Abstract
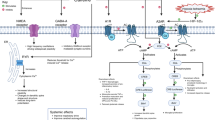
Few signaling molecules have the potential to influence the developing mammal as the nucleoside adenosine. Adenosine levels increase rapidly with tissue hypoxia and inflammation. Adenosine antagonists include the methylxanthines caffeine and theophylline. The receptors that transduce adenosine action are the A1, A2a, A2b, and A3 adenosine receptors (ARs). In the postnatal period, A1AR activation may contribute to white matter injury in the preterm infant by altering oligodendrocyte (OL) development. In models of perinatal brain injury, caffeine is neuroprotective against periventricular white matter injury (PWMI) and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). Supporting the notion that blockade of adenosine action is of benefit in the premature infant, caffeine reduces the incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and CP in clinical studies. In comparison with the adverse effects on the postnatal brain, adenosine acts via A1ARs to play an essential role in protecting the embryo from hypoxia. Embryo protective effects are blocked by caffeine, and caffeine intake during early pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage and fetal growth retardation. Adenosine and adenosine antagonists play important modulatory roles during mammalian development. The protective and deleterious effects of adenosine depend on the time of exposure and target sites of action.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
adenosine receptor
- E:
-
embryonic day
- HIE:
-
hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
- OL:
-
oligodendrocyte
- PreOL:
-
preoligodendrocyte
- PVL:
-
periventricular leukomalacia
- PWMI:
-
periventricular white matter injury
References
Jacobson KA 2009 Introduction to adenosine receptors as therapeutic targets. Handb Exp Pharmacol 193: 1–24
Rivkees SA, Zhao Z, Porter G, Turner C 2001 Influences of adenosine on the fetus and newborn. Mol Genet Metab 74: 160–171
Eckle T, Koeppen M, Eltzschig HK 2009 Role of extracellular adenosine in acute lung injury. Physiology (Bethesda) 24: 298–306
Eltzschig HK, Weissmuller T, Mager A, Eckle T 2006 Nucleotide metabolism and cell-cell interactions. Methods Mol Biol 341: 73–87
Eltzschig HK, Abdulla P, Hoffman E, Hamilton KE, Daniels D, Schonfeld C, Loffler M, Reyes G, Duszenko M, Karhausen J, Robinson A, Westerman KA, Coe IR, Colgan SP 2005 HIF-1-dependent repression of equilibrative nucleoside transporter (ENT) in hypoxia. J Exp Med 202: 1493–1505
Conway SJ, Kruzynska-Frejtag A, Kneer PL, Machnicki M, Koushik SV 2003 What cardiovascular defect does my prenatal mouse mutant have, and why?. Genesis 35: 1–21
Van Linden A, Eltzschig HK 2007 Role of pulmonary adenosine during hypoxia: extracellular generation, signaling and metabolism by surface adenosine deaminase/CD26. Expert Opin Biol Ther 7: 1437–1447
Thompson LF, Eltzschig HK, Ibla JC, Van De Wiele CJ, Resta R, Morote-Garcia JC, Colgan SP 2004 Crucial role for ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) in vascular leakage during hypoxia. J Exp Med 200: 1395–1405
Fredholm BB 2010 Adenosine receptors as drug targets. Exp Cell Res 316: 1284–1288
Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Verkhratsky A, Zimmermann H 2009 Purinergic signalling in the nervous system: an overview. Trends Neurosci 32: 19–29
Fredholm BB, IJzerman AP, Jacobson KA, Klotz KN, Linden J 2001 International Union of Pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 53: 527–552
Fredholm BB, Arslan G, Halldner L, Kull B, Schulte G, Wasserman W 2000 Structure and function of adenosine receptors and their genes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 362: 364–374
Libert F, Parmentier M, Lefort A, Dinsart C, Van Sande J, Maenhaut C, Simons MJ, Dumont JE, Vassart G 1989 Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science 244: 569–572
Maenhaut C, Van Sande J, Libert F, Abramowicz M, Parmentier M, Vanderhaegen JJ, Dumont JE, Vassart G, Schiffmann S 1990 RDC8 codes for an adenosine A2 receptor with physiological constitutive activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 173: 1169–1178
Libert F, Schiffmann SN, Lefort A, Parmentier M, Gerard C, Dumont JE, Vanderhaeghen JJ, Vassart G 1991 The orphan receptor cDNA RDC7 encodes an A1 adenosine receptor. EMBO J 10: 1677–1682
Rivkees SA, Reppert SM 1992 RFL9 encodes an A2b-adenosine receptor. Mol Endocrinol 6: 1598–1604
