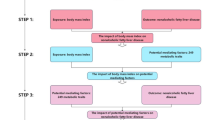
Abstract
Obesity, characterized by excessive body fat accumulation, is a growing global health concern with significant implications for both metabolic and skeletal health. The increasing prevalence of obesity, particularly among children, adolescents, and postmenopausal women, is associated with various bone-related disorders. Obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) collectively influence bone metabolism through systemic factors such as chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and alterations in adipose tissue function. Key mediators, including adipokines like leptin and adiponectin, along with pro-inflammatory cytokines, play crucial roles in modulating bone formation and resorption, thereby contributing to conditions such as osteopenia and osteoporosis. Moreover, the interplay between obesity, NAFLD, and bone health involves complex mechanisms, including gut microbiota dysbiosis and impaired vitamin D metabolism. Understanding these multifaceted interactions is essential for developing targeted interventions to prevent or mitigate the adverse effects of obesity and NAFLD on bone health. This review explores the molecular pathways, metabolic interactions, and associated pathologies linking obesity and NAFLD to bone health.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forte YS, Renovato-Martins M, Barja-Fidalgo C. Cellular and molecular mechanisms associating obesity to bone loss. Cells. 2023;12:521.
Rogero MM, Calder PC. Obesity, inflammation, toll-like receptor 4 and fatty acids. Nutrients. 2018;10:432.
Piché M-E, Tchernof A, Després J-P. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 2020;126:1477–500.
Wang T, He C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: the link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38–50.
Deng T, Lyon CJ, Bergin S, Caligiuri MA, Hsueh WA. Obesity, inflammation, and cancer. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis. 2016;11:421–49.
Stolarczyk E. Adipose tissue inflammation in obesity: a metabolic or immune response?. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017;37:35–40.
Stern JH, Smith GI, Chen S, Unger RH, Klein S, Scherer PE. Obesity dysregulates fasting-induced changes in glucagon secretion. J Endocrinol. 2019;243:149–60.
Basolo A, Ando T, Chang DC, Hollstein T, Krakoff J, Piaggi P, et al. Reduced albumin concentration predicts weight gain and higher ad libitum energy intake in humans. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:642568.
Tanzadehpanah H, Mahaki H, Moradi M, Afshar S, Rajabi O, Najafi R, et al. Human serum albumin binding and synergistic effects of gefitinib in combination with regorafenib on colorectal cancer cell lines. Colorectal Cancer. 2018;7:CRC03.
Tanzadehpanah H, Mahaki H, Moradi M, Afshar S, Moghadam NH, Salehzadeh S, et al. The use of molecular docking and spectroscopic methods for investigation of the interaction between regorafenib with human serum albumin (HSA) and calf thymus DNA (ct-DNA) in the presence of different site markers. Protein Pept Lett. 2021;28:290–303.
Ahmed B, Konje JC. The epidemiology of obesity in reproduction. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2023;89:102342.
Ataey A, Jafarvand E, Adham D, Moradi-Asl E. The relationship between obesity, overweight, and the human development index in world health organization eastern mediterranean region countries. J Prev Med Public Health. 2020;53:98.
Organization WH. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic: report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organization; 2000.
Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Acosta-Cazares B, Acuin C, et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128· 9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390:2627–42.
Chen Y, Peng Q, Yang Y, Zheng S, Wang Y, Lu W. The prevalence and increasing trends of overweight, general obesity, and abdominal obesity among Chinese adults: a repeated cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2019;19:1–18.
Jia W. Obesity in China: its characteristics, diagnostic criteria, and implications. Front Med. 2015;9:129–33.
Wariri O, Alhassan JAK, Mark G, Adesiyan O, Hanson L. Trends in obesity by socioeconomic status among non-pregnant women aged 15–49 y: a cross-sectional, multi-dimensional equity analysis of demographic and health surveys in 11 sub-Saharan Africa countries, 1994–2015. Int Health. 2021;13:436–45.
Tydeman-Edwards R, Van Rooyen FC, Walsh CM. Obesity, undernutrition and the double burden of malnutrition in the urban and rural southern Free State, South Africa. Heliyon. 2018;4.
Abels ER, Breakefield XO. Introduction to extracellular vesicles: biogenesis, RNA cargo selection, content, release, and uptake. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016;36:301–12.
Mehrvar A, Akbari M, Khosroshahi EM, Nekavand M, Mokhtari K, Baniasadi M, et al. The impact of exosomes on bone health: a focus on osteoporosis. Pathol Res Pract. 2024;263:155618.
Drapkina OM, Elkina AY, Sheptulina AF, Kiselev AR. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and bone tissue metabolism: current findings and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:8445.
Nachit M, Leclercq IA. Emerging awareness on the importance of skeletal muscle in liver diseases: time to dig deeper into mechanisms!. Clin Sci. 2019;133:465–81.
Qiao J, Wu Y, Ren Y. The impact of a high fat diet on bones: potential mechanisms. Food Funct. 2021;12:963–75.
Hafner H, Chang E, Carlson Z, Zhu A, Varghese M, Clemente J, et al. Lactational high-fat diet exposure programs metabolic inflammation and bone marrow adiposity in male offspring. Nutrients. 2019;11:1393.
Weinhold B. Epigenetics: the science of change. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences; Environmental Health Perspectives; 2006.
Mahmoud AM. An overview of epigenetics in obesity: the role of lifestyle and therapeutic interventions. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:1341.
Dolinoy DC. The agouti mouse model: an epigenetic biosensor for nutritional and environmental alterations on the fetal epigenome. Nutr Rev. 2008;66:S7–S11.
Armutcu F, McCloskey E, Ince M. Obesity significantly modifies signaling pathways associated with bone remodeling and metabolism. J Cell Signal. 2024;5:183–94.
Riazi K, Azhari H, Charette JH, Underwood FE, King JA, Afshar EE, et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:851–61.
Mantovani A, Petracca G, Beatrice G, Csermely A, Tilg H, Byrne CD, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and increased risk of incident extrahepatic cancers: a meta-analysis of observational cohort studies. Gut. 2022;71:778–88.
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Graham S, Wang X, Cai D, Huang M, et al. Causal relationships between NAFLD, T2D and obesity have implications for disease subphenotyping. J Hepatol. 2020;73:263–76.
Simon TG, Roelstraete B, Hagström H, Sundström J, Ludvigsson JF. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and incident major adverse cardiovascular events: results from a nationwide histology cohort. Gut. 2022;71:1867–75.
Liu Z, Suo C, Fan H, Zhang T, Jin L, Chen X. Dissecting causal relationships between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease proxied by chronically elevated alanine transaminase levels and 34 extrahepatic diseases. Metabolism. 2022;135:155270.
Zheng M, Xu J, Feng Z. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and bone mineral density: Mendelian randomization and mediation analysis. Bone Rep. 2024;22:101785.
Ahn S, Seo D, Kim S, Nam M-S, Hong S. The relationship between fatty liver index and bone mineral density in Koreans: KNHANES 2010–2011. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29:181–90.
Kinjo M, Setoguchi S, Solomon DH. Bone mineral density in adults with the metabolic syndrome: analysis in a population-based US sample. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4161–4.
Krishnan S, Anderson MP, Fields DA, Misra M. Abdominal obesity adversely affects bone mass in children. World J Clin Pediatr. 2018;7:43.
Gilsanz V, Chalfant J, Mo AO, Lee DC, Dorey FJ, Mittelman SD. Reciprocal relations of subcutaneous and visceral fat to bone structure and strength. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:3387–93.
Oh M-S, Kim S, Jang J-H, Park JY, Kang H-S, Lee MS, et al. Associations among the degree of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome, degree of obesity in children, and parental obesity. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016;19:199–206.
Marcovecchio ML, Chiarelli F. Obesity and growth during childhood and puberty. Nutr Growth. 2013;106:135–41.
Chaplais E, Naughton G, Greene D, Dutheil F, Pereira B, Thivel D, et al. Effects of interventions with a physical activity component on bone health in obese children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2018;36:12–30.
Zhao Y, Qin R, Ma X, Qin Z, Yang Z, Hong H, et al. Adiposity is not beneficial to bone mineral density in 0–5 year old Chinese children: the Jiangsu bone health study. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020;14:39–46.
Kanis J, Burlet N, Cooper C, Delmas P, Reginster J-Y, Borgstrom F, et al. European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19:399–428.
Méndez JP, Rojano-Mejía D, Pedraza J, Coral-Vázquez RM, Soriano R, García-García E, et al. Bone mineral density in postmenopausal Mexican-Mestizo women with normal body mass index, overweight, or obesity. Menopause. 2013;20:568–72.
Cherif R, Mahjoub F, Sahli H, Cheour E, Vico L, Sakly M, et al. Positive association of obesity and insulin resistance with bone mineral density in Tunisian postmenopausal women. J Clin Densitom. 2018;21:163–71.
