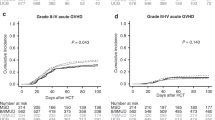
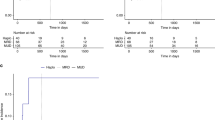
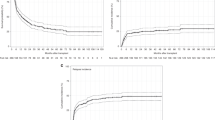
Abstract
Lack of HLA-matched related/unrelated donor remains a barrier to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) for adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML), with ongoing uncertainty about optimal donor type if more than one alternative donor is available. To assess the relationship between donor type, pre-HCT measurable residual disease (MRD), and post-HCT outcomes, we retrospectively analyzed 1265 myelodysplastic neoplasm (MDS)/AML and AML patients allografted in first or second remission with an HLA-matched sibling (MSD) or unrelated donor (MUD), HLA-mismatched unrelated donor (MMD), an HLA-haploidentical donor, or umbilical cord blood (UCB) at a single institution. Relapse risk was non-significantly higher after HLA-haploidentical and lower after UCB HCT. Non-relapse mortality (NRM) was significantly higher in patients undergoing MMD HCT, HLA-haploidentical HCT, and UCB, translating into significantly lower relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival for MMD and HLA-haploidentical HCT. There was a significant interaction between conditioning intensity and post-HCT outcomes for UCB HCT with better RFS for UCB HCT after MAC but higher NRM after non-MAC. In patients with pre-HCT MRD receiving MAC, relapse risk was significantly lower and RFS higher in those who underwent UCB HCT in comparison to MSD/MUD. Together, UCB HCT is a valuable alternative for MAC HCT, particularly in patients with pre-HCT MRD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset analyzed in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Freeman SD, Hills RK, Virgo P, Khan N, Couzens S, Dillon R, et al. Measurable residual disease at induction redefines partial response in acute myeloid leukemia and stratifies outcomes in patients at standard risk without NPM1 mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1486–97.
Terwijn M, van Putten WLJ, Kelder A, van der Velden VHJ, Brooimans RA, Pabst T, et al. High prognostic impact of flow cytometric minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia: data from the HOVON/SAKK AML 42A study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3889–97.
Paiva B, Vidriales M-B, Sempere A, Tarín F, Colado E, Benavente C, et al. Impact of measurable residual disease by decentralized flow cytometry: a PETHEMA real-world study in 1076 patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2021;35:2358–70.
Othus M, Wood BL, Stirewalt DL, Estey EH, Petersdorf SH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Effect of measurable (‘minimal’) residual disease (MRD) information on prediction of relapse and survival in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30:2080–3.
Krönke J, Schlenk RF, Jensen K-O, Tschürtz F, Corbacioglu A, Gaidzik VI, et al. Monitoring of minimal residual disease in NPM1 -mutated acute myeloid leukemia: a study from the German-Austrian acute myeloid leukemia study group. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2709–16.
Balsat M, Renneville A, Thomas X, de Botton S, Caillot D, Marceau A, et al. Postinduction minimal residual disease predicts outcome and benefit from allogeneic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 mutation: a study by the acute leukemia French Association Group. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:185–93.
Morita K, Kantarjian HM, Wang F, Yan Y, Bueso-Ramos C, Sasaki K, et al. Clearance of somatic mutations at remission and the risk of relapse in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1788–97.
Rothenberg-Thurley M, Amler S, Goerlich D, Köhnke T, Konstandin NP, Schneider S, et al. Persistence of pre-leukemic clones during first remission and risk of relapse in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2018;32:1598–608.
Chen Y, Cortes J, Estrov Z, Faderl S, Qiao W, Abruzzo L, et al. Persistence of cytogenetic abnormalities at complete remission after induction in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: prognostic significance and the potential role of allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2507–13.
Gragert L, Eapen M, Williams E, Freeman J, Spellman S, Baitty R, et al. HLA match likelihoods for hematopoietic stem-cell grafts in the U.S. registry. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:339–48.
Niederwieser D, Baldomero H, Bazuaye N, Bupp C, Chaudhri N, Corbacioglu S, et al. One and a half million hematopoietic stem cell transplants: continuous and differential improvement in worldwide access with the use of non-identical family donors. Haematologica. 2022;107:1045–53.
Warlick ED, Peffault de Latour R, Shanley R, Robin M, Bejanyan N, Xhaard A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia: similar outcomes regardless of donor type. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21:357–63.
Gooptu M, Romee R, St. Martin A, Arora M, Al Malki M, Antin JH, et al. HLA-haploidentical vs matched unrelated donor transplants with posttransplant cyclophosphamide-based prophylaxis. Blood. 2021;138:273–82.
