Abstract
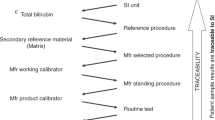
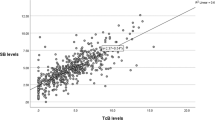
Despite growing concerns about the adverse effects of painful procedures in neonates, current guidelines continue to recommend using total serum bilirubin (TSB) levels to make decisions in the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia. Transcutaneous bilirubin assessment (TcB) has been studied extensively, but its presumed reliability is only based on how well it correlates with TSB. This assumes that TSB is the “gold standard” for determining the risk of bilirubin-induced neurotoxicity, although there is no direct evidence linking specific TSB levels to that risk. Furthermore, TSB levels are subject to variability due to the margin of error of the laboratory analysis. TcBs avoid skin-breaking procedures and have the additional advantages of decreased turn-around time, nursing and laboratory staff time, and costs. TcB procedures could be standardized, and new guidelines with increased reliance on them could significantly reduce painful procedures in these patients without increasing the risk of bilirubin neurotoxicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kemper A, Newman T, Slaughter J, Maisels J, Watchko J, Downs S, et al. Clinical practice guideline revision: management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics. 2022;150:e2022058859.
Selvanathan T, Miller S. Brain health in preterm infants: importance of early-life pain and analgesia exposure. Pediatr Res. 2024;96:1397–403.
McPherson C, Miller S, El-Dib M, Massaro A, Inder T. The influence of pain, agitation, and their management on the immature brain. Pediatr Res. 2020;88:168–75.
Valeri B, Holsti L, Linhares M. Neonatal pain and developmental outcomes in children born preterm: a systematic review. Clin J Pain. 2015;31:355–62.
Valeri B, Ranger M, Chau C, Cepeda I, Synnes A, Linhares M, et al. Neonatal invasive procedures predict pain intensity at school age in children born very preterm. Clin J Pain. 2016;32:1086–93.
Cong X, Wu J, Vittner D, Xu W, Hussain N, Galvin S, et al. The impact of cumulative pain/stress on neurobehavioral development of preterm infants in the NICU. Early Hum Dev. 2017;108:9–16.
Cook K, De Asis-Cruz J, Kim J, Basu S, Andescavage N, Murnick J, et al. Experience of early-life pain in premature infants is associated with atypical cerebellar development and later neurodevelopmental deficits. BMC Med. 2023;21:435.
Vinall J, Noel M, Disher T, Caddell K, Campbell-Yeo M. Memories of infant pain in the neonatal intensive care unit influence posttraumatic stress symptoms in mothers of infants born preterm. Clin J Pain. 2018;34:936–43.
Syed A, Hamzah F, Embong H, Ahmed S. A randomised comparative study assessing parental anxiety levels during bilirubin measurement in neonatal jaundice: a comparison of conventional blood taking and transcutaneous bilirubin method. Med Health. 2025;20:271–80.
Hynes S, Moore Z, Patton D, O’Connor T, Nugent L. Accuracy of transcutaneous bilirubin versus serum bilirubin measurement in preterm infants receiving phototherapy: a systematic review. Adv Neonatal Care. 2020;20:E118–26. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANC.0000000000000738.
Okwundu C, Olowoyeye A, Uthman OA, Smith J, Wiysonge CS, Bhutani VK, et al. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry versus total serum bilirubin measurement for newborns (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;5:CD012660.
Weber J, Vadasz-Chates N, Wade C, Micetic B, Gerkin R, Rao S. Transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring in preterm infants of 23 to 34 weeks’ gestation. Am J Perinatol. 2023;40:788–92. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1731277.
Fatih Ozden M, Kahvecioglu D, Tas M, Cetinkaya AK, Oktem A. Can transcutaneous bilirubin levels obtained from covered skin replace serum bilirubin measurement in neonates undergoing phototherapy? Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2025;19:183–9. https://doi.org/10.2478/abm-2025-0025.
Konana O, Bahr T, Strike H, Coleman J, Snow G, Christensen R. Decision accuracy and safety of transcutaneous bilirubin screening at Intermountain Healthcare. J Pediatr. 2021;228:53–7.
Nagar G, Vandermeer B, Campbell S, Kumar M. Reliability of transcutaneous bilirubin devices in preterm infants: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2013;132:871–81.
Jegathesan T, Campbell D, Ray J, Shah V, Berger H, Hayeems R, et al. Transcutaneous versus total serum bilirubin measurements in preterm infants. Neonatology. 2021;118:443–53.
Kurokawa D, Nakamura H, Yokota T, Iwatani S, Morisawa T, Katayama Y, et al. Screening for hyperbilirubinemia in Japanese very low birth weight infants using transcutaneous bilirubinometry. J Pediatr. 2016;168:77–81.
Sankar M, Rangasamy R, Joe P, Katheria A, Villosis M, Cortes M, et al. Transcutaneous bilirubin levels in extremely preterm infants less than 30 weeks gestation. J Perinatol. 2023;43:220–5.
Arman D, Topcuoğlu S, Gürsoy T, Ovalı F, Karatekin G. The accuracy of transcutaneous bilirubinometry in preterm infants. J Perinatol. 2020;40:212–8.
Bhargava V, Tawfik D, Niebuhr B, Jain S. Transcutaneous bilirubin estimation in extremely low birth weight infants receiving phototherapy: a prospective observational study. BMC Pediatr. 2018;18:227.
Juster-Reicher A, Flidel-Rimon O, Rozin I, Shinwell E. Correlation of transcutaneous bilirubinometry (TcB) and total serum bilirubin (TsB) levels after phototherapy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;28:1329–31.
