Abstract
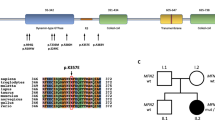
SH3TC2, known as the causative gene of autosomal recessive demyelinating Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4C (CMT4C), was also found linked to a mild mononeuropathy of the median nerve with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Using DNA microarray, Illumina MiSeq, and Ion proton, we carried out gene panel sequencing among 1483 Japanese CMT patients, containing 397 patients with demyelinating CMT. From seven patients with demyelinating CMT, we identified eight recessive variants in the SH3TC2 gene, consisting of five novel (pathogenic/likely pathogenic) and three reported variants. Additionally, from two patients with axonal CMT, we detected a reported recessive variant, p.Arg77Trp, which was herein reclassified as variant with unknown significance. Of the seven CMT4C patients (six females and one male), 2/7 patients developed symptoms at their first decade, and 5/7 patients lost their ambulation around age 50. Scoliosis was observed from more than half (4/7) of these patients, whereas hearing loss is the most common symptom of central nervous system (6/7). No median nerve mononeuropathy was recorded from their family members. We identified recessive variants in SH3TC2 from 1.76% of demyelinating CMT patients. An uncommon gender difference was recognized and the wild spectrum of these variants suggests mutational diversity of SH3TC2 in Japan.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Senderek J, Bergmann C, Stendel C, Kirfel J, Verpoorten N, De Jonghe P, et al. Mutations in a gene encoding a novel SH3/TPR domain protein cause autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4C neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73:1106–19.
Lassuthova P, Mazanec R, Vondracek P, Siskova D, Haberlova J, Sabova J, et al. High frequency of SH3TC2 mutations in Czech HMSN I patients. Clin Genet. 2011;80:334–45.
Yger M, Stojkovic T, Tardieu S, Maisonobe T, Brice A, Echaniz-Laguna A, et al. Characteristics of clinical and electrophysiological pattern of Charcot-Marie-Tooth 4C. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2012;17:112–22.
Manganelli F, Tozza S, Pisciotta C, Bellone E, Iodice R, Nolano M, et al. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: frequency of genetic subtypes in a Southern Italy population. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2014;19:292–8.
Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Tolle D, Senderek J, Eggermann K, Elbracht M, Kornak U, et al. Diagnostic algorithms in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathies: experiences from a German genetic laboratory on the basis of 1206 index patients. Clin Genet. 2016;89:34–43.
Iguchi M, Hashiguchi A, Ito E, Toda K, Urano M, Shimizu Y, et al. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C in Japan: report of a case. Muscle Nerve. 2013;47:283–6.
Ichikawa K, Numasawa K, Takeshita S, Hashiguchi A, Takashima H. Novel mutations in SH3TC2 in a young Japanese girl with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C. Pediatr Int. 2016;58:1252–4.
Hayashi M, Abe A, Murakami T, Yamao S, Arai H, Hattori H, et al. Molecular analysis of the genes causing recessive demyelinating Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in Japan. J Hum Genet. 2013;58:273–8.
Gooding R, Colomer J, King R, Angelicheva D, Marns L, Parman Y, et al. A novel Gypsy founder mutation, p.Arg1109X in the CMT4C gene, causes variable peripheral neuropathy phenotypes. J Med Genet. 2005;42:e69.
Claramunt R, Sevilla T, Lupo V, Cuesta A, Millan JM, Vilchez JJ, et al. The p.R1109X mutation in SH3TC2 gene is predominant in Spanish Gypsies with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4. Clin Genet. 2007;71:343–9.
Gosselin I, Thiffault I, Tetreault M, Chau V, Dicaire MJ, Loisel L, et al. Founder SH3TC2 mutations are responsible for a CMT4C French-Canadians cluster. Neuromuscul Disord. 2008;18:483–92.
Lupski JR, Reid JG, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Rio Deiros D, Chen DC, Nazareth L, et al. Whole-genome sequencing in a patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1181–91.
Zhao Z, Hashiguchi A, Hu J, Sakiyama Y, Okamoto Y, Tokunaga S, et al. Alanyl-tRNA synthetase mutation in a family with dominant distal hereditary motor neuropathy. Neurology. 2012;78:1644–9.
Maeda K, Idehara R, Hashiguchi A, Takashima H. A family with distal hereditary motor neuropathy and a K141Q mutation of small heat shock protein HSPB1. Intern Med. 2014;53:1655–8.
Higuchi Y, Hashiguchi A, Yuan J, Yoshimura A, Mitsui J, Ishiura H, et al. Mutations in MME cause an autosomal-recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2. Ann Neurol. 2016;79:659–72.
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24.
Pyle A, Griffin H, Yu-Wai-Man P, Duff J, Eglon G, Pickering-Brown S, et al. Prominent sensorimotor neuropathy due to SACS mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing. Arch Neurol. 2012;69:1351–4.
Yoshimura A, Yuan JH, Hashiguchi A, Hiramatsu Y, Ando M, Higuchi Y, et al. Clinical and mutational spectrum of Japanese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease caused by GDAP1 variants. Clin Genet. 2017;92:274–80.
Brewer MH, Ma KH, Beecham GW, Gopinath C, Baas F, Choi BO, et al. Haplotype-specific modulation of a SOX10/CREB response element at the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C locus SH3TC2. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:5171–87.
Vijay S, Chiu M, Dacks JB, Roberts RC. Exclusive expression of the Rab11 effector SH3TC2 in Schwann cells links integrin-alpha6 and myelin maintenance to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862:1279–90.
Gouttenoire EA, Lupo V, Calpena E, Bartesaghi L, Schupfer F, Medard JJ, et al. Sh3tc2 deficiency affects neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling. Glia. 2013;61:1041–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients and their families for participating in this study and their physicians for submitting the clinical samples. Also the authors thank Mrs. Aya Ebina and Tomoko Onishi for their excellent technical assistant. This study was supported in part by grants from the research on the Nervous and Mental Disorders and Research Committee for Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease, Neuropathy, Ataxic Disease and Applying Health and Technology of Ministry of Health, Welfare and Labour, Japan. This research is also supported by the Research program for conquering intractable disease from Japan Agency for Medical Research and development (AMED), and JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number 26461275).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, JH., Hashiguchi, A., Okamoto, Y. et al. Clinical and mutational spectrum of Japanese patients with recessive variants in SH3TC2 . J Hum Genet 63, 281–287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-017-0388-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-017-0388-5
This article is cited by
-
Clinical genetics of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
Screening for SH3TC2 variants in Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease in a cohort of Chinese patients
Acta Neurologica Belgica (2022)
-
Compound heterozygous mutations of SH3TC2 in Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 4C patients
Journal of Human Genetics (2019)