Mehta RS, Holtan SG, Wang T, Hemmer MT, Spellman SR, Arora M, et al. Composite GRFS and CRFS outcomes after adult alternative donor HCT. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:2062–76.
Rashidi A, Hamadani M, Zhang M-J, Wang H-L, Abdel-Azim H, Aljurf M, et al. Outcomes of haploidentical vs matched sibling transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission. Blood Adv. 2019;3:1826–36.
Versluis J, Labopin M, Ruggeri A, Socie G, Wu D, Volin L, et al. Alternative donors for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in poor-risk AML in CR1. Blood Adv. 2017;1:477–85.
Yanada M, Konuma T, Yamasaki S, Harada K, Iwasaki M, Kobayashi A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation from alternative donors in acute myelogenous leukemia: a comparative analysis. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27:1005.e1–1005.e8.
Shouval R, Fein JA, Labopin M, Kröger N, Duarte RF, Bader P, et al. Outcomes of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation from HLA-matched and alternative donors: a European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation registry retrospective analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6:e573–e584.
Baron F, Ngoya M, Labopin M, Cornelissen JJ, Ganser A, Forcade E, et al. Comparison of long-term outcome for AML patients alive free of disease 2 years after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with umbilical cord blood versus unrelated donor: a study from the ALWP of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021;56:2742–8.
Fuchs EJ, O’Donnell PV, Eapen M, Logan B, Antin JH, Dawson P, et al. Double unrelated umbilical cord blood vs HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation: the BMT CTN 1101 trial. Blood. 2021;137:420–8.
Ruggeri A, Labopin M, Sanz G, Piemontese S, Arcese W, Bacigalupo A, et al. Comparison of outcomes after unrelated cord blood and unmanipulated haploidentical stem cell transplantation in adults with acute leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29:1891–1900.
Sanz J, Montoro J, Solano C, Valcárcel D, Sampol A, Ferrá C, et al. Prospective randomized study comparing myeloablative unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation versus HLA-haploidentical related stem cell transplantation for adults with hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2020;26:358–66.
Sharma P, Purev E, Haverkos B, Pollyea DA, Cherry E, Kamdar M, et al. Adult cord blood transplant results in comparable overall survival and improved GRFS vs matched related transplant. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2227–35.
Wagner JE, Ballen KK, Zhang M-J, Allbee-Johnson M, Karanes C, Milano F, et al. Comparison of haploidentical and umbilical cord blood transplantation after myeloablative conditioning. Blood Adv. 2021;5:4064–72.
Milano F, Gooley T, Wood B, Woolfrey A, Flowers ME, Doney K, et al. Cord-blood transplantation in patients with minimal residual disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:944–53.
Chang Y-J, Wang Y, Liu Y-R, Xu L-P, Zhang X-H, Chen H, et al. Haploidentical allograft is superior to matched sibling donor allograft in eradicating pre-transplantation minimal residual disease of AML patients as determined by multiparameter flow cytometry: a retrospective and prospective analysis. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:134.
Baron F, Labopin M, Ruggeri A, Sierra J, Robinson S, Labussière‐Wallet H, et al. Impact of detectable measurable residual disease on umbilical cord blood transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2020;95:1057–65.
Canaani J, Labopin M, Huang XJ, Ciceri F, Van Lint MT, Bruno B, et al. Minimal residual disease status predicts outcome of acute myeloid leukaemia patients undergoing T-cell replete haploidentical transplantation. An analysis from the Acute Leukaemia Working Party (ALWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplan. Br J Haematol. 2018;183:411–20.
Horgan C, Mullanfiroze K, Rauthan A, Patrick K, Butt NA, Mirci-Danicar O, et al. T-cell replete cord transplants give superior outcomes in high-risk and relapsed/refractory pediatric myeloid malignancy. Blood Adv. 2023;7:2155–65.
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian RP, Borowitz MJ, Calvo KR, Kvasnicka H-M, et al. International consensus classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemias: integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood. 2022;140:1200–28.
Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, Craddock C, DiNardo CD, Dombret H, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140:1345–77.
Breems DA, Van Putten WLJ, De Greef GE, Van Zelderen-Bhola SL, Gerssen-Schoorl KBJ, Mellink CHM, et al. Monosomal karyotype in acute myeloid leukemia: a better indicator of poor prognosis than a complex karyotype. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4791–7.
