Abstract
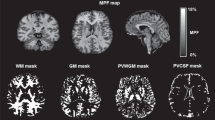
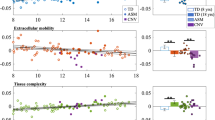
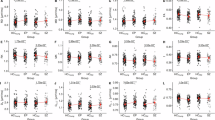
Myelin abnormalities in white matter have been implicated in the pathophysiology of psychotic spectrum disorders (PSD), which are characterized by brain dysconnectivity as a core feature. Among evidence from in vivo MRI studies, diffusion imaging findings have largely supported disrupted white matter integrity in PSD; however, they are not specific to myelin changes. Using a multimodal imaging approach, the current study aimed to further delineate myelin and microstructural changes in the white matter of a young PSD cohort. We utilized quantitative magnetization transfer (qMT) imaging combined with advanced diffusion imaging to estimate specific myelin-related biophysical properties in 51 young adult PSD patients compared with 38 age-matched healthy controls. The macromolecular proton fraction (MPF) obtained from qMT was used as a specific marker of myelin content. Additionally, MPF was employed along with diffusion metrics of axonal density (vic) and extra-cellular volume fraction to derive the g-ratio, a measure of relative myelin sheath thickness defined as the ratio of inner to outer axonal diameter. Compared to controls, we observed a widespread MPF reduction and localized g-ratio increase in patients, primarily those with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or depressive schizoaffective disorder. No between-group differences were noted in vic, suggesting similar axonal densities across groups. Correlation analysis revealed that lower MPF was significantly related to poorer working memory performance in PSD, while the HC group showed a positive association for working memory with both g-ratio and vic. The pattern of changes observed in our multimodal imaging markers suggests that PSD, depending on symptomatology, is characterized by specific alterations in white matter integrity and myelin-axonal geometry of major white matter tracts, which may impact working memory function. These findings provide a more detailed view of myelin-related white matter changes in early stages of PSD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Please contact the corresponding author for data and code sharing.
References
Uranova NA, Vostrikov VM, Orlovskaya DD, Rachmanova VI. Oligodendroglial density in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and mood disorders: a study from the Stanley Neuropathology Consortium. Schizophr Res. 2004;67:269–75.
Uranova NA, Vikhreva OV, Rachmanova VI, Orlovskaya DD. Ultrastructural alterations of myelinated fibers and oligodendrocytes in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: a postmortem morphometric study. Schizophr Res Treat. 2011;2011:325789.
Uranova NA, Orlovskaya DD, Vikhreva O, Zimina I, Kolomeets N, Vostrikov V, et al. Electron microscopy of oligodendroglia in severe mental illness. Brain Res Bull. 2001;55:597–610.
Tkachev D, Mimmack ML, Ryan MM, Wayland M, Freeman T, Jones PB, et al. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Lancet. 2003;362:798–805.
Yu H, Bi W, Liu C, Zhao Y, Zhang D, Yue W. A hypothesis-driven pathway analysis reveals myelin-related pathways that contribute to the risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014;51:140–5.
Yu G, Su Y, Guo C, Yi C, Yu B, Chen H, et al. Pathological oligodendrocyte precursor cells revealed in human schizophrenic brains and trigger schizophrenia-like behaviors and synaptic defects in genetic animal model. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:5154–66.
Kelly S, Jahanshad N, Zalesky A, Kochunov P, Agartz I, Alloza C, et al. Widespread white matter microstructural differences in schizophrenia across 4322 individuals: results from the ENIGMA schizophrenia DTI working group. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1261–9.
Gonenc A, Frazier JA, Crowley DJ, Moore CM. Combined diffusion tensor imaging and transverse relaxometry in early-onset bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010;49:1260–8.
Raghava JM, Mandl RCW, Nielsen MO, Fagerlund B, Glenthoj BY, Rostrup E, et al. Multimodal assessment of white matter microstructure in antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia patients and confounding effects of recreational drug use. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021;15:36–48.
