Abstract
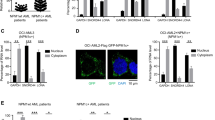
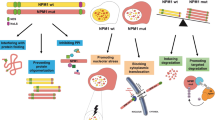
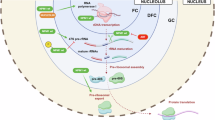
Nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1) is a nucleolar chaperone protein frequently mutated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). ARF and Sentrin/SUMO Specific Peptidase 3 (SENP3) control NPM1 functions through dynamic SUMOylation/de-SUMOylation. Mutated NPM1 is an oncoprotein that exhibits an aberrant cytoplasmic localization (NPM1c) and disrupts PML/P53 signaling. Studies reported increased survival of patients with NPM1c AML when retinoic acid (RA) was added to chemotherapy or hypomethylating agents. Ex vivo, RA initiates NPM1c degradation, P53 activation and cell death. Yet, the molecular mechanisms involved remain elusive. Here we show that in NPM1c AML cell lines or patients’ blasts, NPM1c-triggered mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress drive NPM1c stabilization through SENP3 upregulation. RA decreases mitochondrial ROS production, driving degradation of SENP3, ARF stabilization, PML-dependent NPM1c hyperSUMOylation followed by RNF4-dependent ubiquitination and degradation. Thus, the feedback loop stabilizing NPM1c protein can be interrupted by RA-triggered enhanced mitochondrial fitness, mechanistically explaining the benefit of RA in chemotherapy or hypomethylating agents-treated AMLs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available and deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under the accession number GSE298593 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE298593]. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Falini B, Bolli N, Liso A, Martelli M, Mannucci R, Pileri S, et al. Altered nucleophosmin transport in acute myeloid leukaemia with mutated NPM1: molecular basis and clinical implications. Leukemia. 2009;23:1731–43.
Lam YW, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Lamond AI. The nucleolus. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:1335–7.
Falini B, Martelli MP, Bolli N, Sportoletti P, Liso A, Tiacci E, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1): is it a distinct entity?. Blood. 2011;117:1109–20.
Falini B, Brunetti L, Sportoletti P, Martelli MP. NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: from bench to bedside. Blood. 2020;136:1707–21.
Grisendi S, Bernardi R, Rossi M, Cheng K, Khandker L, Manova K, et al. Role of nucleophosmin in embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Nature. 2005;437:147–53.
Itahana K, Bhat KP, Jin A, Itahana Y, Hawke D, Kobayashi R, et al. Tumor suppressor ARF degrades B23, a nucleolar protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1151–64.
Haindl M, Harasim T, Eick D, Muller S. The nucleolar SUMO-specific protease SENP3 reverses SUMO modification of nucleophosmin and is required for rRNA processing. EMBO Rep. 2008;9:273–9.
Mukhopadhyay D, Dasso M. Modification in reverse: the SUMO proteases. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32:286–95.
Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E, Alcalay M, Rosati R, Pasqualucci L, et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:254–66.
Dohner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, Craddock C, DiNardo CD, Dombret H, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140:1345–77.
Falini B, Dillon R. Criteria for diagnosis and molecular monitoring of NPM1-mutated AML. Blood Cancer Discov. 2024;5:8–20.
Khoury JD, Solary E, Abla O, Akkari Y, Alaggio R, Apperley JF, et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022;36:1703–19.
Bolli N, Nicoletti I, De Marco MF, Bigerna B, Pucciarini A, Mannucci R, et al. Born to be exported: COOH-terminal nuclear export signals of different strength ensure cytoplasmic accumulation of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6230–7.
Brunetti L, Gundry MC, Sorcini D, Guzman AG, Huang YH, Ramabadran R, et al. Mutant NPM1 maintains the leukemic state through HOX expression. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:499–512.e9.
Wu HC, Rerolle D, Berthier C, Hleihel R, Sakamoto T, Quentin S, et al. Actinomycin D targets NPM1c-primed mitochondria to restore PML-driven senescence in AML therapy. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:3198–213.
de The H. Differentiation therapy revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18:117–27.
de The H, Pandolfi PP, Chen Z. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: a paradigm for oncoprotein-targeted cure. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:552–60.
Burnett AK, Hills RK, Green C, Jenkinson S, Koo K, Patel Y, et al. The impact on outcome of the addition of all-trans retinoic acid to intensive chemotherapy in younger patients with nonacute promyelocytic acute myeloid leukemia: overall results and results in genotypic subgroups defined by mutations in NPM1, FLT3, and CEBPA. Blood. 2010;115:948–56.
Schlenk RF, Frohling S, Hartmann F, Fischer JT, Glasmacher A, del Valle F, et al. Phase III study of all-trans retinoic acid in previously untreated patients 61 years or older with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2004;18:1798–803.
Cao Y, Liu Y, Shang L, Wei W, Shen Y, Gu Q, et al. Decitabine and all-trans retinoic acid synergistically exhibit cytotoxicity against elderly AML patients via miR-34a/MYCN axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;125:109878.
Lübbert M, Grishina O, Schmoor C, Schlenk RF, Jost E, Crysandt M, et al. Valproate and retinoic acid in combination with decitabine in elderly nonfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia: results of a multicenter, randomized, 2 × 2, phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:257–70.
