Abstract
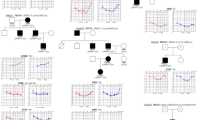
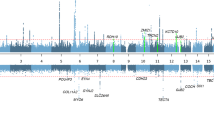
X-linked inheritance is very rare and is estimated to account for only 1–5% of all nonsyndromic hearing loss cases. We found a multiplex family from China segregating with X-linked nonsyndromic hearing loss. After exclusive analysis of 10 common variations of three hearing loss-related genes, GJB2, mtDNA12srRNA and SLC26A4, a novel truncated variant of SMPX, c.87dupA (p.Gly30Argfs*12) (NCBI ClinVar Submission ID: SUB3136126), was identified by whole-exome sequencing. This variant was co-segregated with hearing loss in the entire family and was absent in 576 unrelated ethnically and geographically matched controls. We also detected a single nucleotide variation in two male controls with normal hearing, SMPX c.55A>G (p.Asn19Asp), which has been annotated as a rare variant in the Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (dbSNP) (rs759552778) and Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC) databases. This study has enriched the mutation spectrum of the SMPX gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Yan D, Liu XZ. Cochlear molecules and hereditary deafness. Front. Biosci. 2008;13:4972–83.
Petersen MB, Wang Q, Willems PJ. Sex-linked deafness. Clin Genet. 2008;73:14–23.
Dobyns WB. The pattern of inheritance of X-linked traits is not dominant or recessive, just X-linked. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 2006;95:11–5.
Mittal R, Patel K, Mittal J, Chan B, Yan D, Grati M, et al. Association of PRPS1 mutations with disease phenotypes. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:127013.
de Kok YJ, van der Maarel SM, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Huber I, Monaco AP, Malcolm S, et al. Association between X-linked mixed deafness and mutations in the POU domain gene POU3F4. Science. 1995;267:685–8.
Lalwani AK, Brister JR, Fex J, Grundfast KM, Pikus AT, Ploplis B, et al. A new nonsyndromic X-linked sensorineural hearing impairment linked to Xp21.2. Am J Hum Genet. 1994;55:685–94.
Schraders M, Haas SA, Weegerink NJ, Oostrik J, Hu H, Hoefsloot LH, et al. Next-generation sequencing identifies mutations of SMPX, which encodes the small muscle protein, X-linked, as a cause of progressive hearing impairment. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;88:628–34.
Wang QJ, Li QZ, Rao SQ, Lee K, Huang XS, Yang WY, et al. AUNX1, a novel locus responsible for X linked recessive auditory and peripheral neuropathy, maps to Xq23-27.3. J Med Genet. 2006;43:e33–e33.
Zong L, Guan J, Ealy M, Zhang Q, Wang D, Wang H, et al. Mutations in apoptosis-inducing factor cause X-linked recessive auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder. J Med Genet. 2015;52:523–31.
Rost S, Bach E, Neuner C, Nanda I, Dysek S, Bittner RE, et al. Novel form of X-linked nonsyndromic hearing loss with cochlear malformation caused by a mutation in the type IV collagen gene COL4A6. Eur J Human Genet. 2014;22:208–15.
Niu Z, Feng Y, Mei L, Sun J, Wang X, Wang J, et al. A novel frameshift mutation of SMPX causes a rare form of X-linked nonsyndromic hearing loss in a Chinese family. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0178384.
Patzak D, Zhuchenko O, Lee CC, Wehnert M. Identification, mapping, and genomic structure of a novel X-chromosomal human gene (SMPX) encoding a small muscular protein. Hum Genet. 1999;105:506–12.
Huebner AK, Gandia M, Frommolt P, Maak A, Wicklein EM, Thiele H, et al. Nonsense mutations in SMPX, encoding a protein responsive to physical force, result in X-chromosomal hearing loss. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;88:621–7.
Abdelfatah N, Merner N, Houston J, Benteau T, Griffin A, Doucette L, et al. A novel deletion in SMPX causes a rare form of X-linked progressive hearing loss in two families due to a founder effect. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:66–9.
Wang H, Wang X, He C, Li H, Qing J, Grati M, et al. Exome sequencing identifies a novel CEACAM16 mutation associated with autosomal dominant nonsyndromic hearing loss DFNA4B in a Chinese family. J Hum Genet. 2015;60:119–26.
Cai XZ, Li Y, Xia L, Peng Y, He CF, Jiang L, et al. Exome sequencing identifies POU4F3 as the causative gene for a large Chinese family with non-syndromic hearing loss. J Hum Genet. 2017;62:317–20.
Liu XZ, Xie D, Yuan HJ, de Brouwer AP, Christodoulou J, Yan D. Hearing loss and PRPS1 mutations: Wide spectrum of phenotypes and potential therapy. Int J Audiol. 2013;52:23–8.
Stanton SG, Griffin A, Stockley TL, Brown C, Young TL, Benteau T, et al. X-linked hearing loss: two gene mutation examples provide generalizable implications for clinical care. Am J Audiol. 2014;23:190–200.
Bademci G, Lasisi A, Yariz KO, Montenegro P, Menendez I, Vinueza R, et al. Novel domain-specific POU3F4 mutations are associated with X-linked deafness: examples from different populations. BMC Med Genet. 2015;16:9.
Du W, Han MK, Wang DY, Han B, Zong L, Lan L, et al. A POU3F4 mutation causes nonsyndromic hearing loss in a Chinese X-linked recessive family. Chin Med J. 2017;130:88–92.
Pollak A, Lechowicz U, Kedra A, Stawinski P, Rydzanicz M, Furmanek M, et al. Novel and de novo mutations extend association of POU3F4 with distinct clinical and radiological phenotype of hearing loss. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0166618.
Palmer S, Groves N, Schindeler A, Yeoh T, Biben C, Wang CC, et al. The small muscle-specific protein Csl modifies cell shape and promotes myocyte fusion in an insulin-like growth factor 1-dependent manner. J Cell Biol. 2001;153:985–98.
Schindeler A, Lavulo L, Harvey RP. Muscle costameric protein, Chisel/Smpx, associates with focal adhesion complexes and modulates cell spreading in vitro via a Rac1/p38 pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2005;307:367–80.
Acknowledgements
We greatly thank the pedigree members for agreeing to participate in this study. We also appreciate the help and advice of our colleagues. This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (also called 973 Program) (No. 2014CB541702; 2014CB943003), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81771023; 81470705; 81301172; 81500803), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2017M620359) and the Graduate Innovation Fundation of Central South University (No. 2017ZZTS213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Niu, Z., Fan, L. et al. A novel mutation in the SMPX gene associated with X-linked nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss in a Chinese family. J Hum Genet 63, 723–730 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-018-0443-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-018-0443-x
This article is cited by
-
Genomic and phenotypic landscapes of X-linked hereditary hearing loss in the Chinese population
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2024)
-
Differentiation and functioning of the lateral line organ in zebrafish require Smpx activity
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Missense mutations in small muscle protein X-linked (SMPX) cause distal myopathy with protein inclusions
Acta Neuropathologica (2021)