Tonnesen S, Kaufmann T, Doan NT, Alnaes D, Cordova-Palomera A, Meer DV, et al. White matter aberrations and age-related trajectories in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder revealed by diffusion tensor imaging. Sci Rep. 2018;8:14129.
Mancini M, Karakuzu A, Cohen-Adad J, Cercignani M, Nichols TE, Stikov N. An interactive meta-analysis of MRI biomarkers of myelin. Elife 2020;9:e61523.
Yarnykh VL. Fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping from a single off-resonance magnetization transfer measurement. Magn Reson Med. 2012;68:166–78.
Mandl RC, Schnack HG, Luigjes J, van den Heuvel MP, Cahn W, Kahn RS, et al. Tract-based analysis of magnetization transfer ratio and diffusion tensor imaging of the frontal and frontotemporal connections in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2010;36:778–87.
Mandl RC, Pasternak O, Cahn W, Kubicki M, Kahn RS, Shenton ME, et al. Comparing free water imaging and magnetization transfer measurements in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2015;161:126–32.
Kubicki M, Park H, Westin CF, Nestor PG, Mulkern RV, Maier SE, et al. DTI and MTR abnormalities in schizophrenia: analysis of white matter integrity. NeuroImage. 2005;26:1109–18.
Lewandowski KE, Ongur D, Sperry SH, Cohen BM, Sehovic S, Goldbach JR, et al. Myelin vs axon abnormalities in white matter in bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:1243–9.
Palaniyappan L, Al-Radaideh A, Mougin O, Das T, Gowland P, Liddle PF. Aberrant myelination of the cingulum and Schneiderian delusions in schizophrenia: a 7T magnetization transfer study. Psychol Med. 2019;49:1890–6.
Gangadin SS, Mandl RCW, de Witte LD, van Haren NEM, Schutte MJL, Begemann MJH, et al. Lower fractional anisotropy without evidence for neuro-inflammation in patients with early-phase schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Schizophr Res. 2024;264:557–66.
Henkelman RM, Huang X, Xiang QS, Stanisz GJ, Swanson SD, Bronskill MJ. Quantitative interpretation of magnetization transfer. Magn Reson Med. 1993;29:759–66.
Yarnykh VL, Bowen JD, Samsonov A, Repovic P, Mayadev A, Qian P, et al. Fast whole-brain three-dimensional macromolecular proton fraction mapping in multiple sclerosis. Radiology. 2015;274:210–20.
Underhill HR, Rostomily RC, Mikheev AM, Yuan C, Yarnykh VL. Fast bound pool fraction imaging of the in vivo rat brain: association with myelin content and validation in the C6 glioma model. NeuroImage. 2011;54:2052–65.
Khodanovich MY, Sorokina IV, Glazacheva VY, Akulov AE, Nemirovich-Danchenko NM, Romashchenko AV, et al. Histological validation of fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping as a quantitative myelin imaging method in the cuprizone demyelination model. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46686.
Samsonov AA, Alexander AL, Mossahebi P, Wu YC, Duncan ID, Field AS. Quantitative MR imaging of two-pool magnetization transfer model parameters in myelin mutant shaking pup. NeuroImage. 2012;62:1390–8.
Smirnova LP, Yarnykh VL, Parshukova DA, Kornetova EG, Semke AV, Usova AV, et al. Global hypomyelination of the brain white and gray matter in schizophrenia: quantitative imaging using macromolecular proton fraction. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:365.
Sui YV, Bertisch H, Lee HH, Storey P, Babb JS, Goff DC, et al. Quantitative macromolecular proton fraction Mapping reveals altered cortical myelin profile in schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Cereb Cortex Commun. 2021;2:tgab015.
Lewandowski KE, Du F, Fan X, Chen X, Huynh P, Ongur D. Role of glia in prefrontal white matter abnormalities in first episode psychosis or mania detected by diffusion tensor spectroscopy. Schizophr Res. 2019;209:64–71.
Lazar M. Working memory: how important is white matter? Neuroscientist. 2017;23:197–210.
Nuechterlein KH, Green MF, Kern RS, Baade LE, Barch DM, Cohen JD, et al. The MATRICS consensus cognitive battery, part 1: test selection, reliability, and validity. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165:203–13.
