Abstract
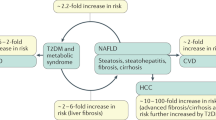
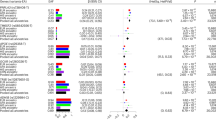
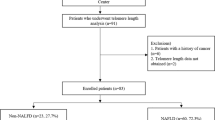
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is frequent among obese individuals with metabolic syndrome. Variants PNPLA3 p.I148M, TM6SF2 p.E167K and MBOAT7 rs641738 are associated with higher liver fat contents. Here we analyzed 63 biopsied non-obese, non-diabetic patients with NAFLD (39 men, age: 20–72 years) recruited within the German NAFLD CSG program. The frequencies of the PNPLA3, TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 polymorphisms were compared with the remaining patients in the NAFLD CSG cohort and with a control population (n = 174). Serum CK18-M30 was measured by ELISA. In non-obese NAFLD patients, the frequency of the PNPLA3 p.I148M allele (74.6%), but not of the TM6SF2 or MBOAT7 polymorphisms, was significantly (P < 0.05) higher as compared to the other patients in the NAFLD CSG cohort (54.9%) or controls (40.2%). The presence of the minor PNPLA3 p.I148M risk allele increased the risk of developing NAFLD (OR = 3.29, P < 0.001) and was associated with higher steatosis, fibrosis, and serum CK18-M30 levels (all P < 0.05). According to the population attributable fraction (PAF), 49.8% of NAFLD cases could be eliminated if the PNPLA3 mutation was absent. The MBOAT7 polymorphism was more frequent (P = 0.019) in patients with severe hepatic steatosis. In conclusion, PNPLA3, and to a lesser extent, MBOAT7 variants are associated with NAFLD risk and modulate liver injury in non-obese patients without diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Med. 2017;15:45.
Bellentani S. The epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2017;37(Suppl 1):81–4.
Leung JC, Loong TC, Wei JL, Wong GL, Chan AW, Choi PC, et al. Histological severity and clinical outcomes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese patients. Hepatology. 2017;65:54–64.
Younossi ZM, Stepanova M, Negro F, Hallaji S, Younossi Y, Lam B, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals in the United States. Medicine. 2012;91:319–27.
Kim D, Kim WR. Nonobese fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:474–85.
Loomba R, Schork N, Chen CH, Bettencourt R, Bhatt A, Ang B, et al. Heritability of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis based on a prospective twin study. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1784–93.
Romeo S, Kozlitina J, Xing C, Pertsemlidis A, Cox D, Pennacchio LA, et al. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1461–5.
Kozlitina J, Smagris E, Stender S, Nordestgaard BG, Zhou HH, Tybjærg-Hansen A, et al. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet. 2014;46:352–6.
Mancina RM, Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Pingitore P, Meroni M, Rametta R, Borén J, et al. The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals of European descent. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1219–30.
Anstee QM, Day CP. The genetics of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: spotlight on PNPLA3 and TM6SF2. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35:270–90.
Luukkonen PK, Zhou Y, Nidhina Haridas PA, Dwivedi OP, Hyötyläinen T, Ali A, et al. Impaired hepatic lipid synthesis from polyunsaturated fatty acids in TM6SF2 E167K variant carriers with NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2017;67:128–36.
Arslanow A, Stokes CS, Weber SN, Grünhage F, Lammert F, Krawczyk M. The common PNPLA3 variant p.I148M is associated with liver fat contents as quantified by controlled attenuation parameter (CAP). Liver Int. 2016;36:418–26.
Krawczyk M, Rau M, Schattenberg JM, Bantel H, Pathil A, Demir M, et al. Combined effects of the PNPLA3rs738409, TM6SF2 rs58542926, and MBOAT7 rs641738 variants on NAFLD severity: a multicenter biopsy-based study. J Lipid Res. 2017;58:247–55.
Ku NO, Strnad P, Bantel H, Omary MB. Keratins: Biomarkers and modulators of apoptotic and necrotic cell death in the liver. Hepatology. 2016;64:966–76.
Consultation WHOE. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004;363:157–63.
Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H, Graubard BI. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2013;309:71–82.
Feldman A, Eder SK, Felder TK, Kedenko L, Paulweber B, Stadlmayr A, et al. Clinical and metabolic characterization of lean caucasian subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:102–10.
Joka D, Wahl K, Moeller S, Schlue J, Vaske B, Bahr MJ, et al. Prospective biopsy-controlled evaluation of cell death biomarkers for prediction of liver fibrosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2012;55:455–64.
Krawczyk M, Portincasa P, Lammert F. PNPLA3-associated steatohepatitis: toward a gene-based classification of fatty liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2013;33:369–79.
Pirazzi C, Adiels M, Burza MA, Mancina RM, Levin M, Ståhlman M, et al. Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 (PNPLA3) I148M (rs738409) affects hepatic VLDL secretion in humans and in vitro. J Hepatol. 2012;57:1276–82.
BasuRay S, Smagris E, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH. The PNPLA3 variant associated with fatty liver disease (I148M) accumulates on lipid droplets by evading ubiquitylation. Hepatology. 2017;66:1111–24.
Casper M, Krawczyk M, Behrmann I, Glanemann M, Lammert F. Variant PNPLA3 increases the HCCrisk: prospective study in patients treated at the Saarland University Medical Center. Z Gastroenterol. 2016;54:585–6.
Valenti L, Motta BM, Soardo G, Iavarone M, Donati B, Sangiovanni A, et al. PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism, clinical presentation, and survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e75982.
Krawczyk M, Stokes CS, Romeo S, Lammert F. HCC and liver disease risks in homozygous PNPLA3p.I148M carriers approach monogenic inheritance. J Hepatol. 2015;62:980–1.
Funding
This study was supported, in part, by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF LiSyM 031L0051 to FL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Andreas Geier and Frank Lammert contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krawczyk, M., Bantel, H., Rau, M. et al. Could inherited predisposition drive non-obese fatty liver disease? Results from German tertiary referral centers. J Hum Genet 63, 621–626 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-018-0420-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-018-0420-4
This article is cited by
-
Evolutionäre Aspekte der mit metabolischer Dysfunktion assoziierten steatotischen Lebererkrankung (MASLD)
Die Gastroenterologie (2025)
-
Breite Datenbasis: NAFLD und Typ-2-Diabetes hängen sehr eng zusammen
Info Diabetologie (2021)
-
Das Deutsche NAFLD-Register
Der Gastroenterologe (2020)
-
Correlation of triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among the non-obese Chinese population with normal blood lipid levels: a retrospective cohort research
Lipids in Health and Disease (2019)