Głogowska-Szeląg J, Kos-Kudła B, Marek B, Nowak M, Siemińska L. Assessment of selected adipocytokines in obese women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Endokrynol Pol. 2019;70:478–83.
Arango-Lopera V, Arroyo P, Gutiérrez-Robledo LM, Pérez-Zepeda MU, Cesari M. Mortality as an adverse outcome of sarcopenia. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17:259–62.
Chen YS, Guo Q, Guo LJ, Liu T, Wu XP, Lin ZY, et al. GDF 8 inhibits bone formation and promotes bone resorption in mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;44:500–8.
Saad FA. Novel insights into the complex architecture of osteoporosis molecular genetics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020;1462:37–52.
Cui Y, Yi Q, Sun W, Huang D, Zhang H, Duan L, et al. Molecular basis and therapeutic potential of myostatin on bone formation and metabolism in orthopedic disease. Biofactors. 2023;49:21–31.
Santos VRD, Christofaro DGD, Gomes IC, Freitas Júnior IF, Gobbo LA. Relationship between obesity, sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity, and bone mineral density in elderly subjects aged 80 years and over. Rev Bras Ortop. 2018;53:300–5.
Florencio-Silva R, Sasso GRdS, Sasso-Cerri E, Simões MJ, Cerri PS. Biology of bone tissue: structure, function, and factors that influence bone cells. BioMed Res Int. 2015;2015:421746.
Baniasadi M, Talebi S, Mokhtari K, Zabolian AH, Khosroshahi EM, Entezari M, et al. Role of non-coding RNAs in osteoporosis. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;253:155036.
Hou Z, Wang Z, Tao Y, Bai J, Yu B, Shen J, et al. KLF2 regulates osteoblast differentiation by targeting of Runx2. Lab Investig. 2019;99:271–80.
Chiu YH, Ritchlin CT. DC-STAMP: a key regulator in osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231:2402–7.
Chen X, Wang Z, Duan N, Zhu G, Schwarz EM, Xie C. Osteoblast–osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59:99–107.
Tresguerres F, Torres J, López-Quiles J, Hernández G, Vega J, Tresguerres I. The osteocyte: a multifunctional cell within the bone. Ann Anat. 2020;227:151422.
Cao JJ. Effects of obesity on bone metabolism. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:1–7.
Fintini D, Cianfarani S, Cofini M, Andreoletti A, Ubertini GM, Cappa M, et al. The bones of children with obesity. Front Endocrinol. 2020;11:200.
Cao JJ, Gregoire BR, Gao H. High-fat diet decreases cancellous bone mass but has no effect on cortical bone mass in the tibia in mice. Bone. 2009;44:1097–104.
Halade GV, El Jamali A, Williams PJ, Fajardo RJ, Fernandes G. Obesity-mediated inflammatory microenvironment stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone loss in mice. Exp Gerontol. 2011;46:43–52.
Shu L, Beier E, Sheu T, Zhang H, Zuscik MJ, Puzas EJ, et al. High-fat diet causes bone loss in young mice by promoting osteoclastogenesis through alteration of the bone marrow environment. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96:313–23.
Bonewald LF, Johnson ML. Osteocytes, mechanosensing and Wnt signaling. Bone. 2008;42:606–15.
Lecka-Czernik B, Stechschulte L, Czernik P, Dowling A. High bone mass in adult mice with diet-induced obesity results from a combination of initial increase in bone mass followed by attenuation in bone formation; implications for high bone mass and decreased bone quality in obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;410:35–41.
Greco E, Lenzi A, Migliaccio S. The obesity of bone. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2015;6:273–86.
Liu X, Wu Y, Li Y, Li K, Hou S, Ding M, et al. Vitamin D receptor (VDR) mediates the quiescence of activated hepatic stellate cells (aHSCs) by regulating M2 macrophage exosomal smooth muscle cell-associated protein 5 (SMAP-5). J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2023;24:248–61.
Marcucci G, Domazetovic V, Nediani C, Ruzzolini J, Favre C, Brandi ML. Oxidative stress and natural antioxidants in osteoporosis: novel preventive and therapeutic approaches. Antioxidants. 2023;12:373.
Harrison SA, Ruane PJ, Freilich B, Neff G, Patil R, Behling C, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa trial of efruxifermin for patients with compensated NASH cirrhosis. JHEP Rep. 2023;5:100563.
Jules J, Wang S, Shi Z, Liu J, Wei S, Feng X. The IVVY motif and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) sites in the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK) cooperate to induce osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:23738–50.
Ohori F, Kitaura H, Ogawa S, Shen W-R, Qi J, Noguchi T, et al. IL-33 inhibits TNF-α-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1130.
Marahleh A, Kitaura H, Ohori F, Kishikawa A, Ogawa S, Shen W-R, et al. TNF-α directly enhances osteocyte RANKL expression and promotes osteoclast formation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2925.
Shinohara H, Teramachi J, Okamura H, Yang D, Nagata T, Haneji T. Double stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is necessary for TNF-α-induced osteoclast formation in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116:1957–67.
Jeong B-C. ATF3 mediates the inhibitory action of TNF-α on osteoblast differentiation through the JNK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499:696–701.
Ye X, Huang H, Zhao N, Zhang J, Yang P. Inhibition of Runx2 signaling by TNF-α in ST2 murine bone marrow stromal cells undergoing osteogenic differentiation. Vitr Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016;52:1026–33.
Muluke M, Gold T, Kiefhaber K, Al-Sahli A, Celenti R, Jiang H, et al. Diet-induced obesity and its differential impact on periodontal bone loss. J Dent Res. 2016;95:223–9.
Zhang K, Wang C, Chen Y, Ji X, Chen X, Tian L, et al. Preservation of high-fat diet-induced femoral trabecular bone loss through genetic target of TNF-α. Endocrine. 2015;50:239–49.
Srikanthan K, Feyh A, Visweshwar H, Shapiro JI, Sodhi K. Systematic review of metabolic syndrome biomarkers: a panel for early detection, management, and risk stratification in the West Virginian population. Int J Med Sci. 2016;13:25.
Galozzi P, Bindoli S, Doria A, Sfriso P. The revisited role of interleukin-1 alpha and beta in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders and in comorbidities. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20:102785.
Cao Y, Jansen ID, Sprangers S, Stap J, Leenen PJ, Everts V, et al. IL-1β differently stimulates proliferation and multinucleation of distinct mouse bone marrow osteoclast precursor subsets. J Leucoc Biol. 2016;100:513–23.
Son HS, Lee J, Lee HI, Kim N, Jo Y-J, Lee G-R, et al. Benzydamine inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption via down-regulation of interleukin-1β expression. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10:462–74.
Lazzerini PE, Capperucci C, Spreafico A, Capecchi PL, Niccolini S, Ferrata P, et al. Rosuvastatin inhibits spontaneous and IL-1β-induced interleukin-6 production from human cultured osteoblastic cells. Jt Bone Spine. 2013;80:195–200.
Hah Y-S, Kang H-G, Cho H-Y, Shin S-H, Kim U-K, Park B-W, et al. JNK signaling plays an important role in the effects of TNF-α and IL-1β on in vitro osteoblastic differentiation of cultured human periosteal-derived cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40:4869–81.
Yang H, Liu Q, Ahn JH, Kim SB, Kim YC, Sung SH, et al. Luteolin downregulates IL-1β-induced MMP-9 and-13 expressions in osteoblasts via inhibition of ERK signalling pathway. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2012;27:261–6.
McKnight Q, Jenkins S, Li X, Nelson T, Marlier A, Cantley LG, et al. IL-1β drives production of FGF-23 at the onset of chronic kidney disease in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35:1352–62.
Rupp T, Butscheidt S, Vettorazzi E, Oheim R, Barvencik F, Amling M, et al. High FGF23 levels are associated with impaired trabecular bone microarchitecture in patients with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30:1655–62.
He B, Yin X, Hao D, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Zhang K, et al. Blockade of IL-6 alleviates bone loss induced by modeled microgravity in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;98:678–83.
Graf C, Ferrari N. Metabolic health—the role of adipo-myokines. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:6159.
Holecki M, Wiecek A. Relationship between body fat mass and bone metabolism. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2010;120:361–7.
Morcov C, Vulpoi C, Branisteanu D. Relationship between bone mineral density, weight, and estrogen levels in pre and postmenopausal women. Med Surg J. 2012;116:946–50.
Ricci R, Bevilacqua F. The potential role of leptin and adiponectin in obesity: a comparative review. Vet J. 2012;191:292–8.
Achari AE, Jain SK. Adiponectin, a therapeutic target for obesity, diabetes, and endothelial dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:1321.