Fink JS, Weaver DR, Rivkees SA, Peterfreund RA, Pollack AE, Adler EM, Reppert SM 1992 Molecular cloning of the rat A2 adenosine receptor: selective co- expression with D2 dopamine receptors in rat striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 14: 186–195
Reppert SM, Weaver DR, Stehle JH, Rivkees SA 1991 Molecular cloning and characterization of a rat A1-adenosine receptor that is widely expressed in brain and spinal cord. Mol Endocrinol 5: 1037–1048
Zhou QY, Li C, Olah ME, Johnson RA, Stiles GL, Civelli O 1992 Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: the A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89: 7432–7436
Aherne CM, Kewley EM, Eltzschig HK 2010 The resurgence of A2B adenosine receptor signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta In press
Barbhaiya H, McClain R, Ijzerman A, Rivkees SA 1996 Site-directed mutagenesis of the human A1 adenosine receptor: influences of acidic and hydroxy residues in the first four transmembrane domains on ligand binding. Mol Pharmacol 50: 1635–1642
Jaakola VP, Griffith MT, Hanson MA, Cherezov V, Chien EY, Lane JR, Ijzerman AP, Stevens RC 2008 The 2.6 angstrom crystal structure of a human A2A adenosine receptor bound to an antagonist. Science 322: 1211–1217
Trivedi BH, Bridges AJ, Bruns RF 1990 Structure-activity relationships of adenosine A1 and A2 receptors. Williams M Adenosine and Adenosine Receptors. Humana Press, Clifton pp 57–106
Stehle JH, Rivkees SA, Lee JJ, Weaver DR, Deeds JD, Reppert SM 1992 Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel A2- adenosine receptor subtype. Mol Endocrinol 6: 384–393
Blazynski C 1993 Characterization of adenosine A2 receptors in bovine retinal pigment epithelial membranes. Exp Eye Res 56: 595–599
Rivkees SA, Thevananther S, Hao H 2000 Are A3 adenosine receptors expressed in the brain?. Neuroreport 11: 1025–1030
Lopes LV, Rebola N, Pinheiro PC, Richardson PJ, Oliveira CR, Cunha RA 2003 Adenosine A3 receptors are located in neurons of the rat hippocampus. Neuroreport 14: 1645–1648
Swanson TH, Drazba JA, Rivkees SA 1995 Adenosine A1 receptors are located predominantly on axons in the rat hippocampal formation. J Comp Neurol 363: 517–531
Rebola N, Coelho JE, Costenla AR, Lopes LV, Parada A, Oliveira CR, Soares-da-Silva P, de Mendonca A, Cunha RA 2003 Decrease of adenosine A1 receptor density and of adenosine neuromodulation in the hippocampus of kindled rats. Eur J Neurosci 18: 820–828
Turner CP, Pulciani D, Rivkees SA 2002 Reduction in intracellular calcium levels induces injury in developing neurons. Exp Neurol 178: 21–32
Fredholm BB, Chen JF, Masino SA, Vaugeois JM 2005 Actions of adenosine at its receptors in the CNS: insights from knockouts and drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45: 385–412
Rivkees SA 1995 The ontogeny of cardiac and neural A1 adenosine receptor expression in rats. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 89: 202–213
Olanrewaju HA, Qin W, Feoktistov I, Scemama JL, Mustafa SJ 2000 Adenosine A(2A) and A(2B) receptors in cultured human and porcine coronary artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279: H650–H656
Eckle T, Faigle M, Grenz A, Laucher S, Thompson LF, Eltzschig HK 2008 A2B adenosine receptor dampens hypoxia-induced vascular leak. Blood 111: 2024–2035
Lu Q, Harrington EO, Newton J, Casserly B, Radin G, Warburton R, Zhou Y, Blackburn MR, Rounds S 2010 Adenosine protected against pulmonary edema through transporter- and receptor A2-mediated endothelial barrier enhancement. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 298: L755–L767
Linden J 2006 New insights into the regulation of inflammation by adenosine. J Clin Invest 116: 1835–1837
Sitkovsky M, Lukashev D 2005 Regulation of immune cells by local-tissue oxygen tension: HIF1 alpha and adenosine receptors. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 712–721
Zaynagetdinov R, Ryzhov S, Goldstein AE, Yin H, Novitskiy SV, Goleniewska K, Polosukhin VV, Newcomb DC, Mitchell D, Morschl E, Zhou Y, Blackburn MR, Peebles RS Jr Biaggioni I, Feoktistov I 2010 Attenuation of chronic pulmonary inflammation in A2B adenosine receptor knockout mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 42: 564–571
Bazzichi L, Trincavelli L, Rossi A, De Feo F, Lucacchini A, Bombardieri S, Martini C 2005 A2B adenosine receptor activity is reduced in neutrophils from patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther 7: R189–R195
Linden J 1994 Cloned adenosine A3 receptors: pharmacological properties, species differences and receptor functions. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15: 298–306
