Abstract
Background:
Protein intake may modulate cardiac structure and function in pathological conditions, but there is a lack of knowledge on potential effects in healthy infants.
Methods:
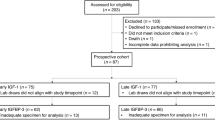
Secondary analysis of an ongoing randomized clinical trial comparing two groups of infants receiving a higher (HP) or lower (LP) protein content formula in the first year of life, and compared with an observational group of breastfed (BF) infants. Growth and dietary intake were assessed periodically from birth to 2 y. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) axis parameters were analyzed at 6 mo in a blood sample. At 2 y, cardiac mass and function were assessed by echocardiography.
Results:
HP infants (n = 50) showed a higher BMI z-score at 2 y compared with LP (n = 47) or BF (n = 44). Cardiac function parameters were increased in the HP group compared with the LP and were directly related to the protein intake during the first 6 mo of life. Moreover, there was an increase in free IGF-1 in the HP group at 6 mo.
Conclusion:
A moderate increase in protein supply during the first year of life is associated with higher cardiac function parameters at 2 y. IGF-1 axis modifications may, at least in part, underlie these effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lucas A. Programming by early nutrition: an experimental approach. J Nutr 1998;128:Suppl 2:401S–6S.
Koletzko B. Early nutrition and its later consequences: new opportunities. Adv Exp Med Biol 2005;569:1–12.
Escribano J, Luque V, Ferre N, et al. Increased protein intake augments kidney volume and function in healthy infants. Kidney Int 2011;79:783–90.
Metges CC. Longterm effects of pre- and postnatal exposure to low and high dietary protein levels. Evidence from epidemiological studies and controlled animal experiments. Adv Exp Med Biol 2005;569:64–8.
Murray BM, Campos SP, Schoenl M, MacGillivray MH. Effect of dietary protein intake on renal growth: possible role of insulin-like growth factor-I. J Lab Clin Med 1993;122:677–85.
Koletzko B, von Kries R, Closa R, et al.; European Childhood Obesity Trial Study Group. Lower protein in infant formula is associated with lower weight up to age 2 y: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;89:1836–45.
Luque V, Escribano J, Grote V, et al.; European Childhood Obesity Project. Does insulin-like growth factor-1 mediate protein-induced kidney growth in infants? A secondary analysis from a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Res 2013;74:223–9.
Elmes MJ, Gardner DS, Langley-Evans SC. Fetal exposure to a maternal low-protein diet is associated with altered left ventricular pressure response to ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Br J Nutr 2007;98:93–100.
Kothari SS, Patel TM, Shetalwad AN, Patel TK. Left ventricular mass and function in children with severe protein energy malnutrition. Int J Cardiol 1992;35:19–25.
Ocal B, Unal S, Zorlu P, Tezic HT, Oğuz D. Echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac functions and left ventricular mass in children with malnutrition. J Paediatr Child Health 2001;37:14–7.
Faddan NH, Sayh KI, Shams H, Badrawy H. Myocardial dysfunction in malnourished children. Ann Pediatr Cardiol 2010;3:113–8.
Moreira AS, Teixeira Teixeira M, da Silveira Osso F, et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy induced by overnutrition early in life. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2009;19:805–10.
Maison P, Tropeano AI, Macquin-Mavier I, Giustina A, Chanson P. Impact of somatostatin analogs on the heart in acromegaly: a metaanalysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:1743–7.
Minniti G, Jaffrain-Rea ML, Moroni C, et al. Echocardiographic evidence for a direct effect of GH/IGF-I hypersecretion on cardiac mass and function in young acromegalics. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1998;49:101–6.
Heineke J, Molkentin JD. Regulation of cardiac hypertrophy by intracellular signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006;7:589–600.
Cittadini A, Strömer H, Katz SE, et al. Differential cardiac effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in the rat. A combined in vivo and in vitro evaluation. Circulation 1996;93:800–9.
Zhou YT, Grayburn P, Karim A, et al. Lipotoxic heart disease in obese rats: implications for human obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97:1784–9.
Scognamiglio R, Piccolotto R, Negut C, Tiengo A, Avogaro A. Oral amino acids in elderly subjects: effect on myocardial function and walking capacity. Gerontology 2005;51:302–8.
Weber M, Grote V, Closa-Monasterolo R, et al.; European Childhood Obesity Trial Study Group. Lower protein content in infant formula reduces BMI and obesity risk at school age: follow-up of a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2014;99:1041–51.
Chess DJ, Lei B, Hoit BD, Azimzadeh AM, Stanley WC. Effects of a high saturated fat diet on cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction in response to pressure overload. J Card Fail 2008;14:82–8.
Iacobellis G, Ribaudo MC, Zappaterreno A, Iannucci CV, Di Mario U, Leonetti F. Adapted changes in left ventricular structure and function in severe uncomplicated obesity. Obes Res 2004;12:1616–21.
Escribano J, Luque V, Ferre N, et al.; European Childhood Obesity Trial Study Group. Effect of protein intake and weight gain velocity on body fat mass at 6 months of age: the EU Childhood Obesity Programme. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012;36:548–53.
