Abstract
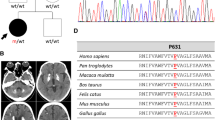
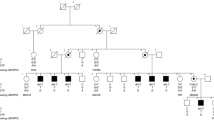
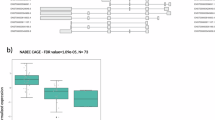
Primary familial brain calcification (PFBC) is a rare disease characterized by brain calcifications that mainly affect the basal ganglia, thalamus, and cerebellum. Among the four autosomal-dominant genes known to be associated with the disease, SLC20A2 pathogenic variants are the most common, accounting for up to 40% of PFBC dominant cases; variants include both point mutations, small insertions/deletions and intragenic deletions. Over the last 7 years, we have collected a group of 50 clinically diagnosed PFBC patients, who were screened for single nucleotide changes and small insertions/deletions in SLC20A2 by Sanger sequencing. We found seven pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants: four were previously described by our group, and three are reported here (c.303delG, c.21delG, and c.1795-1G>A). We developed and validated a synthetic Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) assay for SLC20A2 deletions, covering all ten coding exons and the 5′ UTR (SLC20A2-MLPA). Using this method, we screened a group of 43 PFBC-patients negative for point mutations and small insertions/deletions, and identified two novel intragenic deletions encompassing exon 6 NC_000008.10:g.(42297172_42302163)_(423022281_42317413)del, and exons 7–11 including the 3′UTR NC_000008.10:g.(?_42275320)_(42297172_42302163)del. Overall, SLC20A2 deletions may be highly underestimated PFBC cases, and we suggest MLPA should be included in the routine molecular test for PFBC diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary material.
References
Westenberger A, Balck A, Klein C. Primary familial brain calcifications: genetic and clinical update. Curr Opin Neurol. 2019;32:571–8.
Nicolas G, Charbonnier C, de Lemos RR, Richard AC, Guillin O, Wallon D, et al. Brain calcification process and phenotypes according to age and sex: lessons from SLC20A2, PDGFB, and PDGFRB mutation carriers. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015;168:586–94.
Legati A, Giovannini D, Nicolas G, Lopez-Sanchez U, Quintans B, Oliveira JR, et al. Mutations in XPR1 cause primary familial brain calcification associated with altered phosphate export. Nat Genet. 2015;47:579–81.
Arkadir D, Lossos A, Rahat D, Abu Snineh M, Schueler-Furman O, Nitschke S, et al. MYORG is associated with recessive primary familial brain calcification. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019;6:106–13.
Forouhideh Y, Muller K, Ruf W, Assi M, Seker T, Tunca C, et al. A biallelic mutation links MYORG to autosomal-recessive primary familial brain calcification. Brain. 2019;142:e4.
Peng Y, Wang P, Chen Z, Jiang H. A novel mutation in MYORG causes primary familial brain calcification with central neuropathic pain. Clin Genet. 2019;95:433–5.
Yao XP, Cheng X, Wang C, Zhao M, Guo XX, Su HZ, et al. Biallelic mutations in MYORG cause autosomal recessive primary familial brain calcification. Neuron. 2018;98:1116–23 e5.
David S, Ferreira J, Quenez O, Rovelet-Lecrux A, Richard AC, Verin M, et al. Identification of partial SLC20A2 deletions in primary brain calcification using whole-exome sequencing. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016;24:1630–4.
Hsu SC, Sears RL, Lemos RR, Quintans B, Huang A, Spiteri E, et al. Mutations in SLC20A2 are a major cause of familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. Neurogenetics. 2013;14:11–22.
Wang C, Li Y, Shi L, Ren J, Patti M, Wang T, et al. Mutations in SLC20A2 link familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification with phosphate homeostasis. Nat Genet. 2012;44:254–6.
Jensen N, Schroder HD, Hejbol EK, Fuchtbauer EM, de Oliveira JR, Pedersen L. Loss of function of Slc20a2 associated with familial idiopathic Basal Ganglia calcification in humans causes brain calcifications in mice. J Mol Neurosci. 2013;51:994–9.
