Abstract
Objective
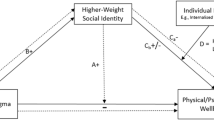
To systematically review studies that have assessed the mediating role of internalised weight stigma on the relationship between experienced/perceived weight stigma and any biopsychosocial outcomes.
Methods
PsycINFO, PsycExtra, Web of Science, CINAHL, Medline and Embase were systematically searched. Identified studies were double screened (HB and XPG).
Results
Seventeen studies (across 16 articles) met our inclusion criteria (N = 21,172), and almost all studies measured only psychological outcomes (n = 15). Eight studies found consistent evidence for internalised weight stigma as a mediator of the relationship between experienced/perceived weight stigma and disordered eating outcomes. Preliminary evidence was found for the mediating role of internalised weight stigma on the relationship between experienced/perceived weight stigma and body shame, body dissatisfaction, exercise behaviour, healthcare experiences and behaviours, bodily pain and parental weight talk. However, the findings were inconsistent for depression and anxiety, although only two studies reported these.
Conclusion
This review provides preliminary evidence for internalised weight stigma as an intervening variable in the relationship between experienced/perceived weight stigma and adverse health outcomes. Results suggest that there are potential benefits of interventions addressing internalised weight stigma to improve health outcomes. However, these findings must be considered in the context of the psychometric limitations of the Weight Bias Internalisation Scale, which was used in all but one study.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emmer C, Bosnjak M, Mata J. The association between weight stigma and mental health: a meta‐analysis. Obes Rev. 2020;21:e12935.
Hunger JM, Dodd DR, Smith AR. Weight discrimination, anticipated weight stigma, and disordered eating. Eat Behav. 2020;37:101383.
Puhl R, Brownell KD. Bias, discrimination, and obesity. Obes Res. 2001;9:788–805.
Puhl RM, Heuer CA. The stigma of obesity: a review and update. Obesity. 2009;17:941.
Agerström J, Rooth D-O. The role of automatic obesity stereotypes in real hiring discrimination. J Appl Psychol. 2011;96:790.
Rubino F, Puhl RM, Cummings DE, Eckel RH, Ryan DH, Mechanick JI, et al. Joint international consensus statement for ending stigma of obesity. Nat Med. 2020;26:485–97.
Myers A, Rosen JC. Obesity stigmatization and coping: relation to mental health symptoms, body image, and self-esteem. Int J Obes. 1999;23:221–30.
Hunger JM, Major B. Weight stigma mediates the association between BMI and self-reported health. Health Psychol. 2015;34:172.
Tomiyama AJ. Weight stigma is stressful. a review of evidence for the Cyclic Obesity/Weight-Based Stigma model. Appetite. 2014;82:8–15.
Daly M, Robinson E, Sutin AR. Does knowing hurt? Perceiving oneself as overweight predicts future physical health and well-being. Psychol Sci. 2017;28:872–81.
Papadopoulos S, Brennan L. Correlates of weight stigma in adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic literature review. Obesity. 2015;23:1743–60.
Jackson SE, Steptoe A, Beeken RJ, Croker H, Wardle J. Perceived weight discrimination in England: a population-based study of adults aged⩾ 50 years. Int J Obes. 2015;39:858–64.
Wu YK, Berry DC. Impact of weight stigma on physiological and psychological health outcomes for overweight and obese adults: a systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:1030–42.
Callahan D. Children, stigma, and obesity. JAMA Pediatr. 2013;167:791–2.
Latner JD, Puhl RM, Stunkard AJ. Cultural attitudes and biases toward obese persons. In: Akabas SR, Lederman SA, Moore BJ, (eds.) Textbook of obesity: biological, psychological and cultural influences. 1st ed, United Kingdom, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2012. p. 42–57.
Sutin AR, Stephan Y, Terracciano A. Weight discrimination and risk of mortality. Psychol Sci. 2015;26:1803–11.
Hunger JM, Major B, Blodorn A, Miller CT. Weighed down by stigma: how weight‐based social identity threat contributes to weight gain and poor health. Soc Personal Psychol Compass. 2015;9:255–68.
Puhl R, Suh Y. Health consequences of weight stigma: implications for obesity prevention and treatment. Curr Obes Rep. 2015;4:182–90.
Vartanian LR, Porter AM. Weight stigma and eating behavior: a review of the literature. Appetite. 2016;102:3–14.
Almeida L, Savoy S, Boxer P. The role of weight stigmatization in cumulative risk for binge eating. J Clin Psychol. 2011;67:278–92.
Schvey NA, Puhl RM, Brownell KD. The impact of weight stigma on caloric consumption. Obesity. 2011;19:1957–62.
Major B, Hunger JM, Bunyan DP, Miller CT. The ironic effects of weight stigma. J Exp Soc Psychol. 2014;51:74–80.
