Abstract
Objective
To determine the relationship between interventricular septal position (SP) and right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) and mortality in infants with severe BPD (sBPD).
Study design
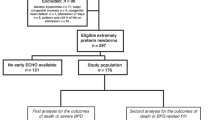
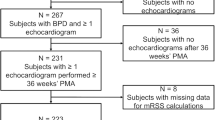
Infants with sBPD in the Children’s Hospitals Neonatal Database who had echocardiograms 34–44 weeks’ postmenstrual age (PMA) were included. SP and RVSP were categorized normal, abnormal (flattened/bowed SP or RVSP > 40 mmHg) or missing.
Results
Of 1157 infants, 115 infants (10%) died. Abnormal SP or RVSP increased mortality (SP 19% vs. 8% normal/missing, RVSP 20% vs. 9% normal/missing, both p < 0.01) in unadjusted and multivariable models, adjusted for significant covariates (SP OR 1.9, 95% CI 1.2–3.0; RVSP OR 2.2, 95% CI 1.1–4.7). Abnormal parameters had high specificity (SP 82%; RVSP 94%), and negative predictive value (SP 94%, NPV 91%) for mortality.
Conclusions
Abnormal SP or RVSP is independently associated with mortality in sBPD infants. Negative predictive values distinguish infants most likely to survive.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
The computer code used to generate statistical analyses may be made available upon request to the Children’s Hospitals Neonatal Consortium.
References
Abman SH, Collaco JM, Shepherd EG, Keszler M, Cuevas-Guaman M, Welty SE. et al. Interdisciplinary care of Children with Severe Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2017;181:12–28.e1.
Lagatta JM, Hysinger EB, Zaniletti I, Wymore EM, Vyas-Read S, Yallapragada S, et al. The impact of pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia through 1 year. J Pediatr. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.07.035.
Berkelhamer SK, Mestan KK, Steinhorn RH. Pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2013;37:124–131.
Slaughter JL, Pakrashi T, Jones DE, South AP, Shah TA. Echocardiographic detection of pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia requiring prolonged positive pressure ventilation. J Perinatol. 2011;31:635–640.
Abman SH, Hansmann G, Archer SL, Ivy DD, Adatia I, Chung WK, et al. Pediatric pulmonary hypertension: guidelines from the American Heart Association and American Thoracic Society. Circulation. 2015;132:2037–2099.
Weismann CG, Asnes JD, Bazzy-Asaad A, Tolomeo C, Ehrenkranz RA, Bizzarro MJ. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants: results of a prospective screening program. J Perinatol. 2017;37:572–577.
Mourani PM, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, Ivy DD, Abman SH. Clinical utility of echocardiography for the diagnosis and management of pulmonary vascular disease in young children with chronic lung disease. Pediatrics. 2008;121:317–325.
McCrary AW, Barker PCA, Torok RD, Spears TG, Li JS, Hornik CP, et al. Agreement of an echocardiogram-based diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension in infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia among masked reviewers. J Perinatol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-018-0277-6.
Carlton EF, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, DiMaria MV, Miller JI, Poindexter BB, et al. Reliability of echocardiographic indicators of pulmonary vascular disease in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.03.027.
Murthy K, Porta NFM, Lagatta JM, Zaniletti I, Truog WE, Grover TR, et al. Inter-center variation in death or tracheostomy placement in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol. 2017;37:723–727.
Hysinger EB, Friedman NL, Padula MA, Shinohara RT, Zhang H, Panitch HB, et al. Tracheobronchomalacia is associated with increased morbidity in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14. https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201702-178OC.
Mirza H, Ziegler J, Ford S, Padbury J, Tucker R, Laptook A. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants: prevalence and association with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2014;165:909–14.e1.
del Cerro MJ, Sabate Rotes A, Carton A, Deiros L, Bret M, Cordeiro M, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical findings, cardiovascular anomalies and outcomes. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014;49:49–59.
Olsen IE, Groveman SA, Lawson ML, Clark RH, Zemel BS. New intrauterine growth curves based on United States data. Pediatrics. 2010;125:e214–24.
