Abstract
Background
Obesity is an important public health issue. Virtual reality provides an opportunity to increase benefits of traditional exercise programs with more immersive, interactive, and enjoyable experiences for weight control.
Objectives
This study aimed to explore the efficacy of virtual reality-enhanced exergames for obesity-related outcomes, including body weight, body mass index, body fat, and waist circumference.
Methods
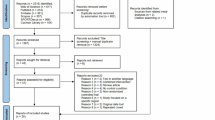
Six electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, Medline, and CINAHL Plus, were searched for randomized controlled trials. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted using a random-effects model. In total, 12 qualified studies were selected for both qualitative and quantitative syntheses.
Results
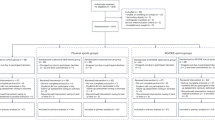
Virtual reality-enhanced exergames exerted small significant effects on improving body weight, body mass index, and body fat percentage. Low heterogeneity and no significant publication bias were found among the studies.
Conclusions
Creating an immersive virtual world is an interesting and effective strategy for users to engage in physical activity. Virtual reality-enhanced exergames are recommended for weight control and obesity prevention across populations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wharton S, Lau DCW, Vallis M, Sharma AM, Biertho L, Campbell-Scherer D, et al. Obesity in adults: A clinical practice guideline. CMAJ. 2020;192:E875–91.
Jastreboff AM, Kotz CM, Kahan S, Kelly AS, Heymsfield SB. Obesity as a Disease: The Obesity Society 2018 Position Statement. Obesity. 2019;27:7–9.
Malik VS, Willet WC, Hu FB. Nearly a decade on — trends, risk factors and policy implications in global obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16:615–6.
World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and overweight. WHO; 2024. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Anderson E, Durstine JL. Physical activity, exercise, and chronic diseases: A brief review. Sports Med Health Sci. 2019;1:3–10.
Oppert JM, Bellicha A, van Baak MA, Battista F, Beaulieu K, Blundell JE, et al. Exercise training in the management of overweight and obesity in adults: Synthesis of the evidence and recommendations from the European Association for the Study of Obesity Physical Activity Working Group. Obes Rev. 2021;22. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13273.
Al-Rasheed A, Alabdulkreem E, Alduailij M, Alduailij M, Alhalabi W, Alharbi S, et al. Virtual Reality in the Treatment of Patients with Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review. Sustainability. 2022;14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063324.
Cummings JJ, Bailenson JN. How Immersive Is Enough? A Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Immersive Technology on User Presence. Media Psychol. 2016;19:272–309.
Tatnell P, Atorkey P, Tzelepis F. The Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Interventions on Smoking, Nutrition, Alcohol, Physical Activity and/or Obesity Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710821.
Ho RST, Chan EKY, Liu KKY, Wong SHS. Active video game on children and adolescents’ physical activity and weight management: A network meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2022;32:1268–86.
Viana RB, de Oliveira VN, Dankel SJ, Loenneke JP, Abe T, da Silva WF, et al. The effects of exergames on muscle strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31:1592–611.
Erçelik ZE, Çağlar S. Effectiveness of active video games in overweight and obese adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2022;27:98–104.
Gao Z, Chen S, Pasco D, Pope Z. A meta-analysis of active video games on health outcomes among children and adolescents. Obes Rev. 2015;16:783–94.
Oliveira JS, Pinheiro MB, Fairhall N, Walsh S, Franks TC, Kwok W, et al. Evidence on Physical Activity and the Prevention of Frailty and Sarcopenia Among Older People: A Systematic Review to Inform the World Health Organization Physical Activity Guidelines. J Phys Act Health. 2020;17:1247–58.
Hernández-Jiménez C, Sarabia R, Paz-Zulueta M, Paras-Bravo P, Pellico A, Azcona LR, et al. Impact of active video games on body mass index in children and adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the quality of primary studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16132424.
Chen Y, Cao L, Xu Y, Zhu M, Guan B, Ming WK. Effectiveness of virtual reality in cardiac rehabilitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Nurs Stud. 2022;133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2022.104323.
Yen HY, Hsu H, Huang WH. Virtual reality natural experiences for mental health: comparing the effects between different immersion levels. Virtual Real. 2024;28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-024-00958-5.