Daly M, Sutin AR, Robinson E. Perceived weight discrimination mediates the prospective association between obesity and physiological dysregulation: evidence from a population-based cohort. Psychol Sci. 2019;30:1030–9.
Lee KM, Hunger JM, Tomiyama AJ. Weight stigma and health behaviors: evidence from the Eating in America Study. Int J Obes. 2021;4:1499–509.
Major B, Rathbone JA, Blodorn A, Hunger JM. The countervailing effects of weight stigma on weight-loss motivation and perceived capacity for weight control. Pers Soc Psychol Bullet. 2020;46:1331–43.
Dixon JB. The effect of obesity on health outcomes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;316:104–8.
Durso LE, Latner JD. Understanding self‐directed stigma: development of the weight bias internalization scale. Obesity. 2008;16:S80–S6.
Tylka TL, Annunziato RA, Burgard D, Daníelsdóttir S, Shuman E, Davis C, et al. The weight-inclusive versus weight-normative approach to health: evaluating the evidence for prioritizing well-being over weight loss. J Obes. 2014;2014:983495.
Olson KL, Mensinger JL. Weight-related stigma mediates the relationship between weight status and bodily pain: a conceptual model and call for further research. Body image. 2019;30:159–64.
Pötzsch A, Rudolph A, Schmidt R, Hilbert A. Two sides of weight bias in adolescent binge‐eating disorder: adolescents’ perceptions and maternal attitudes. Int J Eat Disord. 2018;51:1339–45.
Forbes Y, Donovan C. The role of internalised weight stigma and self‐compassion in the psychological well‐being of overweight and obese women. Aust Psychol. 2019;54:471–82.
O’Brien KS, Latner JD, Puhl RM, Vartanian LR, Giles C, Griva K, et al. The relationship between weight stigma and eating behavior is explained by weight bias internalization and psychological distress. Appetite. 2016;102:70–6.
Magallares A, Bolaños-Rios P, Ruiz-Prieto I, de Valle PB, Irles JA, Jáuregui-Lobera I. The mediational effect of weight self-stigma in the relationship between blatant and subtle discrimination and depression and anxiety. Span J Psychol. 2017;20:e4, 1–7.
Pearl RL, Puhl RM, Dovidio JF. Differential effects of weight bias experiences and internalization on exercise among women with overweight and obesity. J Health Psychol. 2015;20:1626–32.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4:1.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008.
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:210.
Cashin A, McAuley J, Lamb SE, Hopewell S, Kamper S, Williams C, et al. Items for consideration in a reporting guideline for mediation analyses: a Delphi study. 2020;26:106.
Hayes AF. Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: a regression-based approach. Guilford publications; 2017.
Puhl RM, Lessard LM, Himmelstein MS, Foster GD. The roles of experienced and internalized weight stigma in healthcare experiences: Perspectives of adults engaged in weight management across six countries. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0251566.
Meadows A, Higgs S. A bifactor analysis of the Weight Bias Internalization Scale: What are we really measuring? Body Image. 2020;33:137–51.
Oehlhof MEW. Self-objectification among overweight and obese women: an application of structural equation modeling. Bowling Green State University; 2011.
Braun TD, Quinn DM, Stone A, Gorin AA, Ferrand J, Puhl RM, et al. Weight bias, shame, and self‐compassion: risk/protective mechanisms of depression and anxiety in prebariatic surgery patients. Obesity. 2020;28:1974–83.
Romano KA, Heron KE, Henson JM. Examining associations among weight stigma, weight bias internalization, body dissatisfaction, and eating disorder symptoms: does weight status matter? Body Image. 2021;37:38–49.
Zuba A, Warschburger P. The role of weight teasing and weight bias internalization in psychological functioning: a prospective study among school-aged children. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017;26:1245–55.
Thompson JK, Cattarin J, Fowler B, Fisher E. The perception of teasing scale (POTS): a revision and extension of the physical appearance related teasing scale (PARTS). J Pers Assess. 1995;65:146–57.
Remmert JE, Convertino AD, Roberts SR, Godfrey KM, Butryn ML. Stigmatizing weight experiences in health care: Associations with BMI and eating behaviours. Obes Sci Pract. 2019;5:555–63.
Elison ZM. Psychological well-being in overweight adults: the effects of percieved weight discrimination, internalized weight stigma, and coping. Purdue University; 2017.
Durso LE, Latner JD, Hayashi K. Perceived discrimination is associated with binge eating in a community sample of non-overweight, overweight, and obese adults. Obes Facts. 2012;5:869–80.
Pudney EV, Himmelstein MS, Puhl RM. The role of weight stigma in parental weight talk. Pediatr Obes. 2019;14:e12534.
Pearl RL, Puhl RM. Measuring internalized weight attitudes across body weight categories: validation of the modified weight bias internalization scale. Body Image. 2014;11:89–92.