Al-Ghanem G, Shah P, Thomas S, Banfield L, Helou El S, Fusch C. et al. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary hypertension: a meta-analysis. J Perinatol. 2017;37:414–419.
Ali Z, Schmidt P, Dodd J, Jeppesen DL. Predictors of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary hypertension in newborn children. Dan Med J. 2013;60:A4688.
Baker CD, Abman SH, Mourani PM. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Allergy, Immunol, Pulmonol. 2014;27:8–16.
Murthy K, Savani RC, Lagatta JM, Zaniletti I, Wadhawan R, Truog W, et al. Predicting death or tracheostomy placement in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol. 2014;34:543–548.
Abraham S, Weismann CG. Left ventricular end-systolic eccentricity index for assessment of pulmonary hypertension in infants. Echocardiography. 2016;33:910–915.
Zivanovic S, Pushparajah K, Calvert S, Marlow N, Razavi R, Peacock JL. et al. Pulmonary artery pressures in school-age children born prematurely. J Pediatr. 2017;191:42–49.e3.
Watson T, McCracken CE, Slesnick T, Kanaan U, Border WL, Sachdeva R. Quantitative assessment of ventricular septal contour for estimation of right ventricular pressure. Echocardiography. 2016;33:444–9. quiz 443
McCrary AW, Malowitz JR, Hornick CP, Hill KD, Cotten CM, Tatum GH, et al. Differences in eccentricity index and systolic-diastolic ratio in extremely low-birth-weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia at risk of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Perinatol. 2016;33:57–62.
Altit G, Lee HC, Hintz S, Tacy TA, Feinstein JA, Bhombal S. Practices surrounding pulmonary hypertension and bronchopulmonary dysplasia amongst neonatologists caring for premature infants. J Perinatol. 2018;38:361–367.
Mehler K, Udink Ten Cate FE, Keller T, Bangen U, Kribs A, Oberthuer A. An echocardiographic screening program helps to identify pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birthweight infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a single-center experience. Neonatology. 2018;113:81–88.
An HS, Bae EJ, Kim GB, Kwon BS, Beak JS, Kim EK, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Korean Circ J. 2010;40:131–136.
Khemani E, McElhinney DB, Rhein L, Andrade O, Lacro RV, Thomas KC, et al. Pulmonary artery hypertension in formerly premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical features and outcomes in the surfactant era. Pediatrics. 2007;120:1260–1269.
Martin RJ, Di Fiore JM, Walsh MC. Hypoxic episodes in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Clin Perinatol. 2015;42:825–838.
Kovesi T, Abdurahman A, Blayney M. Elevated carbon dioxide tension as a predictor of subsequent adverse events in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lung. 2006;184:7–13.
Thome UH, Dreyhaupt J, Genzel-Boroviczeny O, Bohnhorst B, Schmid M, Fuchs H, et al. Influence of PCO2 control on clinical and neurodevelopmental outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Neonatology. 2018;113:221–230.
Brown MK, Poeltler DM, Hassen KO, Lazarus DV, Brown VK, Stout JJ, et al. Incidence of hypocapnia, hypercapnia, and acidosis and the associated risk of adverse events in preterm neonates. Respir Care. 2018;63:943–949.
Krishnan U, Feinstein JA, Adatia I, Austin ED, Mullen MP, Hopper RK, et al. Evaluation and management of pulmonary hypertension in children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.05.029.
Funding
The Children’s Hospitals Neonatal Consortium (501-c3 organization) supported the statistical analyses presented in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
SV-R, EMW, KM, JML: Research question and design, data analysis and interpretation, draft preparation, editing, and revision of the manuscript. IZ: Statistical analysis of the manuscript. MAP, WET, WAE, RCS, SY, JWL, HZ, EBH, TRG, GN, LDN, NFMP, KPP, RD: Data interpretation, editing and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyas-Read, S., Wymore, E.M., Zaniletti, I. et al. Utility of echocardiography in predicting mortality in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol 40, 149–156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0508-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0508-5