Rivkees SA, Chen M, Kulkarni J, Browne J, Zhao Z 1999 Characterization of the murine A1 adenosine receptor promoter, potent regulation by GATA-4 and Nkx2.5. J Biol Chem 274: 14204–14209
Turner CP, Yan H, Schwartz M, Othman T, Rivkees SA 2002 A1 adenosine receptor activation induces ventriculomegaly and white matter loss. Neuroreport 13: 1199–1204
Adén U, Leverin AL, Hagberg H, Fredholm BB 2001 Adenosine A(1) receptor agonism in the immature rat brain and heart. Eur J Pharmacol 426: 185–192
Millar D, Schmidt B 2004 Controversies surrounding xanthine therapy. Semin Neonatol 9: 239–244
Fredholm BB 1995 Astra Award Lecture. Adenosine, adenosine receptors and the actions of caffeine. Pharmacol Toxicol 76: 93–101
Fredholm BB, Chen JF, Cunha RA, Svenningsson P, Vaugeois JM 2005 Adenosine and brain function. Int Rev Neurobiol 63: 191–270
Johansson B, Halldner L, Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA, Poelchen W, Gimenez-Llort L, Escorihuela RM, Fernandez-Teruel A, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Xu XJ, Hardemark A, Betsholtz C, Herlenius E, Fredholm BB 2001 Hyperalgesia, anxiety, and decreased hypoxic neuroprotection in mice lacking the adenosine A1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 9407–9412
Coelho JE, Rebola N, Fragata I, Ribeiro JA, de Mendonca A, Cunha RA 2006 Hypoxia-induced desensitization and internalization of adenosine A1 receptors in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 138: 1195–1203
Blackburn MR, Datta SK, Kellems RE 1998 Adenosine deaminase-deficient mice generated using a two-stage genetic engineering strategy exhibit a combined immunodeficiency. J Biol Chem 273: 5093–5100
Turner CP, Seli M, Ment L, Stewart W, Yan H, Johansson B, Fredholm BB, Blackburn M, Rivkees SA 2003 A1 adenosine receptors mediate hypoxia-induced ventriculomegaly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 11718–11722
Back SA, Rivkees SA 2004 Emerging concepts in periventricular white matter injury. Semin Perinatol 28: 405–414
Ment LR, Schwartz M, Makuch RW, Stewart WB 1998 Association of chronic sublethal hypoxia with ventriculomegaly in the developing rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 111: 197–203
Othman T, Yan H, Rivkees SA 2003 Oligodendrocytes express functional A1 adenosine receptors that stimulate cellular migration. Glia 44: 166–172
Stevens B, Porta S, Haak LL, Gallo V, Fields RD 2002 Adenosine: a neuron-glial transmitter promoting myelination in the CNS in response to action potentials. Neuron 36: 855–868
Akundi RS, Rivkees SA 2009 Hypoxia alters cell cycle regulatory protein expression and induces premature maturation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. PLoS ONE 4: e4739
Fogal B, McClaskey C, Yan S, Yan H, Rivkees SA 2010 Diazoxide promotes oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation and myelination. PLoS ONE 5: e10906
Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Davis P, Doyle LW, Barrington KJ, Ohlsson A, Solimano A, Tin W 2006 Caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. N Engl J Med 354: 2112–2121
Back SA, Craig A, Luo NL, Ren J, Akundi RS, Ribeiro I, Rivkees SA 2006 Protective effects of caffeine on chronic hypoxia-induced perinatal white matter injury. Ann Neurol 60: 696–705
Thomson MA, Yoder BA, Winter VT, Giavedoni L, Chang LY, Coalson JJ 2006 Delayed extubation to nasal continuous positive airway pressure in the immature baboon model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: lung clinical and pathological findings. Pediatrics 118: 2038–2050
Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Davis P, Doyle LW, Barrington KJ, Ohlsson A, Solimano A, Tin W 2007 Long-term effects of caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. N Engl J Med 357: 1893–1902
Davis PG, Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Doyle LW, Asztalos E, Haslam R, Sinha S, Tin W 2010 Caffeine for apnea of prematurity trial: benefits may vary in subgroups. J Pediatr 156: 382–387
Fatemi A, Wilson MA, Johnston MV 2009 Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the term infant. Clin Perinatol 36: 835–858 vii
Rice JE III Vannucci RC, Brierley JB 1981 The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9: 131–141
Bona E, Aden U, Gilland E, Fredholm BB, Hagberg H 1997 Neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia: the effect of adenosine receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 36: 1327–1338
Aden U 2010 Adenosine, Caffeine and Hypoxic Ischemia. Presented at 48th Nobel Symposium. Caffeine and Health, Stockholm