Lillis J, Luoma JB, Levin ME, Hayes SC. Measuring weight self‐stigma: the weight self‐stigma questionnaire. Obesity. 2010;18:971–6.
Sarwer DB, Polonsky HM. Body image and body contouring procedures. Aesthet Surg J. 2016;36:1039–47.
Fischer L, Wekerle A-L, Sander J, Nickel F, Billeter AT, Zech U, et al. Is there a reason why obese patients choose either conservative treatment or surgery? Obes Surg. 2017;27:1684–90.
Makarawung D, Monpellier V, van den Brink F, Woertman L, Zijlstra H, Mink van der Molen A, et al. Body image as a potential motivator for bariatric surgery: a case-control study. Obes Surg. 2020;30:3768–75.
Papadopoulos S, de la Piedad Garcia X, Brennan L. Evaluation of the psychometric properties of self‐reported weight stigma measures: a systematic literature review. Obes Rev. 2021;22:e13267.
Lee MS, Gonzalez BD, Small BJ, Thompson JK. Internalized weight bias and psychological wellbeing: an exploratory investigation of a preliminary model. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0216324.
Ratcliffe D, Ellison N. Obesity and internalized weight stigma: a formulation model for an emerging psychological problem. Behav Cog Psychother. 2015;43:239.
Foster ED, Deardorff A. Open science framework (OSF). J Med Libr Assoc: JMLA. 2017;105:203.
Preacher KJ, Kelley K. Effect size measures for mediation models: quantitative strategies for communicating indirect effects. Psychol Methods. 2011;16:93.
Götz M, O’Boyle EH, Gonzalez-Mulé E, Banks GC, Bollmann SS. The “Goldilocks Zone”:(Too) many confidence intervals in tests of mediation just exclude zero. Psychol Bull. 2020;147:95–114.
Wen Z, Fan X. Monotonicity of effect sizes: Questioning kappa-squared as mediation effect size measure. Psychol Methods. 2015;20:193.
Tomiyama AJ, Epel ES, McClatchey TM, Poelke G, Kemeny ME, McCoy SK, et al. Associations of weight stigma with cortisol and oxidative stress independent of adiposity. Health Psychol. 2014;33:862.
Schvey NA, Puhl RM, Brownell KD. The stress of stigma: exploring the effect of weight stigma on cortisol reactivity. Psychosom Med. 2014;76:156–62.
Norcini Pala A, Hart RP, Steca P. Minority stress, depression and HIV-progression biomarkers: an exploratory study on a sample of Italian HIV-positive gay and bisexual men. J Gay Lesbian Ment Health. 2015;19:244–60.
Terwee CB, Prinsen C, Chiarotto A, De Vet H, Bouter LM, Alonso J, et al. COSMIN methodology for assessing the content validity of PROMs—user manual. Amsterdam: VU University Medical Center; 2018.
Meadows A, Higgs S. The multifaceted nature of weight-related self-stigma: validation of the two-factor weight bias internalization scale (WBIS-2F). Front Psychol. 2019;10:808.
Austen E, Pearl RL, Griffiths S. Inconsistencies in the conceptualisation and operationalisation of internalized weight stigma: a potential way forward. Body Image. 2020;36:3–5.
Romano E, Haynes A, Robinson E. Weight perception, weight stigma concerns, and overeating. Obesity. 2018;26:1365–71.
Robinson E, Haynes A, Sutin A, Daly M. Self‐perception of overweight and obesity: a review of mental and physical health outcomes. Obes Sci Pract. 2020;6:552–61.
Pearl RL, Hopkins CH, Berkowitz RI, Wadden TA. Group cognitive-behavioral treatment for internalized weight stigma: a pilot study. Eat Weight Disord. 2018;23:357–62.
Funding
HB is supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program (RTP) scholarship through ACU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation, systematic search, and double screening: XPG and HB. Data extraction: HB. XPG and HB wrote the manuscript; LB and LK edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bidstrup, H., Brennan, L., Kaufmann, L. et al. Internalised weight stigma as a mediator of the relationship between experienced/perceived weight stigma and biopsychosocial outcomes: a systematic review. Int J Obes 46, 1–9 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-021-00982-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-021-00982-4
This article is cited by
-
Patient autonomy and metabolic bariatric surgery: an empirical perspective
BMC Medical Ethics (2025)
-
Assessing exposure to weight stigma: development and initial validation of the Weight Stigma Exposure Inventory (WeSEI)
Journal of Eating Disorders (2025)
-
Weight Stigma in the Metabolic Bariatric Surgery Context: Current State of the Literature, Conceptual Model, and Looking Forward
Current Obesity Reports (2025)
-
Weight stigma in healthcare settings: the experience of Arab and Jewish bariatric surgery candidates in Israel
Israel Journal of Health Policy Research (2024)
-
Testing the validity of the Norwegian translation of the modified weight bias internalization scale
Journal of Eating Disorders (2024)