China SP, Sanyal S, Chattopadhyay N. Adiponectin signaling and its role in bone metabolism. Cytokine. 2018;112:116–31.
Xie C, Chen Q. Adipokines: new therapeutic target for osteoarthritis?. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019;21:1–9.
Wang F, Wang P-X, Wu X-L, Dang S-Y, Chen Y, Ni Y-Y, et al. Deficiency of adiponectin protects against ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in mice. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e68497.
Tu Q, Zhang J, Dong LQ, Saunders E, Luo E, Tang J, et al. Adiponectin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via APPL1-mediated suppression of Akt1. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:12542–53.
Abbott MJ, Roth TM, Ho L, Wang L, O’Carroll D, Nissenson RA. Negative skeletal effects of locally produced adiponectin. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0134290.
Liu H, Liu S, Ji H, Zhao Q, Liu Y, Hu P, et al. An adiponectin receptor agonist promote osteogenesis via regulating bone-fat balance. Cell Prolif. 2021;54:e13035.
Yin G, Liu H, Li J, Liu Y, Liu X, Luo E. Adenoviral delivery of adiponectin ameliorates osteogenesis around implants in ovariectomized rats. J Gene Med. 2019;21:e3069.
Yue R, Zhou BO, Shimada IS, Zhao Z, Morrison SJ. Leptin receptor promotes adipogenesis and reduces osteogenesis by regulating mesenchymal stromal cells in adult bone marrow. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18:782–96.
Li W, Xu P, Wang C, Ha X, Gu Y, Wang Y, et al. The effects of fat-induced obesity on bone metabolism in rats. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2017;11:454–63.
Li J, Gao Y, Yu T, Lange JK, LeBoff MS, Gorska A, et al. Obesity and leptin influence vitamin D metabolism and action in human marrow stromal cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;198:105564.
Maggio AB, Belli DC, Puigdefabregas JWB, Rizzoli R, Farpour-Lambert NJ, Beghetti M, et al. High bone density in adolescents with obesity is related to fat mass and serum leptin concentrations. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014;58:723–8.
Nakamura Y, Nakano M, Suzuki T, Sato J, Kato H, Takahashi J, et al. Two adipocytokines, leptin and adiponectin, independently predict osteoporotic fracture risk at different bone sites in postmenopausal women. Bone. 2020;137:115404.
Dimitri P, Jacques R, Paggiosi M, King D, Walsh J, Taylor Z, et al. Leptin may play a role in bone microstructural alterations in obese children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:594–602.
Wee NK, Enriquez RF, Nguyen AD, Horsnell H, Kulkarni R, Khor EC, et al. Diet-induced obesity suppresses cortical bone accrual by a neuropeptide Y-dependent mechanism. Int J Obes. 2018;42:1925–38.
Erener T, Ceritoğlu KU, Aktekin CN, Dalgic AD, Keskin D, Geneci F, et al. Investigation of the effect of ghrelin on bone fracture healing in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2021;48:1382–90.
Xiao L, Zhang H, Wang Y, Li J, Yang G, Wang L, et al. Dysregulation of the ghrelin/RANKL/OPG pathway in bone mass is related to AIS osteopenia. Bone. 2020;134:115291.
Gamberi T, Magherini F, Modesti A, Fiaschi T. Adiponectin signaling pathways in liver diseases. Biomedicines. 2018;6:52.
Alzahrani B, Iseli T, Ramezani-Moghadam M, Ho V, Wankell M, Sun EJ, et al. The role of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 in liver fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864:700–8.
Okada-Iwabu M, Yamauchi T, Iwabu M, Honma T, Hamagami K-I, Matsuda K, et al. A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature. 2013;503:493–9.
Kim Y, Lim JH, Kim MY, Kim EN, Yoon HE, Shin SJ, et al. The adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in a model of type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29:1108–27.
Adhyatmika A, Beljaars L, Putri KS, Habibie H, Boorsma CE, Reker-Smit C, et al. Osteoprotegerin is more than a possible serum marker in liver fibrosis: a study into its function in human and murine liver. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12:471.
Alkhathami K, Soman A, Chandy S, Ramamoorthy B, Alqahtani B. Comparing the effects of retro and forward walking on serum adiponectin levels in obese young adults. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023;18:917–25.
Kleerekoper M, Nelson DA, Peterson EL, Wilson PS, Jacobsen G, Longcope C. Body composition and gonadal steroids in older white and black women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;79:775–9.
Di F, Gao D, Yao L, Zhang R, Qiu J, Song L. Differences in metabonomic profiles of abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1077604.
Kirk B, Feehan J, Lombardi G, Duque G. Muscle, bone, and fat crosstalk: the biological role of myokines, osteokines, and adipokines. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18:388–400.
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006;444:1027–31.
Chelakkot C, Ghim J, Ryu SH. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1–9.
Liu H, Wang P, Cao M, Li M, Wang F. Protective role of oligomycin against intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction caused by IFN-γ and TNF-α. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;29:799–808.
Saad M, Santos A, Prada P. Linking gut microbiota and inflammation to obesity and insulin resistance. Physiology. 2016;31:283–93.
Luo Y, Chen G-L, Hannemann N, Ipseiz N, Krönke G, Bäuerle T, et al. Microbiota from obese mice regulate hematopoietic stem cell differentiation by altering the bone niche. Cell Metab. 2015;22:886–94.
Rios JL, Bomhof MR, Reimer RA, Hart DA, Collins KH, Herzog W. Protective effect of prebiotic and exercise intervention on knee health in a rat model of diet-induced obesity. Sci Rep. 2019;9:3893.
Eaimworawuthikul S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Yasom S, Wanchai K, Suntornsaratoon P, et al. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics on jawbone in obese-insulin resistant rats. Eur J Nutr. 2019;58:2801–10.
Wu X, Zhao K, Fang X, Lu F, Zhang W, Song X, et al. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory bone loss by saikosaponin D is associated with regulation of the RANKL/RANK pathway. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2021:4741–57.
Li L, Rao S, Cheng Y, Zhuo X, Deng C, Xu N, et al. Microbial osteoporosis: the interplay between the gut microbiota and bones via host metabolism and immunity. MicrobiologyOpen. 2019;8:e00810.
Grüner N, Ortlepp AL, Mattner J. Pivotal role of intestinal microbiota and intraluminal metabolites for the maintenance of gut–bone physiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:5161.
Ji Y, Yin Y, Li Z, Zhang W. Gut microbiota-derived components and metabolites in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Nutrients. 2019;11:1712.
Han Y, You X, Xing W, Zhang Z, Zou W. Paracrine and endocrine actions of bone—the functions of secretory proteins from osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Bone Res. 2018;6:16.
Ho BB, Bergwitz C. FGF23 signalling and physiology. J Mol Endocrinol. 2021;66:R23–32.
Mizokami A, Kawakubo-Yasukochi T, Hirata M. Osteocalcin and its endocrine functions. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;132:1–8.
Mosialou I, Shikhel S, Liu J-M, Maurizi A, Luo N, He Z, et al. MC4R-dependent suppression of appetite by bone-derived lipocalin 2. Nature. 2017;543:385–90.
Guedes JAC, Esteves J, Morais M, Zorn T, Furuya DT. Osteocalcin improves insulin resistance and inflammation in obese mice: participation of white adipose tissue and bone. Bone. 2018;115:68–82.
Zhou B, Li H, Liu J, Xu L, Guo Q, Zang W, et al. Autophagic dysfunction is improved by intermittent administration of osteocalcin in obese mice. Int J Obes. 2016;40:833–43.
Hanks LJ, Casazza K, Judd SE, Jenny NS, Gutiérrez OM. Associations of fibroblast growth factor-23 with markers of inflammation, insulin resistance and obesity in adults. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0122885.
Hu X, Ma X, Luo Y, Xu Y, Xiong Q, Pan X, et al. Associations of serum fibroblast growth factor 23 levels with obesity and visceral fat accumulation. Clin Nutr. 2018;37:223–8.
Grethen E, Hill KM, Jones R, Cacucci BM, Gupta CE, Acton A, et al. Serum leptin, parathyroid hormone, 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D, fibroblast growth factor 23, bone alkaline phosphatase, and sclerostin relationships in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol. 2012;97:1655–62.
Xu L, Zhang L, Zhang H, Yang Z, Qi L, Wang Y, et al. The participation of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) in the progression of osteoporosis via JAK/STAT pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:3819–28.
Saito M, Marumo K. Bone quality in diabetes. Front Endocrinol. 2013;4:72.
Liu C, Jiang D. High glucose-induced LIF suppresses osteoblast differentiation via regulating STAT3/SOCS3 signaling. Cytokine. 2017;91:132–9.
Yang L, Liu J, Shan Q, Geng G, Shao P. High glucose inhibits proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast in alveolar bone by inducing pyroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;522:471–8.