Paras G, Morsink LM, Othus M, Milano F, Sandmaier BM, Zarling LC, et al. Conditioning intensity and peritransplant flow cytometric MRD dynamics in adult AML. Blood. 2022;139:1694–706.
Morsink LM, Sandmaier BM, Othus M, Palmieri R, Granot N, Bezerra ED, et al. Conditioning intensity, pre-transplant flow cytometric measurable residual disease, and outcome in adults with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Cancers. 2020;12:2339.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2005;106:2912–9.
Walter RB, Othus M, Borthakur G, Ravandi F, Cortes JE, Pierce SA, et al. Prediction of early death after induction therapy for newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia with pretreatment risk scores: a novel paradigm for treatment assignment. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4417–24.
Walter RB, Gooley TA, Wood BL, Milano F, Fang M, Sorror ML, et al. Impact of pretransplantation minimal residual disease, as detected by multiparametric flow cytometry, on outcome of myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1190–7.
Walter RB, Buckley SA, Pagel JM, Wood BL, Storer BE, Sandmaier BM, et al. Significance of minimal residual disease before myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for AML in first and second complete remission. Blood. 2013;122:1813–21.
Walter RB, Gyurkocza B, Storer BE, Godwin CD, Pagel JM, Buckley SA, et al. Comparison of minimal residual disease as outcome predictor for AML patients in first complete remission undergoing myeloablative or nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2015;29:137–44.
Araki D, Wood BL, Othus M, Radich JP, Halpern AB, Zhou Y, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: time to move toward a minimal residual disease–based definition of complete remission? J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:329–36.
Zhou Y, Othus M, Araki D, Wood BL, Radich JP, Halpern AB, et al. Pre- and post-transplant quantification of measurable (‘minimal’) residual disease via multiparameter flow cytometry in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30:1456–64.
Wood BL. Acute myeloid leukemia minimal residual disease detection: the difference from normal approach. Curr Protoc Cytom. 2020;93:e73.
Walter RB, Sandmaier BM, Storer BE, Godwin CD, Buckley SA, Pagel JM, et al. Number of courses of induction therapy independently predicts outcome after allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first morphological remission. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21:373–8.
Hoffmann AP, Besch AL, Othus M, Morsink LM, Wood BL, Mielcarek M, et al. Early achievement of measurable residual disease (MRD)-negative complete remission as predictor of outcome after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020;55:669–72.
Morsink LM, Bezerra ED, Othus M, Wood BL, Fang M, Sandmaier BM, et al. Comparative analysis of total body irradiation (TBI)-based and non-TBI-based myeloablative conditioning for acute myeloid leukemia in remission with or without measurable residual disease. Leukemia. 2020;34:1701–5.
Morsink LM, Othus M, Bezerra ED, Wood BL, Fang M, Sandmaier BM, et al. Impact of pretransplant measurable residual disease on the outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in adult monosomal karyotype AML. Leukemia. 2020;34:1577–87.
Rodriguez-Arboli E, Othus M, Freeman S, Buccisano F, Ngai LL, Thomas I, et al. Optimal prognostic threshold for measurable residual disease positivity by multiparameter flow cytometry in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Leukemia. 2024;38:2266–9.
Leisenring WM, Martin PJ, Petersdorf EW, Regan AE, Aboulhosn N, Stern JM, et al. An acute graft-versus-host disease activity index to predict survival after hematopoietic cell transplantation with myeloablative conditioning regimens. Blood. 2006;108:749–55.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: I. Diagnosis and Staging Working Group Report. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:945–56.
Baron F, Labopin M, Ruggeri A, Ehninger G, Bonifazi F, Stelljes M, et al. Umbilical cord blood versus unrelated donor transplantation in adults with primary refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: a report from Eurocord, the Acute Leukemia Working Party and the Cord Blood Committee of the Cellular Therapy and Immunobiology Working Party of the EBMT. Blood Cancer J. 2019;9:46.
Dholaria B, Labopin M, Sanz J, Ruggeri A, Cornelissen J, Labussière-Wallet H, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with cord blood versus mismatched unrelated donor with post-transplant cyclophosphamide in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:76.
Garcia JG, Grillo S, Cao Q, Brunstein CG, Arora M, MacMillan ML, et al. Low 5-year health care burden after umbilical cord blood transplantation. Blood Adv. 2021;5:853–60.
Malard F, Milpied N, Blaise D, Chevallier P, Michallet M, Lioure B, et al. Effect of graft source on unrelated donor hemopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults with acute myeloid leukemia after reduced-intensity or nonmyeloablative conditioning: a study from the Société Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Thérapie Cellulaire. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21:1059–67.