Lemos RR, Ramos EM, Legati A, Nicolas G, Jenkinson EM, Livingston JH, et al. Update and mutational analysis of SLC20A2: a major cause of primary familial brain calcification. Hum Mutat. 2015;36:489–95.
Pasanen P, Makinen J, Myllykangas L, Guerreiro R, Bras J, Valori M, et al. Primary familial brain calcification linked to deletion of 5’ noncoding region of SLC20A2. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;136:59–63.
Grutz K, Volpato CB, Domingo A, Alvarez-Fischer D, Gebert U, Schifferle G, et al. Primary familial brain calcification in the ‘IBGC2’ kindred: all linkage roads lead to SLC20A2. Mov Disord. 2016;31:1901–4.
Guo XX, Su HZ, Zou XH, Lai LL, Lu YQ, Wang C, et al. Identification of SLC20A2 deletions in patients with primary familial brain calcification. Clinical Genet. 2019;96:53–60.
Rubino E, Giorgio E, Gallone S, Pinessi L, Orsi L, Gentile S, et al. Novel mutation of SLC20A2 in an Italian patient presenting with migraine. J Neurol. 2014;261:2019–21.
Di Gregorio E, Riberi E, Belligni EF, Biamino E, Spielmann M, Ala U, et al. Copy number variants analysis in a cohort of isolated and syndromic developmental delay/intellectual disability reveals novel genomic disorders, position effects and candidate disease genes. Clin Genet. 2017;92:415–22.
Di Gregorio E, Savin E, Biamino E, Belligni EF, Naretto VG, D’Alessandro G, et al. Large cryptic genomic rearrangements with apparently normal karyotypes detected by array-CGH. Mol Cytogenet. 2014;7:82.
Biamino E, Di Gregorio E, Belligni EF, Keller R, Riberi E, Gandione M, et al. A novel 3q29 deletion associated with autism, intellectual disability, psychiatric disorders, and obesity. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2016;171:290–9.
Bartoletti-Stella A, Gasparini L, Giacomini C, Corrado P, Terlizzi R, Giorgio E, et al. Messenger RNA processing is altered in autosomal dominant leukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24:2746–56.
Rubino E, Giorgio E, Godani M, Grosso E, Zibetti M, Lopiano L, et al. Three novel missense mutations in SLC20A2 associated with idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. J Neurol Sci. 2017;377:62–4.
Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV, Samocha KE, Banks E, Fennell T, et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature. 2016;536:285–91.
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24.
Menon S, Muglan JA, Shimon L, Stewart D, Snow B, Hayes M, et al. Down the stairs dystonia—a novel task‐specific focal isolated syndrome. Mov Disord—Clin Pract. 2016;4:121–4.
Gagliardi M, Morelli M, Annesi G, Nicoletti G, Perrotta P, Pustorino G, et al. A new SLC20A2 mutation identified in southern Italy family with primary familial brain calcification. Gene. 2015;568:109–11.
Chen WJ, Yao XP, Zhang QJ, Ni W, He J, Li HF, et al. Novel SLC20A2 mutations identified in southern Chinese patients with idiopathic basal ganglia calcification. Gene. 2013;529:159–62.
Baker M, Strongosky AJ, Sanchez-Contreras MY, Yang S, Ferguson W, Calne DB, et al. SLC20A2 and THAP1 deletion in familial basal ganglia calcification with dystonia. Neurogenetics. 2014;15:23–30.
Ramos EM, Carecchio M, Lemos R, Ferreira J, Legati A, Sears RL, et al. Primary brain calcification: an international study reporting novel variants and associated phenotypes. Eur J Hum Genet. 2018;26:1462–77.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participating families. This work was supported by Fondazione Umberto Veronesi (Postdoctoral Fellowship 2017) to EG; Ricerca Locale MURST ex 60% and the “Associazione E.E. Rulfo per la ricerca biomedica” to AB; Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca – MIUR “Dipartimenti di eccellenza 2018-2020” to Department of Medical Sciences- University of Torino (Project D15D18000410001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giorgio, E., Garelli, E., Carando, A. et al. Design of a multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification assay for SLC20A2: identification of two novel deletions in primary familial brain calcification. J Hum Genet 64, 1083–1090 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-019-0668-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-019-0668-3