Bornstein S, Moschetta M, Kawano Y, Sacco A, Huynh D, Brooks D, et al. Metformin affects cortical bone mass and marrow adiposity in diet-induced obesity in male mice. Endocrinology. 2017;158:3369–85.
Mosialou I, Shikhel S, Luo N, Petropoulou PI, Panitsas K, Bisikirska B, et al. Lipocalin-2 counteracts metabolic dysregulation in obesity and diabetes. J Exp Med. 2020;217:e20191261.
Kim H-J, Ohk B, Kang WY, Seong SJ, Suk K, Lim M-S, et al. Deficiency of lipocalin-2 promotes proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast precursors via regulation of c-fms expression and nuclear factor-kappa B activation. J Bone Metab. 2016;23:8–15.
Villalvilla A, García-Martín A, Largo R, Gualillo O, Herrero-Beaumont G, Gómez R. The adipokine lipocalin-2 in the context of the osteoarthritic osteochondral junction. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29243.
Costa D, Lazzarini E, Canciani B, Giuliani A, SpanÒ R, Marozzi K, et al. Altered bone development and turnover in transgenic mice over-expressing lipocalin-2 in bone. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228:2210–21.
Rucci, Capulli N, Piperni M, Cappariello SG, Lau A, Frings P, et al. Lipocalin 2: a new mechanoresponding gene regulating bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30:357–68.
Tanzadehpanah H, Asoodeh A, Chamani J. An antioxidant peptide derived from Ostrich (Struthio camelus) egg white protein hydrolysates. Food Res Int. 2012;49:105–11.
Kharazmi-Khorassani J, Asoodeh A, Tanzadehpanah H. Antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of thymosin alpha-1 (Thα1) peptide. Bioorg Chem. 2019;87:743–52.
Pisoschi AM, Pop A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: a review. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;97:55–74.
Engin AB, Engin A. Obesity and lipotoxicity. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2017.
Chattopadhyay M, Khemka VK, Chatterjee G, Ganguly A, Mukhopadhyay S, Chakrabarti S. Enhanced ROS production and oxidative damage in subcutaneous white adipose tissue mitochondria in obese and type 2 diabetes subjects. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;399:95–103.
Yang Y, Sun Y, Mao W-W, Zhang H, Ni B, Jiang L. Oxidative stress induces downregulation of TP53INP2 and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs during osteoporosis through the autophagy degradation pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:226–37.
Kanda Y, Hinata T, Kang SW, Watanabe Y. Reactive oxygen species mediate adipocyte differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2011;89:250–8.
Dong X, Bi L, He S, Meng G, Wei B, Jia S, et al. FFAs-ROS-ERK/P38 pathway plays a key role in adipocyte lipotoxicity on osteoblasts in co-culture. Biochimie. 2014;101:123–31.
Mukherjee R, Moreno-Fernandez ME, Giles DA, Cappelletti M, Stankiewicz TE, Chan CC, et al. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced) oxidase 2 modulates inflammatory vigor during nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in mice. Hepatol Commun. 2018;2:546–60.
Rahman MM, El Jamali A, Halade GV, Ouhtit A, Abou-Saleh H, Pintus G. Nox2 activity is required in obesity-mediated alteration of bone remodeling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:6054361.
Kang IS, Kim C. NADPH oxidase gp91phox contributes to RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by upregulating NFATc1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38014.
Shen C-L, Cao JJ, Dagda RY, Chanjaplammootil S, Lu C, Chyu M-C, et al. Green tea polyphenols benefits body composition and improves bone quality in long-term high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Nutr Res. 2012;32:448–57.
Cao JJ, Picklo MJ. N-acetylcysteine supplementation decreases osteoclast differentiation and increases bone mass in mice fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr. 2014;144:289–96.
Hu X, Li B, Wu F, Liu X, Liu M, Wang C, et al. GPX7 facilitates BMSCs osteoblastogenesis via ER stress and mTOR pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:10454–65.
Matoušková P, Hanousková B, Skálová L. MicroRNAs as potential regulators of glutathione peroxidases expression and their role in obesity and related pathologies. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:1199.
Tanzadehpanah H, Asoodeh A, Saidijam M, Chamani J, Mahaki H. Improving efficiency of an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptide as multifunctional peptides. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018;36:3803–18.
Ali Ahmad M, Karavetian M, Moubareck CA, Wazz G, Mahdy T, Venema K. The association between peptide hormones with obesity and insulin resistance markers in lean and obese individuals in the United Arab Emirates. Nutrients. 2022;14:1271.
Zhao LJ, Jiang H, Papasian CJ, Maulik D, Drees B, Hamilton J, et al. Correlation of obesity and osteoporosis: effect of fat mass on the determination of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23:17–29.
Vestergaard P. Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes—a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18:427–44.
López-Gómez JJ, Castrillón JLP, de Luis Román DA. Impact of obesity on bone metabolism. Endocrinol Nutr. 2016;63:551–9.
Conde J, Scotece M, Gomez R, Lopez V, Gomez-Reino JJ, Gualillo O. Adipokines and osteoarthritis: novel molecules involved in the pathogenesis and progression of disease. Arthritis. 2011;2011:203901.
Hamrick MW, Pennington C, Newton D, Xie D, Isales C. Leptin deficiency produces contrasting phenotypes in bones of the limb and spine. Bone. 2004;34:376–83.
Frühbeck G, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Muruzábal FJ, Burrell MA. The adipocyte: a model for integration of endocrine and metabolic signaling in energy metabolism regulation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;280:E827–47.
Ponrartana S, Aggabao PC, Hu HH, Aldrovandi GM, Wren TA, Gilsanz V. Brown adipose tissue and its relationship to bone structure in pediatric patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:2693–8.
Wei W, Dutchak PA, Wang X, Ding X, Wang X, Bookout AL, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 promotes bone loss by potentiating the effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:3143–8.
Li Q, Hua Y, Yang Y, He X, Zhu W, Wang J, et al. T cell factor 7 (TCF7)/TCF1 feedback controls osteocalcin signaling in brown adipocytes independent of the wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2018;38;e00562–17
Hou J, He C, He W, Yang M, Luo X, Li C. Obesity and bone health: a complex link. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:600181.
Tencerova M, Okla M, Kassem M. Insulin signaling in bone marrow adipocytes. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17:446–54.
Fazeli PK, Horowitz MC, MacDougald OA, Scheller EL, Rodeheffer MS, Rosen CJ, et al. Marrow fat and bone—new perspectives. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:935–45.
Al Saedi A, Goodman C, Myers D, Hayes A, Duque G. Rapamycin affects palmitate-induced lipotoxicity in osteoblasts by modulating apoptosis and autophagy. J Gerontol Ser A. 2020;75:58–63.
Horowitz MC, Berry R, Holtrup B, Sebo Z, Nelson T, Fretz JA, et al. Bone marrow adipocytes. Adipocyte. 2017;6:193–204.
Elbaz A, Wu X, Rivas D, Gimble JM, Duque G. Inhibition of fatty acid biosynthesis prevents adipocyte lipotoxicity on human osteoblasts in vitro. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14:982–91.
Singh L, Tyagi S, Myers D, Duque G. Good, bad, or ugly: the biological roles of bone marrow fat. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16:130–7.
Kaye WH, Wierenga CE, Bischoff-Grethe A, Berner LA, Ely AV, Bailer UF, et al. Neural insensitivity to the effects of hunger in women remitted from anorexia nervosa. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177:601–10.
Bredella MA, Fazeli PK, Miller KK, Misra M, Torriani M, Thomas BJ, et al. Increased bone marrow fat in anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:2129–36.
Justesen J, Stenderup K, Ebbesen E, Mosekilde L, Steiniche T, Kassem M. Adipocyte tissue volume in bone marrow is increased with aging and in patients with osteoporosis. Biogerontology. 2001;2:165–71.
Shen W, Chen J, Punyanitya M, Shapses S, Heshka S, Heymsfield S. MRI-measured bone marrow adipose tissue is inversely related to DXA-measured bone mineral in Caucasian women. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18:641–7.
Li S, Jiang H, Wang B, Gu M, Zhang N, Liang W, et al. Effect of leptin on marrow adiposity in ovariectomized rabbits assessed by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2018;42:588–93.
Putignano P, Dubini A, Toja P, Invitti C, Bonfanti S, Redaelli G, et al. Salivary cortisol measurement in normal-weight, obese and anorexic women: comparison with plasma cortisol. Eur J Endocrinol. 2001;145:165–71.
Cândido FG, Bressan J. Vitamin D: link between osteoporosis, obesity, and diabetes?. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:6569–91.
Wamberg L, Pedersen SB, Rejnmark L, Richelsen B. Causes of vitamin D deficiency and effect of vitamin D supplementation on metabolic complications in obesity: a review. Curr Obes Rep. 2015;4:429–40.