Schlenk RF, Döhner K, Kneba M, Götze K, Hartmann F, Del Valle F, et al. Gene mutations and response to treatment with all-trans retinoic acid in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Results from the AMLSG Trial AML HD98B. Haematologica. 2009;94:54–60.
El Hajj H, Dassouki Z, Berthier C, Raffoux E, Ades L, Legrand O, et al. Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide trigger degradation of mutated NPM1, resulting in apoptosis of AML cells. Blood. 2015;125:3447–54.
Martelli MP, Gionfriddo I, Mezzasoma F, Milano F, Pierangeli S, Mulas F, et al. Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid target NPM1 mutant oncoprotein levels and induce apoptosis in NPM1-mutated AML cells. Blood. 2015;125:3455–65.
Hleihel R, El Hajj H, Wu HC, Berthier C, Zhu HH, Massoud R, et al. A Pin1/PML/P53 axis activated by retinoic acid in NPM1c acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2021;106:3090–9.
Skayneh H, Jishi B, Hleihel R, Hamie M, El Hajj R, Deleuze-Masquefa C, et al. EAPB0503, an imidazoquinoxaline derivative modulates SENP3/ARF mediated SUMOylation, and induces NPM1c degradation in NPM1 mutant AML. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:3421.
Yan S, Sun X, Xiang B, Cang H, Kang X, Chen Y, et al. Redox regulation of the stability of the SUMO protease SENP3 via interactions with CHIP and Hsp90. EMBO J. 2010;29:3773–86.
Carracedo A, Weiss D, Leliaert AK, Bhasin M, de Boer VC, Laurent G, et al. A metabolic prosurvival role for PML in breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:3088–100.
Boutzen H, Saland E, Larrue C, de Toni F, Gales L, Castelli FA, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutations prime the all-trans retinoic acid myeloid differentiation pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med. 2016;213:483–97.
Altucci L, Rossin A, Hirsch O, Nebbioso A, Vitoux D, Wilhelm E, et al. Rexinoid-triggered differentiation and tumor-selective apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia by protein kinase A-mediated desubordination of retinoid X receptor. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8754–65.
McKeown MR, Johannessen L, Lee E, Fiore C, di Tomaso E. Antitumor synergy with SY-1425, a selective RARalpha agonist, and hypomethylating agents in retinoic acid receptor pathway activated models of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2019;104:e138–e42.
Huang M, Thomas D, Li MX, Feng W, Chan SM, Majeti R, et al. Role of cysteine 288 in nucleophosmin cytoplasmic mutations: sensitization to toxicity induced by arsenic trioxide and bortezomib. Leukemia. 2013;27:1970–80.
Kunchala P, Kuravi S, Jensen R, McGuirk J, Balusu R. When the good go bad: Mutant NPM1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2018;32:167–83.
Gu X, Ebrahem Q, Mahfouz RZ, Hasipek M, Enane F, Radivoyevitch T, et al. Leukemogenic nucleophosmin mutation disrupts the transcription factor hub that regulates granulomonocytic fates. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:4260–79.
Kuo ML, den Besten W, Thomas MC, Sherr CJ. Arf-induced turnover of the nucleolar nucleophosmin-associated SUMO-2/3 protease Senp3. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:3378–87.
Yun C, Wang Y, Mukhopadhyay D, Backlund P, Kolli N, Yergey A, et al. Nucleolar protein B23/nucleophosmin regulates the vertebrate SUMO pathway through SENP3 and SENP5 proteases. J Cell Biol. 2008;183:589–95.
Dassouki Z, Sahin U, El Hajj H, Jollivet F, Kfoury Y, Lallemand-Breitenbach V, et al. ATL response to arsenic/interferon therapy is triggered by SUMO/PML/RNF4-dependent Tax degradation. Blood. 2015;125:474–82.
Lallemand-Breitenbach V, Jeanne M, Benhenda S, Nasr R, Lei M, Peres L, et al. Arsenic degrades PML or PML-RARalpha through a SUMO-triggered RNF4/ubiquitin-mediated pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:547–55.
Acin-Perez R, Hoyos B, Zhao F, Vinogradov V, Fischman DA, Harris RA, et al. Control of oxidative phosphorylation by vitamin A illuminates a fundamental role in mitochondrial energy homoeostasis. FASEB J. 2010;24:627–36.
Nohara K, Mallampalli V, Nemkov T, Wirianto M, Yang J, Ye Y, et al. Nobiletin fortifies mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle to promote healthy aging against metabolic challenge. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3923.
Cheung EC, Vousden KH. The role of ROS in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:280–97.
Kim D, Paggi JM, Park C, Bennett C, Salzberg SL. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37:907–15.
Danecek P, Bonfield JK, Liddle J, Marshall J, Ohan V, Pollard MO, et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience. 2021;10:giab008.
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:923–30.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:15545–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HEH and AB planned and designed this study. RH, HS, H-CW, MH, JD, CM conducted the experiments. AK performed the Bioinformatics analysis. RH analyzed the data and reported the study to HEH, AB, MS and HdT contributed to the conceptualization of this study. HEH wrote the original draft. AB reviewed the original draft. HEH validated the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hleihel, R., Skayneh, H., Wu, HC. et al. Retinoic acid disrupts an NPM1c/ROS/SENP3/ARF oncogenic axis in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 39, 2673–2685 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-025-02731-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-025-02731-2