Ruggeri A, Galimard J-E, Labopin M, Rafii H, Blaise D, Ciceri F, et al. Comparison of outcomes after unrelated double-unit cord blood and haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in adults with acute myelogenous leukemia: a study on Behalf of Eurocord and the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28:710.e1–710.e10.
Giannotti F, Labopin M, Shouval R, Sanz J, Arcese W, Angelucci E, et al. Haploidentical transplantation is associated with better overall survival when compared to single cord blood transplantation: an EBMT-Eurocord study of acute leukemia patients conditioned with thiotepa, busulfan, and fludarabine. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:110.
Brunstein CG, O’Donnell PV, Logan B, Dawson P, Costa L, Cutler C, et al. Impact of center experience with donor type on outcomes: a secondary analysis, blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network 1101Open for Accrual June 2012Open for Accrual June 2012. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28:406.e1–406.e6.
Milano F, Gutman JA, Deeg HJ, Nemecek ER, Baumgart J, Thur L, et al. Treosulfan-based conditioning is feasible and effective for cord blood recipients: a phase 2 multicenter study. Blood Adv. 2020;4:3302–10.
Orvain C, Wilson JA, Fang M, Sandmaier BM, Rodríguez-Arbolí E, Wood BL, et al. Relative impact of residual cytogenetic abnormalities and flow cytometric measurable residual disease on outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2022;108:420–32.
Dillon R, Hills R, Freeman S, Potter N, Jovanovic J, Ivey A, et al. Molecular MRD status and outcome after transplantation in NPM1-mutated AML. Blood. 2020;135:680–8.
Anthias C, Dignan FL, Morilla R, Morilla A, Ethell ME, Potter MN, et al. Pre-transplant MRD predicts outcome following reduced-intensity and myeloablative allogeneic hemopoietic SCT in AML. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:679–83.
Buckley SA, Wood BL, Othus M, Hourigan CS, Ustun C, Linden MA, et al. Minimal residual disease prior to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia: a meta-analysis. Haematologica. 2017;102:865–73.
Balligand L, Galambrun C, Sirvent A, Roux C, Pochon C, Bruno B, et al. Single-unit versus double-unit umbilical cord blood transplantation in children and young adults with residual leukemic disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:734–42.
Barker JN, Devlin SM, Naputo KA, Skinner K, Maloy MA, Flynn L, et al. High progression-free survival after intermediate intensity double unit cord blood transplantation in adults. Blood Adv. 2020;4:6064–76.
Vago L, Toffalori C, Ahci M, Lange V, Lang K, Todaro S, et al. Incidence of HLA loss in a global multicentric cohort of post-transplantation relapses: results from the hlaloss collaborative study. Blood. 2018;132:818–818.
Fuchs EJ, McCurdy SR, Solomon SR, Wang T, Herr MR, Modi D, et al. HLA informs risk predictions after haploidentical stem cell transplantation with posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Blood. 2022;139:1452–68.
Acknowledgements
Research reported in this publication was supported by grants P01-CA078902, P01-CA018029, and P30-CA015704 from the National Cancer Institute/National Institutes of Health (NCI/NIH), Bethesda, MD, USA. The authors acknowledge the excellent care provided by the physicians and nurses of the HCT teams, the staff in the Long-Term Follow-up office at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, the Hematopathology Laboratory at the University of Washington, and the patients for participating in our research protocols. R.B.W. acknowledges support from the José Carreras/E. Donnall Thomas Endowed Chair for Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and Design: RBW. Collection and Assembly of Data: CO, FM, ERA, EWP, BMS, FRA, RBW. Data Analysis and Interpretation: CO, FM, MO, RBW. Manuscript Writing: All authors. Final Approval of the Manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Employment or Leadership Position: none; Consultant or Advisory Role: none: Stock Ownership: none; Honoraria: none; Research Funding: none; Expert Testimony: none; Patents: none; Other Remuneration: none.
Ethics approval
All patients were treated on Institutional Review Board (IRB)-approved research protocols (all registered with ClinicalTrials.gov) or standard treatment protocols. All analyses conducted herein were performed under a research protocol approved by the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center’s IRB (#FH2562).
Consent for publication
All patients gave informed consent for study participation in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Orvain, C., Milano, F., Rodríguez-Arbolí, E. et al. Relationship between donor source, pre-transplant measurable residual disease, and outcome after allografting for adults with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 39, 381–390 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-024-02497-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-024-02497-z
This article is cited by
-
Modulators of relapse risk in adults allografted for acute myeloid leukemia in measurable residual disease-positive remission
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2025)