Sukumar D, Schlussel Y, Riedt C, Gordon C, Stahl T, Shapses S. Obesity alters cortical and trabecular bone density and geometry in women. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22:635–45.
Gonzalez-Campoy JM, Castorino K, Ebrahim A, Hurley D, Jovanovic L, Mechanick JI, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for healthy eating for the prevention and treatment of metabolic and endocrine diseases in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/the American College of Endocrinology and the Obesity Society. Endocr Pract. 2013;19:1–82.
Bartrina JA, Majem LS. Objetivos nutricionales para la población española: Consenso de la Sociedad Española de Nutrición Comunitaria 2011. Revista Española de Nutrición Comunitaria. 2011;17:178–99.
Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Giovannucci E, Willett WC, Dietrich T, Dawson-Hughes B. Estimation of optimal serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D for multiple health outcomes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84:18–28.
Drincic A, Fuller E, Heaney RP, Armas LA. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D response to graded vitamin D3 supplementation among obese adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:4845–51.
Shapses S, Sukumar D, Schneider S, Schlussel Y, Brolin R, Taich L. Hormonal and dietary influences on true fractional calcium absorption in women: role of obesity. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23:2607–14.
Calvo MS, Tucker KL. Is phosphorus intake that exceeds dietary requirements a risk factor in bone health?. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013;1301:29–35.
Rosato V, Masarone M, Dallio M, Federico A, Aglitti A, Persico M. NAFLD and extra-hepatic comorbidities: current evidence on a multi-organ metabolic syndrome. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16:3415.
Wang X, Li W, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Qin G. Association between vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: results from a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:17221.
Jamialahmadi H, Nazari SE, TanzadehPanah H, Saburi E, Asgharzadeh F, Khojasteh-Leylakoohi F, et al. Targeting transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) using Pirfenidone, a potential repurposing therapeutic strategy in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2023;13:14357.
Mahdavinejad L, Alahgholi-Hajibehzad M, Eftekharian MM, Zaerieghane Z, Salehi I, Hajilooi M, et al. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields decrease serum levels of interleukin-17, transforming growth factor-β and downregulate Foxp3 expression in the spleen. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018;38:457–62.
Sun S, Xu M, Zhuang P, Chen G, Dong K, Dong R, et al. Effect and mechanism of vitamin D activation disorder on liver fibrosis in biliary atresia. Sci Rep. 2021;11:19883.
He R, Fan L, Song Q, Diao H, Xu H, Ruan W, et al. Protective effect of active vitamin D on liver fibrosis induced by sodium arsenite in SD rats. Wei Sheng yan jiu J Hyg Res. 2022;51:926–33.
Ibrahim MN, Khalifa AA, Hemead DA, Alsemeh AE, Habib MA. 1, 25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol down-regulates 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase and caspase-3 in rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Mol Histol. 2023;54:119–34.
Thomas RL, Jiang L, Adams JS, Xu ZZ, Shen J, Janssen S, et al. Vitamin D metabolites and the gut microbiome in older men. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5997.
Zhang X-L, Chen L, Yang J, Zhao S-S, Jin S, Ao N, et al. Vitamin D alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via restoring gut microbiota and metabolism. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1117644.
Saberi B, Dadabhai AS, Nanavati J, Wang L, Shinohara RT, Mullin GE. Vitamin D levels do not predict the stage of hepatic fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a PRISMA compliant systematic review and meta-analysis of pooled data. World J Hepatol. 2018;10:142.
Jaruvongvanich V, Ahuja W, Sanguankeo A, Wijarnpreecha K, Upala S. Vitamin D and histologic severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49:618–22.
Kumar M, Parchani A, Kant R, Das A. Relationship between vitamin D deficiency and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study from a tertiary care center in Northern India. Cureus. 2023;15.
da Silva TBP, Luiz MM, Delinocente MLB, Steptoe A, de Oliveira C, Alexandre TdS. Is abdominal obesity a risk factor for the incidence of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency in older adults? Evidence from the ELSA study. Nutrients. 2022;14:4164.
Su T, Xiao Y, Xiao Y, Guo Q, Li C, Huang Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal MiR-29b-3p regulates aging-associated insulin resistance. ACS Nano. 2019;13:2450–62.
Hosseini N, Tanzadehpanah H, Mansoori A, Sabzekar M, Ferns GA, Esmaily H, et al. Using a robust model to detect the association between anthropometric factors and T2DM: machine learning approaches. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025;25:49.
Ferron M, Wei J, Yoshizawa T, Del Fattore A, DePinho RA, Teti A, et al. Insulin signaling in osteoblasts integrates bone remodeling and energy metabolism. Cell. 2010;142:296–308.
Srikanthan P, Crandall CJ, Miller-Martinez D, Seeman TE, Greendale GA, Binkley N, et al. Insulin resistance and bone strength: findings from the study of midlife in the United States. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29:796–803.
Shanbhogue VV, Mitchell DM, Rosen CJ, Bouxsein ML. Type 2 diabetes and the skeleton: new insights into sweet bones. Lancet Diab Endocrinol. 2016;4:159–73.
Kanazawa I, Yamaguchi T, Sugimoto T. Effects of intensive glycemic control on serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol Investig. 2012;35:469–72.
Zhang M, Xuan S, Bouxsein ML, Von Stechow D, Akeno N, Faugere MC, et al. Osteoblast-specific knockout of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor gene reveals an essential role of IGF signaling in bone matrix mineralization. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44005–12.
Borges JLC, Bilezikian J, Jones-Leone A, Acusta A, Ambery P, Nino A, et al. A randomized, parallel group, double-blind, multicentre study comparing the efficacy and safety of Avandamet (rosiglitazone/metformin) and metformin on long-term glycaemic control and bone mineral density after 80 weeks of treatment in drug-naive type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Diab Obes Metab. 2011;13:1036–46.
Lecka-Czernik B. Diabetes, bone and glucose-lowering agents: basic biology. Diabetologia. 2017;60:1163–9.
Dormuth CR, Carney G, Carleton B, Bassett K, Wright JM. Thiazolidinediones and fractures in men and women. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:1395–402.
Zhu Z-N, Jiang Y-F, Ding T. Risk of fracture with thiazolidinediones: an updated meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Bone. 2014;68:115–23.
Baggio LL, Drucker DJ. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2131–57.
Sayed SA, Khaliq A, Mahmood A. Evaluating the risk of osteoporosis through bone mass density. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2016;28:730–3.
Muka T, Trajanoska K, Kiefte-de Jong JC, Oei L, Uitterlinden AG, Hofman A, et al. The association between metabolic syndrome, bone mineral density, hip bone geometry and fracture risk: the Rotterdam study. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0129116.
Nelson LR, Bulun SE. Estrogen production and action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:S116–S24.
Qiao D, Li Y, Liu X, Zhang X, Qian X, Zhang H, et al. Association of obesity with bone mineral density and osteoporosis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health. 2020;180:22–8.
Kim HY, Choe JW, Kim HK, Bae SJ, Kim BJ, Lee SH, et al. Negative association between metabolic syndrome and bone mineral density in Koreans, especially in men. Calcif Tissue Int. 2010;86:350–8.
Nanes MS. Tumor necrosis factor-α: molecular and cellular mechanisms in skeletal pathology. Gene. 2003;321:1–15.
Pinheiro MB, Oliveira J, Bauman A, Fairhall N, Kwok W, Sherrington C. Evidence on physical activity and osteoporosis prevention for people aged 65+ years: a systematic review to inform the WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2020;17:1–53.
Marini S, Barone G, Masini A, Dallolio L, Bragonzoni L, Longobucco Y, et al. The effect of physical activity on bone biomarkers in people with osteoporosis: a systematic review. Front Endocrinol. 2020;11:585689.
Rapp K, Cameron ID, Kurrle S, Klenk J, Kleiner A, Heinrich S, et al. Excess mortality after pelvic fractures in institutionalized older people. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21:1835–9.
Ilich JZ, Kelly OJ, Inglis JE, Panton LB, Duque G, Ormsbee MJ. Interrelationship among muscle, fat, and bone: connecting the dots on cellular, hormonal, and whole body levels. Ageing Res Rev. 2014;15:51–60.
Tarantino U, Piccirilli E, Fantini M, Baldi J, Gasbarra E, Bei R. Sarcopenia and fragility fractures: molecular and clinical evidence of the bone-muscle interaction.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97:429–37.
Scott D, Chandrasekara SD, Laslett LL, Cicuttini F, Ebeling PR, Jones G. Associations of sarcopenic obesity and dynapenic obesity with bone mineral density and incident fractures over 5–10 years in community-dwelling older adults. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;99:30–42.
Cao JJ, Picklo MJ. Involuntary wheel running improves but does not fully reverse the deterioration of bone structure of obese rats despite decreasing adiposity. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;97:145–55.
