Abstract
Objective
Compare rates of initial extubation success in preterm infants extubated to NIPPV or NI-NAVA.
Study design
In this pilot study, we randomized 30 mechanically ventilated preterm infants at the time of initial elective extubation to NI-NAVA or NIPPV in a 1:1 assignment. Primary study outcome was initial extubation success.
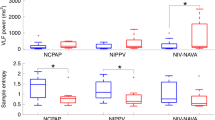
Results
Rates of continuous extubation for 120 h were 92% in the NI-NAVA group and 69% in the NIPPV group (12/13 vs. 9/13, respectively, p = 0.14). Infants extubated to NI-NAVA remained extubated longer (median 18 vs. 4 days, p = 0.02) and experienced lower peak inspiratory pressures (PIP) than infants managed with NIPPV throughout the first 3 days after extubation. Survival analysis through 14 days post extubation showed a sustained difference in the primary study outcome until 12 days post extubation.
Conclusions
Our study is the first to suggest that a strategy of extubating preterm infants to NI-NAVA may be more successful.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chawla S, Natarajan G, Shankaran S, Carper B, Brion LP, Keszler M, et al. Markers of successful extubation in extremely preterm infants, and morbidity after failed extubation. J Pediatr. 2017;189:113–119.e2.
Bancalari E, Gerhardt T. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986;33:1–23.
Downing GJ, Hayen LK, Kilbride HW. Acquired subglottic cysts in the low-birth-weight infant. Characteristics, treatment, and outcome. Am J Dis Child. 1993;147:971–4.
Walsh MC, Morris BH, Wrage LA, Vohr BR, Poole WK, Tyson JE, et al. Extremely low birthweight neonates with protracted ventilation: mortality and 18-month neurodevelopmental outcomes. J Pediatr. 2005;146:798–804.
Lemyre B, Davis PG, De Paoli AG, Kirpalani H. Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) versus nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) for preterm neonates after extubation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;2:CD003212.
Donn SM, Sinha SK. Can mechanical ventilation strategies reduce chronic lung disease? Semin Neonatol. 2003;8:441–8.
Beck J, Campoccia F, Allo J-C, Brander L, Brunet F, Slutsky AS, et al. Improved synchrony and respiratory unloading by neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NAVA) in lung-injured rabbits. Pediatr Res. 2007;61:289–94.
Allo J-C, Beck JC, Brander L, Brunet F, Slutsky AS, Sinderby CA. Influence of neurally adjusted ventilatory assist and positive end-expiratory pressure on breathing pattern in rabbits with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:2997–3004.
Sinderby C, Beck J, Spahija J, de Marchie M, Lacroix J, Navalesi P, et al. Inspiratory muscle unloading by neurally adjusted ventilatory assist during maximal inspiratory efforts in healthy subjects. Chest. 2007;131:711–7.
Beck J, Reilly M, Grasselli G, Mirabella L, Slutsky AS, Dunn MS, et al. Patient-ventilator interaction during neurally adjusted ventilatory assist in low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res. 2009;65:663–8.
Rossor TE, Hunt KA, Shetty S, Greenough A. Neurally adjusted ventilatory assist compared to other forms of triggered ventilation for neonatal respiratory support. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;10:CD012251.
Walsh MC, Kliegman RM. Necrotizing enterocolitis: treatment based on staging criteria. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986;33:179–201.
Walsh MC, Yao Q, Gettner P, Hale E, Collins M, Hensman A, et al. Impact of a physiologic definition on bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates. Pediatrics. 2004;114:1305–11.
Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1723–9.
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978;92:529–34.
An international classification of retinopathy of prematurity. The committee for the classification of retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102:1130–4.
Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Stark AR, et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196:147.e1–8.
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Walsh MC, et al. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2010;126:443–56.
Stein H, Beck J, Dunn M. Non-invasive ventilation with neurally adjusted ventilatory assist in newborns. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;21:154–61.
Firestone KS, Beck J, Stein H. Neurally adjusted ventilatory assist for noninvasive support in neonates. Clin Perinatol. 2016;43:707–24.
Kallio M, Koskela U, Peltoniemi O, Kontiokari T, Pokka T, Suo-Palosaari M, et al. Neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NAVA) in preterm newborn infants with respiratory distress syndrome-a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Pediatr. 2016;175:1175–83.
Chawla S, Natarajan G, Gantz MG, Shankaran S, Carlo WA. Reply. J Pediatr. 2018;194:263–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.11.017.
Giaccone A, Jensen E, Davis P, Schmidt B. Definitions of extubation success in very premature infants: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014;99:F124–7.
Shalish W, Kanbar L, Kovacs L, Chawla S, Keszler M, Rao S, et al. The impact of time interval between extubation and reintubation on death or bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2019;205:70–76.e2.
Shalish W, Kanbar L, Keszler M, Chawla S, Kovacs L, Rao S, et al. Patterns of reintubation in extremely preterm infants: a longitudinal cohort study. Pediatr Res. 2018;83:969–75.
Kirpalani H, Millar D, Lemyre B, Yoder BA, Chiu A, Roberts RS, et al. A trial comparing noninvasive ventilation strategies in preterm infants. N. Engl J Med. 2013;369:611–20.
Manley BJ, Doyle LW, Owen LS, Davis PG. Extubating extremely preterm infants: predictors of success and outcomes following failure. J Pediatr. 2016;173:45–49.
Jensen EA, DeMauro SB, Kornhauser M, Aghai ZH, Greenspan JS, Dysart KC. Effects of multiple ventilation courses and duration of mechanical ventilation on respiratory outcomes in extremely low-birth-weight infants. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169:1011–7.
Donn SM, Sinha SK. Minimising ventilator induced lung injury in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006;91:F226–30.
Stein H, Alosh H, Ethington P, White DB. Prospective crossover comparison between NAVA and pressure control ventilation in premature neonates less than 1500 grams. J Perinatol. 2013;33:452–6.
Lee J, Kim H-S, Sohn JA, Lee JA, Choi CW, Kim E-K, et al. Randomized crossover study of neurally adjusted ventilatory assist in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2012;161:808–13.
Berger J, Mehta P, Bucholz E, Dziura J, Bhandari V. Impact of early extubation and reintubation on the incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in neonates. Am J Perinatol. 2014;31:1063–72.
Acknowledgements
We thank the families for trusting us with the care of their infants enrolled in this trial. We thank the three DSMC members Dr. Jennifer Liedel, Dr. Susan Aucott and Dr. Lily Lou for their inputs during the project to ensure subject safety.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makker, K., Cortez, J., Jha, K. et al. Comparison of extubation success using noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) versus noninvasive neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NI-NAVA). J Perinatol 40, 1202–1210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0578-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0578-4
This article is cited by
-
Perspectives of medical staff on respiratory management with neurally adjusted ventilatory assist in preterm infants
Journal of Perinatology (2025)
-
Non-invasive neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NIV-NAVA) in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU): an Australian NICU experience
BMC Pediatrics (2024)
-
The Diaphragmatic Initiated Ventilatory Assist (DIVA) trial: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial comparing rates of extubation failure in extremely premature infants undergoing extubation to non-invasive neurally adjusted ventilatory assist versus non-synchronized nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation
Trials (2024)
-
Cardiorespiratory measures shortly after extubation and extubation outcomes in extremely preterm infants
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
Ultrasonographic assessment of diaphragmatic function in preterm infants on non-invasive neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NIV-NAVA) compared to nasal intermittent positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV): a prospective observational study
European Journal of Pediatrics (2022)