Stettler N, Zemel BS, Kumanyika S, Stallings VA. Infant weight gain and childhood overweight status in a multicenter, cohort study. Pediatrics 2002;109:194–9.
Webb JG, Kiess MC, Chan-Yan CC. Malnutrition and the heart. CMAJ 1986;135:753–8.
de Simone G, Daniels SR, Devereux RB, et al. Left ventricular mass and body size in normotensive children and adults: assessment of allometric relations and impact of overweight. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992;20:1251–60.
Martin RM, Ness AR, Gunnell D, Emmett P, Davey Smith G ; ALSPAC Study Team. Does breast-feeding in infancy lower blood pressure in childhood? The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Circulation 2004;109:1259–66.
Hoppe C, Udam TR, Lauritzen L, Mølgaard C, Juul A, Michaelsen KF. Animal protein intake, serum insulin-like growth factor I, and growth in healthy 2.5-y-old Danish children. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;80:447–52.
Axelsson I. Effects of high protein intakes. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Progr 2006;58:121–9; discussion 129–31.
Escribano J, Luque V, Ferre N, et al. Increased protein intake augments kidney volume and function in healthy infants. Kidney Int 2011;79:783–90.
Axelsson IE, Ivarsson SA, Räihä NC. Protein intake in early infancy: effects on plasma amino acid concentrations, insulin metabolism, and growth. Pediatr Res 1989;26:614–7.
Karlberg J, Jalil F, Lam B, Low L, Yeung CY. Linear growth retardation in relation to the three phases of growth. Eur J Clin Nutr 1994;48:Suppl 1:S25–43; discussion S43–4.
McMullen JR. Role of insulin-like growth factor 1 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase in a setting of heart disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2008;35:349–54.
Petretta M, Colao A, Sardu C, et al. NT-proBNP, IGF-I and survival in patients with chronic heart failure. Growth Horm IGF Res 2007;17:288–96.
Colao A. The GH-IGF-I axis and the cardiovascular system: clinical implications. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2008;69:347–58.
Langley-Evans SC. Nutritional programming of disease: unravelling the mechanism. J Anat 2009;215:36–51.
Lauer MS, Anderson KM, Kannel WB, Levy D. The impact of obesity on left ventricular mass and geometry. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA 1991;266:231–6.
Schiess S, Grote V, Scaglioni S, et al.; European Childhood Obesity Project. Introduction of complementary feeding in 5 European countries. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2010;50:92–8.
Comission E. Commission Directive 91/321/EEC of 14 May 1991 on infant and follow-on formulae. Off J Eur Comm 1991;35–49.
Mosteller RD. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N Engl J Med 1987;317:1098.
Group WHOMGRS. WHO Child Growth Standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr Suppl 2006;450:S76–85.
Socha P, Grote V, Gruszfeld D, et al.; European Childhood Obesity Trial Study Group. Milk protein intake, the metabolic-endocrine response, and growth in infancy: data from a randomized clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;94:Suppl 6:1776S–84S.
Rosa EC, Moyses VA, Sesso RC, et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy evaluation in obese hypertensive patients: effect of left ventricular mass index criteria. Arq Bras Cardiol 2002;78:341–51.
Sahn DJ, DeMaria A, Kisslo J, Weyman A. Recommendations regarding quantitation in M-mode echocardiography: results of a survey of echocardiographic measurements. Circulation 1978;58:1072–83.
Schofield WN. Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr 1985;39:Suppl 1:5–41.
Butte NF, Wong WW, Hopkinson JM, Heinz CJ, Mehta NR, Smith EO. Energy requirements derived from total energy expenditure and energy deposition during the first 2 y of life. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;72:1558–69.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the families took part enthusiastically in the Childhood Obesity Project. Investigators and their institutions participated in the European Childhood Obesity Project: Beyer J., Fritsch M., Haile G., Handel U., Hannibal I., Kreichauf S., Pawellek I., Schiess S., Verwied-Jorky S., von Kries R., Weber M. (Children’s University Hospital, University of Munich Medical Centre, Munich, Germany), Dobrzańska A., Gruszfeld D., Wierzbicka A., Socha P., Stolarczyk A., Socha J. (Children’s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw, Poland), Carlier C., Dain E., Goyens P., Van Hees J.N., Hoyos J., Langhendries J.P., Martin F., Poncelet P., Xhonneux A., (ULB Bruxelles and CHC St Vincent Liege), Perrin, E. (Danone Research Centre for Specialised Nutrition, Schiphol, The Netherlands), Agostoni C., Giovannini M., Re Dionigi A., Riva E., Scaglioni S., Vecchi F. (University of Milan), Mendez-Riera G., Zaragoza-Jordana M., Gispert-Llaurado M., Rubio-Torrents C. (Universitat Rovira I Virgili, Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collell, R., Closa-Monasterolo, R., Ferré, N. et al. Higher protein intake increases cardiac function parameters in healthy children: metabolic programming by infant nutrition—secondary analysis from a clinical trial. Pediatr Res 79, 880–888 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2016.30
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2016.30