Yen HY, Chiu HL. Virtual Reality Exergames for Improving Older Adults’ Cognition and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021;22:995–1002.
Bourke M, Patterson L, Di Nardo F, Whittaker P, Verma A. Active video games and weight management in overweight children and adolescents—systematic review and meta-analysis. J Public Health. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdad115.
Oliveira CB, Pinto RZ, Saraiva BTC, Tebar WR, Delfino LD, Franco MR, et al. Effects of active video games on children and adolescents: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30:4–12.
Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988.
Melsen WG, Bootsma MCJ, Rovers MM, Bonten MJM. The effects of clinical and statistical heterogeneity on the predictive values of results from meta-analyses. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20:123–9.
Higgins JPT. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557.
Adamo KB, Rutherford JA, Goldfield GS. Effects of interactive video game cycling on overweight and obese adolescent health. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2010;35:805–15.
Barsasella D, Liu MF, Malwade S, Galvin CJ, Dhar E, Chang CC, et al. Effects of Virtual Reality Sessions on the Quality of Life, Happiness, and Functional Fitness among the Older People: A Randomized Controlled Trial from Taiwan. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105892.
Biesek S, Vojciechowski AS, Filho JM, de Ferreira ACRM, Borba VZC, Rabito EI, et al. Effects of exergames and protein supplementation on body composition and musculoskeletal function of prefrail community-dwelling older women: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18179324.
Ferraz DD, Trippo KV, Duarte GP, Neto MG, Bernardes Santos KO, Filho JO. The Effects of Functional Training, Bicycle Exercise, and Exergaming on Walking Capacity of Elderly Patients With Parkinson Disease: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Single-blinded Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99:826–33.
Leandro LAB, de Araújo GCR, Prado JP, de Aquino TN, da Silva JP, Galdino G. Effect of a virtual cardiac rehabilitation program on patients with hypertension: A randomized trial. Fisioterapia em Movimento. 2021;34. https://doi.org/10.1590/FM.2021.34126.
Lee Y, Hong J, Hur M, Seo E. Effects of Virtual Reality Exercise Program on Blood Glucose, Body Composition, and Exercise Immersion in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20:4178.
Maddison R, Foley L, Ni Mhurchu C, Jiang Y, Jull A, Prapavessis H, et al. Effects of active video games on body composition: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94:156–63.
Mologne MS, Hu J, Carrillo E, Gomez D, Yamamoto T, Lu S, et al. The Efficacy of an Immersive Virtual Reality Exergame Incorporating an Adaptive Cable Resistance System on Fitness and Cardiometabolic Measures: A 12-Week Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010210.
Seo E-Y, Kim Y-S, Lee Y-J, Hur M-H. Virtual Reality Exercise Program Effects on Body Mass Index, Depression, Exercise Fun and Exercise Immersion in Overweight Middle-Aged Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20:900.
Silva JPLN, Novaes LFM, dos Santos LCR, Galindo BP, Cavalcante MA, de Araújo BCG, et al. Effects of Conventional and Virtual Reality Cardiovascular Rehabilitation in Body Composition and Functional Capacity of Patients with Heart Diseases: Randomized Clinical Trial. Int J Cardiovasc Sci. 2018. https://doi.org/10.5935/2359-4802.20180071.
Staiano AE, Abraham AA, Calvert SL. Adolescent Exergame Play for Weight Loss and Psychosocial Improvement: A Controlled Physical Activity Intervention. Obesity. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2012.143.
Vieira ÁS da S, Cristina Damas Argel de Melo M, Andreia Raquel Santos Noites SP, Machado JP, Joaquim Gabriel MM. The effect of virtual reality on a home-based cardiac rehabilitation program on body composition, lipid profile and eating patterns: A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Integr Med. 2017;9:69–78.
Peng W, Lin JH, Crouse J. Is playing exergames really exercising? A meta-analysis of energy expenditure in active video games. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2011;14:681–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HYY: Conceptualization; Resources; Writing – Original Draft Preparation. HLC: Formal Analysis; Methodology; Software; Validation; Writing – Original Draft Preparation. HYH: Writing – Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yen, HY., Chiu, HL. & Huang, HY. Virtual reality-enhanced exergames for weight control: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Obes 49, 1667–1675 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01782-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01782-w