Von Lubitz DK, Lin RC, Melman N, Ji XD, Carter MF, Jacobson KA 1994 Chronic administration of selective adenosine A1 receptor agonist or antagonist in cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 256: 161–167
Boissard CG, Lindner MD, Gribkoff VK 1992 Hypoxia produces cell death in the rat hippocampus in the presence of an A1 adenosine receptor antagonist: an anatomical and behavioral study. Neuroscience 48: 807–812
Linden J 2005 Adenosine in tissue protection and tissue regeneration. Mol Pharmacol 67: 1385–1387
Zhou Y, Murthy JN, Zeng D, Belardinelli L, Blackburn MR 2010 Alterations in adenosine metabolism and signaling in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 5: e9224
Wendler CC, Poulsen RR, Ghatpande S, Greene RW, Rivkees SA 2010 Identification of the heart as the critical site of adenosine mediated embryo protection. BMC Dev Biol 10: 57
Wendler CC, Amatya S, McClaskey C, Ghatpande S, Fredholm BB, Rivkees SA 2007 A1 adenosine receptors play an essential role in protecting the embryo against hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 9697–9702
Browne ML 2006 Maternal exposure to caffeine and risk of congenital anomalies: a systematic review. Epidemiology 17: 324–331
Christian MS, Brent RL 2001 Teratogen update: evaluation of the reproductive and developmental risks of caffeine. Teratology 64: 51–78
Ross CP, Persaud TV 1986 Cardiovascular primordium of the rat embryo following in utero exposure to alcohol and caffeine. Can J Cardiol 2: 160–163
Ross CP, Persaud TV 1986 Early embryonic development in the rat following in utero exposure to alcohol and caffeine. Histol Histopathol 1: 13–17
Grosso LM, Triche EW, Belanger K, Benowitz NL, Holford TR, Bracken MB 2006 Caffeine metabolites in umbilical cord blood, cytochrome P-450 1A2 activity, and intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Epidemiol 163: 1035–1041
Cnattingius S, Signorello LB, Anneren G, Clausson B, Ekbom A, Ljunger E, Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Petersson G, Rane A, Granath F 2000 Caffeine intake and the risk of first-trimester spontaneous abortion. N Engl J Med 343: 1839–1845
Weng X, Odouli R, Li DK 2008 Maternal caffeine consumption during pregnancy and the risk of miscarriage: a prospective cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198: 279.e1–279.e8
Vik T, Bakketeig LS, Trygg KU, Lund-Larsen K, Jacobsen G 2003 High caffeine consumption in the third trimester of pregnancy: gender-specific effects on fetal growth. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 17: 324–331
Larroque B, Kaminski M, Lelong N, Subtil D, Dehaene P 1993 Effects of birth weight of alcohol and caffeine consumption during pregnancy. Am J Epidemiol 137: 941–950
Wendler CC, Busovsky-McNeal M, Ghatpande S, Kalinowski A, Russell KS, Rivkees SA 2009 Embryonic caffeine exposure induces adverse effects in adulthood. FASEB J 23: 1272–1278
Momoi N, Tinney JP, Liu LJ, Elshershari H, Hoffmann PJ, Ralphe JC, Keller BB, Tobita K 2008 Modest maternal caffeine exposure affects developing embryonic cardiovascular function and growth. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294: H2248–H2256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by NIH Grants 1R01HD056281, 1R01NS068039, and R21NS051191.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivkees, S., Wendler, C. Adverse and Protective Influences of Adenosine on the Newborn and Embryo: Implications for Preterm White Matter Injury and Embryo Protection. Pediatr Res 69, 271–278 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31820efbcf
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31820efbcf
This article is cited by
-
A phase I trial of caffeine to evaluate safety in infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
Journal of Perinatology (2023)
-
Caffeine is a respiratory stimulant without effect on sleep in the short-term in late-preterm infants
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Antenatal Dexamethasone Treatment Induces Sex-dependent Upregulation of NTPDase1/CD39 and Ecto-5ʹ-nucleotidase/CD73 in the Rat Fetal Brain
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Stimulating and maintaining spontaneous breathing during transition of preterm infants
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Caffeine is associated with improved alveolarization and angiogenesis in male mice following hyperoxia induced lung injury
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2019)