Tang X, Liu G, Kang J, Hou Y, Jiang F, Yuan W, et al. Obesity and risk of hip fracture in adults: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e55077.
De Laet C, Kanis J, Odén A, Johanson H, Johnell O, Delmas P, et al. Body mass index as a predictor of fracture risk: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16:1330–8.
Prieto-Alhambra D, Premaor MO, Fina Avilés F, Hermosilla E, Martinez D, Carbonell-Abella C, et al. The association between fracture and obesity is site-dependent: a population-based study in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27:294–300.
Kang D, Guo L, Guo T, Wang Y, Liu T, Feng X, et al. Association of body composition with bone mineral density in northern Chinese men by different criteria for obesity. J Endocrino Investig. 2015;38:323–31.
Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR, Goldring MB. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:1697.
Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F, Lafeber FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377:2115–26.
Koskinen A, Vuolteenaho K, Nieminen R, Moilanen T, Moilanen E. Leptin enhances MMP-l, MMP-3 and MMP-13 production in human osteoarthritic cartilage and correlates with MMP-1 and MMP-3 in synovial fluid from OA patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol Incl Suppl. 2011;29:57.
Reyes C, Leyland KM, Peat G, Cooper C, Arden NK, Prieto-Alhambra D. Association between overweight and obesity and risk of clinically diagnosed knee, hip, and hand osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:1869–75.
Scotece M, Conde J, Gómez R, López V, Lago F, Gómez-Reino JJ, et al. Beyond fat mass: exploring the role of adipokines in rheumatic diseases. Sci World J. 2011;11:1932–47.
Gremese E, Tolusso B, Gigante MR, Ferraccioli G. Obesity as a risk and severity factor in rheumatic diseases (autoimmune chronic inflammatory diseases). Front Immunol. 2014;5:576.
Rong B, Feng R, Liu C, Wu Q, Sun C. Reduced delivery of epididymal adipocyte-derived exosomal resistin is essential for melatonin ameliorating hepatic steatosis in mice. J Pineal Res. 2019;66:e12561.
Alissa EM, Alzughaibi LS, Marzouki ZM. Relationship between serum resistin, body fat and inflammatory markers in females with clinical knee osteoarthritis. Knee. 2020;27:45–50.
Bao J-P, Chen W-P, Feng J, Hu P-F, Shi Z-L, Wu L-D. Leptin plays a catabolic role on articular cartilage. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37:3265–72.
Kang EH, Lee YJ, Kim TK, Chang CB, Chung J-H, Shin K, et al. Adiponectin is a potential catabolic mediator in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:1–11.
Otero M, Lago R, Gómez R, Lago F, Gomez-Reino JJ, Gualillo O. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, MEK-1 and p38 mediate leptin/interferon-gamma synergistic NOS type II induction in chondrocytes. Life Sci. 2007;81:1452–60.
Kalichman L, Kobyliansky E. Hand osteoarthritis in Chuvashian population: prevalence and determinants. Rheumatol Int. 2009;30:85–92.
Minamino H, Katsushima M, Yoshida T, Hashimoto M, Fujita Y, Shirakashi M, et al. Increased circulating adiponectin is an independent disease activity marker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study using the KURAMA database. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0229998.
Nam JL, Takase-Minegishi K, Ramiro S, Chatzidionysiou K, Smolen JS, Van Der Heijde D, et al. Efficacy of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a systematic literature review informing the 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1113–36.
Zhang Y, Liu J, Yao J, Ji G, Qian L, Wang J, et al. Obesity: pathophysiology and intervention. Nutrients. 2014;6:5153–83.
Feng X, Xu X, Shi Y, Liu X, Liu H, Hou H, et al. Body mass index and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: an updated dose-response meta-analysis. BioMed Res Int. 2019;2019:3579081.
Coelho M, Oliveira T, Fernandes R. State of the art paper Biochemistry of adipose tissue: an endocrine organ. Arch Med Sci. 2013;9:191–200.
Lee YH, Bae SC. Circulating adiponectin and visfatin levels in rheumatoid arthritis and their correlation with disease activity: a meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21:664–72.
Choi HM, Doss HM, Kim KS. Multifaceted physiological roles of adiponectin in inflammation and diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1219.
Liu R, Wu Q, Su D, Che N, Chen H, Geng L, et al. A regulatory effect of IL-21 on T follicular helper-like cell and B cell in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:1–12.
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Hwang D, Yang XO, Kang HS, Ma L, et al. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin-21 but independent of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. Immunity. 2008;29:138–49.
Liu R, Zhao P, Zhang Q, Che N, Xu L, Qian J, et al. Adiponectin promotes fibroblast-like synoviocytes producing interleukin-6 to enhance T follicular helper cells response in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38:11–8.
Liu Y, Hazlewood GS, Kaplan GG, Eksteen B, Barnabe C. Impact of obesity on remission and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2017;69:157–65.
Fujita Y, Watanabe K, Maki K. Serum leptin levels negatively correlate with trabecular bone mineral density in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2012;12:84–94.
Scheller EL, Khoury B, Moller KL, Wee NK, Khandaker S, Kozloff KM, et al. Changes in skeletal integrity and marrow adiposity during high-fat diet and after weight loss. Front Endocrinol. 2016;7:102.
Inzana JA, Kung M, Shu L, Hamada D, Xing LP, Zuscik MJ, et al. Immature mice are more susceptible to the detrimental effects of high fat diet on cancellous bone in the distal femur. Bone. 2013;57:174–83.
Choi HS, Park SJ, Lee ZH, Lim S-K. The effects of a high fat diet containing diacylglycerol on bone in C57BL/6J mice. Yonsei Med J. 2015;56:951–60.
Silva MJ, Eekhoff JD, Patel T, Kenney-Hunt JP, Brodt MD, Steger-May K, et al. Effects of high-fat diet and body mass on bone morphology and mechanical properties in 1100 advanced intercross mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:711–25.
Ionova-Martin S, Wade J, Tang S, Shahnazari M, Ager J, Lane N, et al. Changes in cortical bone response to high-fat diet from adolescence to adulthood in mice. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22:2283–93.
Chen R, Armamento-Villareal R. Obesity and skeletal fragility. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024;109:e466–77.
López-Gómez JJ, Pérez-Castrillón JL, García de Santos I, Pérez-Alonso M, Izaola-Jauregui O, Primo-Martín D, et al. Influence of obesity on bone turnover markers and fracture risk in postmenopausal women. Nutrients. 2022;14:1617.
Turcotte A-F, O’Connor S, Morin SN, Gibbs JC, Willie BM, Jean S, et al. Association between obesity and risk of fracture, bone mineral density and bone quality in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0252487.
Kim MJ, Kim S, Jung HN, Jung CH, Lee WJ, Cho YK. Effects of anti-obesity strategies on bone mineral density: a comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2025;34:41−53.
Jensen SBK, Sørensen V, Sandsdal RM, Lehmann EW, Lundgren JR, Juhl CR, et al. Bone health after exercise alone, GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment, or combination treatment: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:e2416775.
Yu EW. Bone metabolism after bariatric surgery. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29:1507–18.
Mele C, Caputo M, Ferrero A, Daffara T, Cavigiolo B, Spadaccini D, et al. Bone response to weight loss following bariatric surgery. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:921353.
Penna F, Garcia-Castillo L, Costelli P. Extracellular vesicles and exosomes in the control of the musculoskeletal health. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024;22:257–65.
Li SR, Man QW, Gao X, Lin H, Wang J, Su FC, et al. Tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non-cancer diseases: present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12175.
Babuta M, Furi I, Bala S, Bukong TN, Lowe P, Catalano D, et al. Dysregulated autophagy and lysosome function are linked to exosome production by micro-RNA 155 in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2019;70:2123–41.
Liu X, Miao J, Wang C, Zhou S, Chen S, Ren Q, et al. Tubule-derived exosomes play a central role in fibroblast activation and kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2020;97:1181–95.
Lei L-M, Lin X, Xu F, Shan S-K, Guo B, Li F-X-Z, et al. Exosomes and obesity-related insulin resistance. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:651996.
Deng Z-B, Poliakov A, Hardy RW, Clements R, Liu C, Liu Y, et al. Adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles mediate activation of macrophage-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2009;58:2498–505.
Song M, Han L, Chen F-F, Wang D, Wang F, Zhang L, et al. Adipocyte-derived exosomes carrying sonic hedgehog mediate M1 macrophage polarization-induced insulin resistance via Ptch and PI3K pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48:1416–32.
Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Dong Y, Birmingham A, Seo JB, et al. Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miRNAs can modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell. 2017;171:372–84.e12.
Liu T, Sun Y-C, Cheng P, Shao H-G. Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miR-29a regulates obesity-associated insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;515:352–8.
