Abstract
Background
Neonates with apnea of prematurity often fail CPAP because it does not provide adequate support during apnea. NAVA provides proportional ventilator support based on electrical activity of the diaphragm. When the NAVA level is 0 cmH20/mcV, the patient receives minimal support above PEEP when breathing and backup ventilation when apneic. This study compares number of clinically significant events on CPAP versus noninvasive NAVA level 0.
Methods
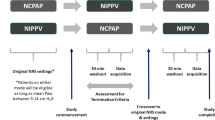
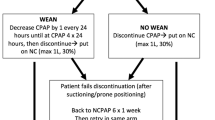
Retrospective study of preterm neonates having apnea of prematurity on nasal CPAP. Patients were then placed on NAVA level 0. The number of events on each mode was collected. Statistics were paired t-test.
Results
Seventeen subjects with gestational age 26.1 ± 1.7 weeks, study age 19.5 ± 12.5 days. Events decreased from 17.9 ± 7.8 on CPAP to 10.2 ± 8.1 events on NAVA level 0 (p = 0.00047).
Conclusions
NAVA level 0 reduced the number of clinically significant events compared with CPAP in premature neonates with apnea of prematurity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eichenwald E. Newborn CoFa. Apnea of prematurity. Pediatrics. 2016;137:1097–105.
Henderson-Smart D, Subramaniam P, Davis P. Continuous positive airway pressure versus theophylline for apnea in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;1–9.
Henderson-Smart D, De Paoli A. Prophylactic methylxanthine for prevention of apnoea in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;1–16.
DiBlasi RM. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for the respiratory care of the newborn infant. Resp Care. 2009;54:1209–35.
Firestone KS, Beck J, Stein H. Neurally adjusted ventilatory assist for non-invasive support in neonates. Clin Perinatol. 2016;43:707–24.
Sinderby C, Beck J. “Neurally adjusted ventilatory assist”. In: Principles and practice of mechanical ventilation. McGraw Hill; 2012.
Stein H, Beck J, Dunn M. Non-invasive ventilation with neurally adjusted ventilatory assist in newborns. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;21:154–61.
Tabacaru CR, Moores RR, Khoury J, Rozycki HJ. NAVA—synchronized compared to nonsynchronized noninvasive ventilation for apnea, bradycardia, and desaturation events in VLBW infants. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019;54:1742–6.
DiBlasi RM. Neonatal noninvasive ventilation techniques: do we really need to intubate? Resp Care. 2011;56:1273–97.
Morgan EL, Firestone KS, Schachinger SW, Stein H. Effects of changes in apnea time on the clinical status of neonates on NIV-NAVA. Resp Care. 2019;64:1096–100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS, LB, and KF contributed to the study design. HS, LB, and BAH contributed to data collection. All authors contributed in writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
HS and KF are on the speakers’ bureau for Getinge and Chiesi USA Inc. BAH and LB have nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Firestone, K., Horany, B.A., de Leon-Belden, L. et al. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure versus noninvasive NAVA in preterm neonates with apnea of prematurity: a pilot study with a novel approach. J Perinatol 40, 1211–1215 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-020-0661-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-020-0661-x
This article is cited by
-
In search of a happy medium for preterm infant respiratory support at birth:
Pediatric Research (2025)
-
The Diaphragmatic Initiated Ventilatory Assist (DIVA) trial: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial comparing rates of extubation failure in extremely premature infants undergoing extubation to non-invasive neurally adjusted ventilatory assist versus non-synchronized nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation
Trials (2024)
-
Non-invasive neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NIV-NAVA) in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU): an Australian NICU experience
BMC Pediatrics (2024)
-
Immature control of breathing and apnea of prematurity: the known and unknown
Journal of Perinatology (2021)