Abstract
Objective
We aim to describe sequential direct bilirubin levels in preterm infants and examine the outcomes of subsequent evaluation of direct hyperbilirubinemia.
Study design
Retrospective electronic chart analysis of preterm infants admitted and surviving the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) stay was performed.
Result
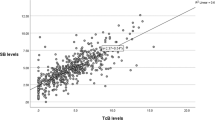
A total of 127 preterm infants had 665 bilirubin measurements (333 direct bilirubin; 332 total bilirubin) during their first NICU stay. Before five days of age, twenty-seven (27/127, 21%) infants had abnormal direct bilirubin estimations. At fourteen days, three of these infants (3/27, 11%) had abnormal values. All three infants had further testing and more direct bilirubin estimations than their cohort. All infants had normal levels by discharge. Age-appropriate direct bilirubin values were based on those described by Feldman et al.
Conclusion
All preterm infants with elevated direct bilirubin had normal values by discharge.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the ethics committee i.e. Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the University of Missouri in Columbia, Missouri (number 2097726) stipulations but may be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request if approved by the IRB.
References
Harpavat S, Garcia-Prats JA, Anaya C, Brandt ML, Lupo PJ, Finegold MJ, et al. Diagnostic yield of newborn screening for biliary atresia using direct or conjugated bilirubin measurements. JAMA. 2020;323:1141.
Kastenberg ZJ, Deneau MR, O’Brien EA, Huynh K, Book LS, Srivastava R, et al. Fractionated bilirubin among 252 892 utah newborns with and without biliary atresia: a 15-year historical birth cohort study. J Pediatr. 2023;257:113339.
Feldman AG, Sokol RJ. Neonatal cholestasis: updates on diagnostics, therapeutics, and prevention. NeoReviews. 2021;22:e819–36.
Chiou FK, Ong C, Phua KB, Chedid F, Kader A. Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia presenting in first fourteen days in term neonates. World J Hepatol. 2017;9:1108.
Teng J, Bohlin K, Nemeth A, Fischler B. Cholestasis after very preterm birth was associated with adverse neonatal outcomes but no significant long‐term liver disease: A population‐based study. Acta Paediatr. 2021;110:141–8.
McPherson C, Miller SP, El-Dib M, Massaro AN, Inder TE. The influence of pain, agitation, and their management on the immature brain. Pediatr Res. 2020;88:168–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM assisted in data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing. OO drafted the Institutional Review Board (IRB) protocol and assisted with data collection. MB, SE, and SG assisted with data collection. CBC and SY assisted in study design and manuscript editing. AV conceived and designed the study and led data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
(a) The authors confirm that all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. (b) Approval has been obtained from the ethics committee (IRB) at the University of Missouri in Columbia, Missouri (number 2097726). (c) No informed consent was required under the ethics committee (IRB) approval as it is a retrospective study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
McCay, A., Onuigbo, O., Boyle, M. et al. Sequential direct bilirubin values in preterm infants. J Perinatol 45, 961–964 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02264-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02264-7