De Silva N, Samblas M, Martínez JA, Milagro FI. Effects of exosomes from LPS-activated macrophages on adipocyte gene expression, differentiation, and insulin-dependent glucose uptake. J Physiol Biochem. 2018;74:559–68.
Pan Y, Hui X, Hoo RLC, Ye D, Chan CYC, Feng T, et al. Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation. J Clin Investig. 2019;129:834–49.
Reaven G. Why a cluster is truly a cluster: insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. Clin Chem. 2008;54:785–7.
Kahn CR, White M. The insulin receptor and the molecular mechanism of insulin action. J Clin Investig. 1988;82:1151–6.
Greere D, Grigorescu F, Manda D, Lautier C, Poiana C. Insulin resistance and pathogenesis of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Acta Endocrinol. 2024;19:349.
Wong SK, Chin K-Y, Suhaimi FH, Ahmad F, Ima-Nirwana S. The relationship between metabolic syndrome and osteoporosis: a review. Nutrients. 2016;8:347.
Lin H-H, Huang C-Y, Hwang L-C. Association between metabolic syndrome and osteoporosis in Taiwanese middle-aged and elderly participants. Arch Osteoporos. 2018;13:1–7.
Drucker DJ. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic application of glucagon-like peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018;27:740–56.
Liu H, Xiao H, Lin S, Zhou H, Cheng Y, Xie B, et al. Effect of gut hormones on bone metabolism and their possible mechanisms in the treatment of osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1372399.
Liu H, Tian Y, Bao X, Li Y. GLP-1RA promotes osteogenic differentiation of jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by modulating CREB/YAP/STAT3/BRD4-mediated proliferation and stemness for osteoporosis treatment. 2025.
Cai T-t, Li H-q, Jiang L-l, Wang H-y, Luo M-h, Su X-f, et al. Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 52-week clinical study. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021:3361309.
Wikarek A, Grabarczyk M, Klimek K, Janoska-Gawrońska A, Suchodolska M, Holecki M. Effect of drugs used in pharmacotherapy of type 2 diabetes on bone density and risk of bone fractures. Medicina. 2024;60:393.
Wolverton D, Blair MM. Fracture risk associated with common medications used in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2017;74:1143–51.
Nelinson DS, Sosa JM, Chilton RJ. SGLT2 inhibitors: a narrative review of efficacy and safety. J Osteopath Med. 2021;121:229–39.
Zhao L-J, Liu Y-J, Liu P-Y, Hamilton J, Recker RR, Deng H-W. Relationship of obesity with osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1640–6.
Compston JE, Watts NB, Chapurlat R, Cooper C, Boonen S, Greenspan S, et al. Obesity is not protective against fracture in postmenopausal women: GLOW. Am J Med. 2011;124:1043–50.
Bredella MA, Torriani M, Ghomi RH, Thomas BJ, Brick DJ, Gerweck AV, et al. Determinants of bone mineral density in obese premenopausal women. Bone. 2011;48:748–54.
Coates PS, Fernstrom JD, Fernstrom MH, Schauer PR, Greenspan SL. Gastric bypass surgery for morbid obesity leads to an increase in bone turnover and a decrease in bone mass. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:1061–5.
Casagrande DS, Repetto G, Mottin CC, Shah J, Pietrobon R, Worni M, et al. Changes in bone mineral density in women following 1-year gastric bypass surgery. Obes Surg. 2012;22:1287–92.
Schafer AL, Kazakia GJ, Vittinghoff E, Stewart L, Rogers SJ, Kim TY, et al. Effects of gastric bypass surgery on bone mass and microarchitecture occur early and particularly impact postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33:975–86.
Johansson H, Kanis JA, Odén A, McCloskey E, Chapurlat RD, Christiansen C, et al. A meta-analysis of the association of fracture risk and body mass index in women. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29:223–33.
Turcot V, Tchernof A, Deshaies Y, Pérusse L, Bélisle A, Marceau S, et al. LINE-1 methylation in visceral adipose tissue of severely obese individuals is associated with metabolic syndrome status and related phenotypes. Clin Epigenetics. 2012;4:1–8.
Petrus P, Bialesova L, Checa A, Kerr A, Naz S, Bäckdahl J, et al. Adipocyte expression of SLC19A1 links DNA hypermethylation to adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:710–21.
Modi A, Khokhar M, Sharma P, Joshi R, Mishra SS, Bharshankar RN, et al. Leptin DNA methylation and its association with metabolic risk factors in a northwest Indian obese population. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021;30:304.
Houde A-A, Légaré C, Biron S, Lescelleur O, Biertho L, Marceau S, et al. Leptin and adiponectin DNA methylation levels in adipose tissues and blood cells are associated with BMI, waist girth and LDL-cholesterol levels in severely obese men and women. BMC Med Genet. 2015;16:1–10.
Houshmand-Oeregaard A, Hansen NS, Hjort L, Kelstrup L, Broholm C, Mathiesen ER, et al. Differential adipokine DNA methylation and gene expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue from adult offspring of women with diabetes in pregnancy. Clin Epigenetics. 2017;9:1–12.
Ott R, Stupin JH, Melchior K, Schellong K, Ziska T, Dudenhausen JW, et al. Alterations of adiponectin gene expression and DNA methylation in adipose tissues and blood cells are associated with gestational diabetes and neonatal outcome. Clin Epigenetics. 2018;10:1–12.
Kim AY, Park YJ, Pan X, Shin KC, Kwak S-H, Bassas AF, et al. Obesity-induced DNA hypermethylation of the adiponectin gene mediates insulin resistance. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7585.
Kuroda A, Rauch TA, Todorov I, Ku HT, Al-Abdullah IH, Kandeel F, et al. Insulin gene expression is regulated by DNA methylation. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e6953.
Nilsson E, Jansson PA, Perfilyev A, Volkov P, Pedersen M, Svensson MK, et al. Altered DNA methylation and differential expression of genes influencing metabolism and inflammation in adipose tissue from subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2014;63:2962–76.
Pinhel MA, Noronha NY, Nicoletti CF, Pereira VA, de Oliveira BA, Cortes-Oliveira C, et al. Changes in DNA methylation and gene expression of insulin and obesity-related gene PIK3R1 after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:4476.
Ahmed SAH, Ansari SA, Mensah-Brown EP, Emerald BS. The role of DNA methylation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Epigenetics. 2020;12:104.
Gemma C, Sookoian S, Alvariñas J, García SI, Quintana L, Kanevsky D, et al. Maternal pregestational BMI is associated with methylation of the PPARGC1A promoter in newborns. Obesity. 2009;17:1032–9.
Brons C, Jacobsen S, Nilsson E, Ronn T, Jensen C, Storgaard H, et al. Deoxyribonucleic acid methylation and gene 570 expression of PPARGC1A in human muscle is influenced by high-fat overfeeding in a 571 birth-weight-dependent manner. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:3048–56.
Perkins E, Murphy SK, Murtha AP, Schildkraut J, Jirtle RL, Demark-Wahnefried W, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2/H19 methylation at birth and risk of overweight and obesity in children. J Pediatr. 2012;161:31–9.
Crujeiras AB, Campion J, Díaz-Lagares A, Milagro FI, Goyenechea E, Abete I, et al. Association of weight regain with specific methylation levels in the NPY and POMC promoters in leukocytes of obese men: a translational study. Regul Pept. 2013;186:1–6.
Dick KJ, Nelson CP, Tsaprouni L, Sandling JK, Aïssi D, Wahl S, et al. DNA methylation and body-mass index: a genome-wide analysis. Lancet. 2014;383:1990–8.
Pan H, Lin X, Wu Y, Chen L, Teh AL, Soh SE, et al. HIF3A association with adiposity: the story begins before birth. Epigenomics. 2015;7:937–50.
Na YK, Hong HS, Lee WK, Kim YH, Kim DS. Increased methylation of interleukin 6 gene is associated with obesity in Korean women. Mol Cells. 2015;38:452–6.
Ali MM, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Naquiallah D, Mirza I, et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia correlates with adipokine hypomethylation and vascular dysfunction. Biomedicines. 2021;9:1034.
Ali MM, Naquiallah D, Qureshi M, Mirza MI, Hassan C, Masrur M, et al. DNA methylation profile of genes involved in inflammation and autoimmunity correlates with vascular function in morbidly obese adults. Epigenetics. 2022;17:93–109.
You D, Nilsson E, Tenen DE, Lyubetskaya A, Lo JC, Jiang R, et al. Dnmt3a is an epigenetic mediator of adipose insulin resistance. Elife. 2017;6:e30766.
Ma X, Kang S. Functional implications of DNA methylation in adipose biology. Diabetes. 2019;68:871–8.
