konstantinov SR, van der Woude CJ, Peppelenbosch MP . Do pregnancy-related changes in the microbiome stimulate innate immunity? Trends Mol Med 2013;19:454–9.
Perez PF, Doré J, Leclerc M, et al. Bacterial imprinting of the neonatal immune system: lessons from maternal cells? Pediatrics 2007;119:e724–32.
Jiménez E, Fernández L, Marín ML, et al. Isolation of commensal bacteria from umbilical cord blood of healthy neonates born by cesarean section. Curr Microbiol 2005;51:270–4.
Roduit C, Wohlgensinger J, Frei R, et al.; PASTURE Study Group. Prenatal animal contact and gene expression of innate immunity receptors at birth are associated with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;127:179–85, 185.e1.
Conrad ML, Ferstl R, Teich R, et al. Maternal TLR signaling is required for prenatal asthma protection by the nonpathogenic microbe Acinetobacter lwoffii F78. J Exp Med 2009;206:2869–77.
Nanthakumar NN, Fusunyan RD, Sanderson I, Walker WA . Inflammation in the developing human intestine: A possible pathophysiologic contribution to necrotizing enterocolitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97:6043–8.
Sanderson IR, Ezzell RM, Kedinger M, et al. Human fetal enterocytes in vitro: modulation of the phenotype by extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996;93:7717–22.
Claud EC, Savidge T, Walker WA . Modulation of human intestinal epithelial cell IL-8 secretion by human milk factors. Pediatr Res 2003;53:419–25.
Rautava J, Jee KJ, Miettinen PJ, et al. ERBB receptors in developing, dysplastic and malignant oral epithelia. Oral Oncol 2008;44:227–35.
Acknowledgements
All authors were involved in designing the research, data analyses, and writing the report. All authors take responsibility for the final report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganguli, K., Collado, M., Rautava, J. et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and its SpaC pilus adhesin modulate inflammatory responsiveness and TLR-related gene expression in the fetal human gut. Pediatr Res 77, 528–535 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.5
This article is cited by
-
The Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Genetic and Metabolic Profiles in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins (2019)
-
Adhesion and Colonization of the Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus Labeled by Dsred2 in Mouse Gut
Current Microbiology (2019)
-
New insights about pilus formation in gut-adapted Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG from the crystal structure of the SpaA backbone-pilin subunit
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Isolated exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG alleviated adipogenesis mediated by TLR2 in mice
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Immunomodulation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG)-derived soluble factors on antigen-presenting cells of healthy blood donors
Scientific Reports (2016)