Abstract
Objective
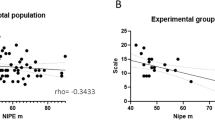
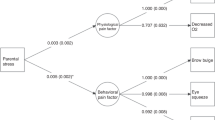
The present study evaluated the correlation of Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPS) and Premature Infant Pain Profile-Revised (PIPP-R), with changes in cerebral oxygenation (ΔcrSO2; measured by near-infrared spectroscopy) in preterm infants during acute painful procedures (heel lance and venepuncture).
Study design
Prospective observational study.
Methods
Sixty-four stable preterm (28–36 weeks) neonates were videotaped. NIPS and PIPP-R scores were assessed on video-recordings by two independent assessors. The primary outcome was correlation of ΔcrSO2 with NIPS and PIPP-R scores.
Results
Moderate to strong correlations were observed between ΔcrSO2 and NIPS, and ΔcrSO2 and PIPP-R (r = 0.71 and 0.78 during heel lance and r = 0.66 and 0.75 during venepuncture, respectively). NIPS score was found easy to understand and perform by the bedside nurses, and took lesser time as compared to PIPP-R during both the procedures.
Conclusion
Both pain scores, NIPS and PIPP-R, had good correlation with ΔcrSO2 during acute painful procedures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Johnston C, Barrington KJ, Taddio A, Carbajal R, Filion F. Pain in Canadian NICUs: have we improved over the past 12 years? Clin J Pain. 2011;27:225–32.
Cruz MD, Fernandes AM, Oliveira CR. Epidemiology of painful procedures performed in neonates: A systematic review of observational studies. Eur J Pain. 2016;20:489–98.
Johnston CC, Stevens BJ. Experience in a neonatal intensive care unit affects pain response. Pediatrics. 1996;98:925–30.
Brummelte S, Grunau RE, Chau V, Poskitt KJ, Brant R, Vinall J, et al. Procedural pain and brain development in premature newborns. Ann Neurol. 2012;71:385–96.
Anand KJ, Scalzo FM. Can adverse neonatal experiences alter brain development and subsequent behavior? Biol Neonate. 2000;77:69–82.
Taddio A, Katz J. The effects of early pain experience in neonates on pain responses in infancy and childhood. Paediatr Drugs. 2005;7:245–57.
Schenk K, Stoffel L, Bürgin R, Stevens B, Bassler D, Schulzke S, et al. The influence of gestational age in the psychometric testing of the Bernese Pain Scale for Neonates. BMC Pediatr. 2019;19:20.
Olsson E, Ahl H, Bengtsson K, Vejayaram DN, Norman E, Bruschettini M, et al. The use and reporting of neonatal pain scales: a systematic review of randomized trials. Pain. 2021;162:353–60.
Stevens BJ, Gibbins S, Yamada J, Dionne K, Lee G, Johnston C, et al. The premature infant pain profile-revised (PIPP-R): initial validation and feasibility. Clin J Pain. 2014;30:238–43.
Obiedat H, Al-Maaitah EI. Critique of the use of neonatal infant pain scale (NIPS). NeonatPediatr Med. 2020;6:186.
Lawrence J, Alcock D, McGrath P, Kay J, MacMurray SB, Dulberg C. The development of a tool to assess neonatal pain. Neonatal Netw. 1993;12:59–66.
Slater R, Fitzgerald M, Meek J. Can cortical responses following noxious stimulation inform us about pain processing in neonates? Semin Perinatol. 2007;31:298–302.
Slater R, Cantarella A, Franck L, Meek J, Fitzgerald M. How well do clinical pain assessment tools reflect pain in infants? PLoS Med. 2008;5:e129.
Schiller CJ. Clinical utility of two neonatal pain assessment measures. Doctoral dissertation, University of Toronto. 1999.
Bembich S, Davanzo R, Brovedani P, Clarici A, Massaccesi S, Demarini S. Functional neuroimaging of breastfeeding analgesia by multichannel near-infrared spectroscopy. Neonatology. 2013;104:255–9.
Shah VS, Ohlsson A. Venepuncture versus heel lance for blood sampling in term neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;10:CD001452.
Xie W, Wang X, Huang R, Chen Y, Guo X. Assessment of four pain scales for evaluating procedural pain in premature infants undergoing heel blood collection. Pediatr Res. 2021;89:1724–31.
Suraseranivongse S, Kaosaard R, Intakong P, Pornsiriprasert S, Karnchana Y, Kaopinpruck J, et al. A comparison of postoperative pain scales in neonates. Br J Anaesth. 2006;97:540–4.
Sarhangi F, Mollahadi M, Ebadi A, Matinzadeh ZK, Tadrisi SD. Validity and reliability of neonatal infant pain scale in neonatal intensive care units in Iran (2010). Pak J Med Sci. 2011;27:1087–91.
Acknowledgements
We wish to convey our sincere thanks to the neonatologists and NICU staff members at All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh for participating in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK recruited patients, collected and analyzed the data, and drafted the initial manuscript; MP and SB supervised data collection and analysis of data and did critical revision and finalization of the manuscript; PS, BP, and SC contributed to the study design, data analysis and interpretation; and All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol was approved by the Institute’s Ethics Committee of AIIMS Rishikesh, Uttarakhand, India (Ref No: AIIMS/IEC/21/35, dated 09/01/2021).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the parent of each subject before enrollment.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Priyadarshi, M., Singh, P. et al. Correlation of clinical pain scores with cerebral oxygenation in preterm neonates during acute painful procedures: a prospective observational study. J Perinatol 43, 584–589 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-022-01543-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-022-01543-x
This article is cited by
-
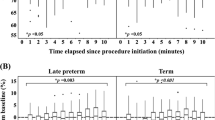
A comparison of the effect of procedural pain on cerebral oxygen saturation between late preterm and term infants
Journal of Perinatology (2024)