Castillo J, López-Rodas G, Franco L. Histone post-translational modifications and nucleosome organisation in transcriptional regulation: some open questions. Protein Rev. 2017;18:65–92.
Yang H, Yang K, Gu H, Sun C. Dynamic post-translational modifications in obesity. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;24:2384.
Mikula M, Majewska A, Ledwon JK, Dzwonek A, Ostrowski J. Obesity increases histone H3 lysine 9 and 18 acetylation at Tnfa and Ccl2 genes in mouse liver. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34:1647–54.
Wheatley KE, Nogueira LM, Perkins SN, Hursting SD. Differential effects of calorie restriction and exercise on the adipose transcriptome in diet-induced obese mice. J Obes. 2011;2011:265417.
Funato H, Oda S, Yokofujita J, Igarashi H, Kuroda M. Fasting and high-fat diet alter histone deacetylase expression in the medial hypothalamus. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e18950.
Tateishi K, Okada Y, Kallin EM, Zhang Y. Role of Jhdm2a in regulating metabolic gene expression and obesity resistance. Nature. 2009;458:757–61.
Rinonapoli G, Pace V, Ruggiero C, Ceccarini P, Bisaccia M, Meccariello L, et al. Obesity and bone: a complex relationship. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:13662.
Paccou J, Hardouin P, Cotten A, Penel G, Cortet B. The role of bone marrow fat in skeletal health: usefulness and perspectives for clinicians. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:3613–21.
Ho-Pham LT, Nguyen UD, Nguyen TV. Association between lean mass, fat mass, and bone mineral density: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:30–8.
Bachmann KN, Fazeli PK, Lawson EA, Russell BM, Riccio AD, Meenaghan E, et al. Comparison of hip geometry, strength, and estimated fracture risk in women with anorexia nervosa and overweight/obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:4664–73.
Xue Y, Hu S, Chen C, He J, Sun J, Jin Y, et al. Myokine Irisin promotes osteogenesis by activating BMP/SMAD signaling via αV integrin and regulates bone mass in mice. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:572.
He X, Hua Y, Li Q, Zhu W, Pan Y, Yang Y, et al. FNDC5/irisin facilitates muscle–adipose–bone connectivity through ubiquitination-dependent activation of runt-related transcriptional factors RUNX1/2. J Biol Chem. 2022;298.
Li H, Wang F, Yang M, Sun J, Zhao Y, Tang D. The effect of irisin as a metabolic regulator and its therapeutic potential for obesity. Int J Endocrinol. 2021;2021:6572342.
Yuksel Ozgor B, Demiral I, Zeybek U, Celik F, Buyru F, Yeh J, et al. Effects of irisin compared with exercise on specific metabolic and obesity parameters in female mice with obesity. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2020;18:141–5.
Ilich JZ, Gilman JC, Cvijetic S, Boschiero D. Chronic stress contributes to osteosarcopenic adiposity via inflammation and immune modulation: the case for more precise nutritional investigation. Nutrients. 2020;12:989.
Al Saedi A, Hassan EB, Duque G. The diagnostic role of fat in osteosarcopenia. J Lab Precis Med. 2019;4.
Kang Y-S, Kim J-C, Kim J-S, Kim SH. Effects of swimming exercise on serum irisin and bone FNDC5 in rat models of high-fat diet-induced osteoporosis. J Sports Sci Med. 2019;18:596.
McCabe LR, Irwin R, Tekalur A, Evans C, Schepper JD, Parameswaran N, et al. Exercise prevents high fat diet-induced bone loss, marrow adiposity and dysbiosis in male mice. Bone. 2019;118:20–31.
Xie W, Han Y, Li F, Gu X, Su D, Yu W, et al. Neuropeptide Y1 receptor antagonist alters gut microbiota and alleviates the ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2020;106:444–54.
Gomes AC, Hoffmann C, Mota JF. The human gut microbiota: metabolism and perspective in obesity. Gut Microbes. 2018;9:308–25.
Méndez-Salazar EO, Ortiz-López MG, Granados-Silvestre MDLÁ, Palacios-González B, Menjivar M. Altered gut microbiota and compositional changes in Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in Mexican undernourished and obese children. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:2494.
Palacios-González B, Ramírez-Salazar EG, Rivera-Paredez B, Quiterio M, Flores YN, Macias-Kauffer L, et al. A multi-omic analysis for low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women suggests a relationship between diet, metabolites, and microbiota. Microorganisms. 2020;8:1630.
Liu JH, Chen CY, Liu ZZ, Luo ZW, Rao SS, Jin L, et al. Extracellular vesicles from child gut microbiota enter into bone to preserve bone mass and strength. Adv Sci. 2021;8:2004831.
Huck O, Mulhall H, Rubin G, Kizelnik Z, Iyer R, Perpich JD, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila reduces Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced inflammation and periodontal bone destruction. J Clin Periodontol. 2020;47:202–12.
Keshavarz Azizi Raftar S, Hoseini Tavassol Z, Amiri M, Ejtahed HS, Zangeneh M, Sadeghi S, et al. Assessment of fecal Akkermansia muciniphila in patients with osteoporosis and osteopenia: a pilot study. J Diab Metab Disord. 2021;20:279–84.
Fernández-Murga ML, Olivares M, Sanz Y. Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 reverses the adverse effects of diet-induced obesity through the gut-bone axis. Bone. 2020;141:115580.
Behera J, Ison J, Voor MJ, Tyagi N. Probiotics stimulate bone formation in obese mice via histone methylations. Theranostics. 2021;11:8605.
Eaimworawuthikul S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Suntornsaratoon P, Charoenphandhu N, Thiennimitr P, et al. Altered gut microbiota ameliorates bone pathology in the mandible of obese–insulin-resistant rats. Eur J Nutr. 2020;59:1453–62.
Tyagi AM, Yu M, Darby TM, Vaccaro C, Li J-Y, Owens JA, et al. The microbial metabolite butyrate stimulates bone formation via T regulatory cell-mediated regulation of WNT10B expression. Immunity. 2018;49:1116–31.e7.
Kim K-J, Lee J, Wang W, Lee Y, Oh E, Park K-H, et al. Austalide K from the fungus Penicillium rudallense prevents LPS-induced bone loss in mice by inhibiting osteoclast differentiation and promoting osteoblast differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:5493.
Goel PN, Egol AJ, Moharrer Y, Brandfield-Harvey B, Ahn J, Ashley JW. Notch signaling inhibition protects against LPS mediated osteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;515:538–43.
Kishikawa A, Kitaura H, Kimura K, Ogawa S, Qi J, Shen W-R, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits inflammation-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vivo through GPR120 by inhibiting TNF-α production in macrophages and directly inhibiting osteoclast formation. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:157.
Jin J, Machado E, Yu H, Zhang X, Lu Z, Li Y, et al. Simvastatin inhibits LPS-induced alveolar bone loss during metabolic syndrome. J Dent Res. 2014;93:294–9.
Guo C, Yuan L, Wang J-G, Wang F, Yang X-K, Zhang F-H, et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces the apoptosis and inhibits osteoblast differentiation through JNK pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. Inflammation. 2014;37:621–31.
Gao A, Wang X, Yu H, Li N, Hou Y, Yu W. Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide (Pg-LPS) on the expression of EphA2 in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Vitr Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016;52:228–34.
Chang Y, Hu C-C, Wu Y-Y, Ueng SW, Chang C-H, Chen M-F. Ibudilast mitigates delayed bone healing caused by lipopolysaccharide by altering osteoblast and osteoclast activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:1169.
Irie N, Takada Y, Watanabe Y, Matsuzaki Y, Naruse C, Asano M, et al. Bidirectional signaling through ephrinA2-EphA2 enhances osteoclastogenesis and suppresses osteoblastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:14637–44.
Xing Q, de Vos P, Faas M, Ye Q, Ren Y. LPS promotes pre-osteoclast activity by up-regulating CXCR4 via TLR-4. J Dent Res. 2011;90:157–62.
Bosetti M, Sabbatini M, Nicolì E, Fusaro L, Cannas M. Effects and differentiation activity of IGF-I, IGF-II, insulin and preptin on human primary bone cells. Growth Factors. 2013;31:57–65.
Jiang S. Roles of calcitonin family of peptides in degenerative musculoskeletal diseases. Staats-und Universitätsbibliothek Hamburg Carl von Ossietzky; ediss.sub.uni-hamburg.de; 2024.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to BioRender (www.biorender.com) for providing the software used to create all figures in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AH; Data curation: AB, KK, and HT; Investigation: AB and AH; Supervision: HY. Validation: KM; Writing—original draft: AB, KK, and KM; Writing—review & editing: HY and HT.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bagherifard, A., Hemmatyar, A., Khosravi, K. et al. The impact of obesity on bone health: molecular pathways, metabolic interactions, and associated pathologies. Int J Obes 50, 87–115 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01907-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01907-1