Thamwiriyakul N, Siripattanapipong P, Bowornkitiwong W, Chaweerat R, Ngernchamn S. Validity of transcutaneous bilirubin measurements during and after phototherapy in term and late preterm infants. Eur J Pediatr. 2024;183:5037–41.
Alsaedi S. Transcutaneous bilirubin measurements can be used to measure bilirubin levels during phototherapy. Int J Pediatr. 2018;2018:4856390.
Hulzebos C, Vader-van Imhoff D, Bos A, Dijk P. Should transcutaneous bilirubin be measured in preterm infants receiving phototherapy? The relationship between transcutaneous and total serum bilirubin in preterm infants with and without phototherapy. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0218131.
Yang S, Liu F, Chen H. Comparison of transcutaneous and serum bilirubin before, under, and after phototherapy in term and late-preterm infants. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019;35:715–24.
Bhutani V, Gourley G, Adler S, Kreamer B, Dalin C, Johnson L. Noninvasive measurement of total serum bilirubin in a multiracial predischarge newborn population to assess the risk of severe hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 2000;106:e17.
Bental YA, Shiff Y, Dorsht N, Litig E, Tuval L, Mimouni FB. Bhutani-based nomograms for the prediction of significant hyperbilirubinaemia using transcutaneous measurements of bilirubin. Acta Paediatr. 2009;98:1902–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2009.01385.x.
Bosschaart N, Kok J, Newsum A, Ouweneel D, Mentink R, van Leeuwen TG, et al. Limitations and opportunities of transcutaneous bilirubin measurements. Pediatrics. 2012;129:689–94.
Greene DN, Liang J, Holmes D, Resch A, Lorey T. Neonatal total bilirubin measurements: still room for harmonization. Clin Biochem. 2014;47:1112–5.
Lo SF, Doumas BT. The status of bilirubin measurements in U.S. laboratories: why is accuracy elusive? Semin Perinatol. 2011;35:141–7.
Hegyi T, Hiatt I, Gertner I, Zanni R, Tolentino T. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry II. Dermal bilirubin kinetics during phototherapy. Pediatr Res. 1983;17:888–91.
Ahmed M, Mostafa S, Fisher G, Reynolds TM. Comparison between transcutaneous bilirubinometry and total serum bilirubin measurements in preterm infants <35 weeks gestation. Ann Clin Biochem. 2010;47:72–7.
McLean S, Baerg K, Smith-Fehr J, Szafron M. Cost savings with transcutaneous screening versus total serum bilirubin measurement for newborn jaundice in hospital and community settings: a cost-minimization analysis. CMAJ Open. 2018;6:E285–91.
Cat FC, Cat A, Cicek T, Gulec SG. Evaluation of the relationship between transcutaneous bilirubin measurement and total serum bilirubin in neonatal patients followed for jaundice. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2021;55:262–7. https://doi.org/10.14744/SEMB.2020.79837.
Agrawal G, Garg K, Sitaraman S, Sarna A. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of different sites for transcutaneous bilirubin measurement in early preterm infants. Indian J Pediatr. 2019;86:32–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-018-2739-4.
Yoruk I, Oguz D, Elevli M, Ataoglu E. Accuracy of transcutaneous bilirubin measurement from unexposed skin with a new generation device in neonates receiving phototherapy. Med Bull Haseki. 2022;60:113–9.
Costa-Posada U, Concheiro-Guisán A, Táboas-Ledo MF, González-Colmenero E, González-Durán ML, Suarez-Albo M, et al. Accuracy of transcutaneous bilirubin on covered skin in preterm and term newborns receiving phototherapy using a JM-105 bilirubinometer. J Perinatol. 2020;40:226–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0557-9.
Sardar S, Sarkar N, Ghosh M, Pal S. An Observational Prospective Study to Compare Transcutaneous Bilirubin with Serum Bilirubin in Preterm Newborn Requiring Phototherapy. J Clin Neonatol. 2021;10:59–67.
Kallimath A, Patnaik S, Suryawanshi P, Deshmukh R, Malshe N. The use of a simple and affordable skin patch for measurement of transcutaneous bilirubin levels in neonates during phototherapy. Front Pediatr. 2024;12:1434770. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2024.1434770.
Chitra R, Prince S, Chandrasekaran A, Sundar S. Development and validation of a noninvasive diffuse reflectance spectroscopic method for bilirubin estimation in neonates. J Biophotonics. 2025;18:e202400505. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.202400505.
Dam-Vervloet AJ, van Erk MD, Doorn N, Lip SGJ, Timmermans NA, Vanwinsen L, et al. Inter-device reproducibility of transcutaneous bilirubin meters. Pediatr Res. 2021;89:770–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-020-01118-6.
Casnocha Lucanova L, Zibolenova J, Matasova K Jr, Matasova K, Zibolen M. The use of transcutaneous bilirubin nomograms for the prevention of bilirubin neurotoxicity in the neonates. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1212667. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1212667.
Varvarigou A, Fouzas S, Skylogianni E, Mantagou L, Bougioukou D, Mantagos S. Transcutaneous bilirubin nomogram for prediction of significant neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 2009;124:1052–9. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2322.
Boo NY, Ishak S. Prediction of severe hyperbilirubinaemia using the Bilicheck transcutaneous bilirubinometer. J Paediatr Child Health. 2007;43:297–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1754.2007.01062.x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wimmer, J.E. Reconsidering transcutaneous bilirubinometry for management of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: is it time for change?. J Perinatol (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02532-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-025-02532-6