Andreasen N, Flaum M, Arndt S, Alliger R, Swayze V. Positive and negative symptoms: assessment and validity. Marneros A, Andreasen NC, Tsuang MT. (eds) Negative Versus Positive Schizophrenia. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1991. pp 28–51.
Grober E, Sliwinski M. Development and validation of a model for estimating premorbid verbal intelligence in the elderly. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1991;13:933–49.
Wechsler D. Wechsler memory scale. Psychological Corporation. 1945.
Cardno AG, Rijsdijk FV, West RM, Gottesman II, Craddock N, Murray RM, et al. A twin study of schizoaffective-mania, schizoaffective-depression, and other psychotic syndromes. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012;159B:172–82.
Craddock N, O’Donovan MC, Owen MJ. Psychosis genetics: modeling the relationship between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and mixed (or “schizoaffective”) psychoses. Schizophr Bull. 2009;35:482–90.
Mossahebi P, Samsonov AA. Rapid and accurate variable flip angle T1 mapping with correction of on-resonance MT effects. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM. MelBourne: ISMRM annual Meeting; 2012. pp 4267.
Yarnykh VL. Time-efficient, high-resolution, whole brain three-dimensional macromolecular proton fraction mapping. Magn Reson Med. 2016;75:2100–6.
Harms MP, Somerville LH, Ances BM, Andersson J, Barch DM, Bastiani M, et al. Extending the human connectome project across ages: imaging protocols for the lifespan development and aging projects. NeuroImage. 2018;183:972–84.
Van Essen DC, Smith SM, Barch DM, Behrens TE, Yacoub E, Ugurbil K, et al. The WU-Minn human connectome project: an overview. NeuroImage. 2013;80:62–79.
Veraart J, Novikov DS, Christiaens D, Ades-Aron B, Sijbers J, Fieremans E. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. NeuroImage. 2016;142:394–406.
Kellner E, Dhital B, Kiselev VG, Reisert M. Gibbs-ringing artifact removal based on local subvoxel-shifts. Magn Reson Med. 2016;76:1574–81.
Tournier JD, Smith R, Raffelt D, Tabbara R, Dhollander T, Pietsch M, et al. MRtrix3: a fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. NeuroImage. 2019;202:116137.
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM. Fsl. NeuroImage. 2012;62:782–90.
Smith SM. Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp. 2002;17:143–55.
Andersson JL, Skare S, Ashburner J. How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: application to diffusion tensor imaging. NeuroImage. 2003;20:870–88.
Jenkinson M, Bannister P, Brady M, Smith S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage. 2002;17:825–41.
Samsonov AA, Mossahebi P, Anderson A, Velikina JV, Johnson KM, Johnson SC et al. High Resolution, Motion Corrected Mapping of Macromolecular Proton Fraction (MPF) in Clinically Acceptable Time Using 3D Undersampled Radials. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM. Milan: ISMRM annual Meeting; 2014. pp 3337.
Mossahebi P, Yarnykh VL, Samsonov A. Analysis and correction of biases in cross-relaxation MRI due to biexponential longitudinal relaxation. Magn Reson Med. 2014;71:830–8.
Andersson JL, Sotiropoulos SN. An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. NeuroImage. 2016;125:1063–78.
Fick RHJ, Wassermann D, Deriche R. The dmipy toolbox: diffusion MRI multi-compartment modeling and microstructure recovery made easy. Front Neuroinform. 2019;13:64.
Zhang H, Schneider T, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Alexander DC. NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage. 2012;61:1000–16.
Stikov N, Campbell JS, Stroh T, Lavelee M, Frey S, Novek J, et al. In vivo histology of the myelin g-ratio with magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage. 2015;118:397–405.
Schmierer K, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Tozer DJ, Boulby PA, Parkes HG, Yousry TA, et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance of postmortem multiple sclerosis brain before and after fixation. Magn Reson Med. 2008;59:268–77.
Cercignani M, Giulietti G, Dowell NG, Spano B, Harrison NA, Bozzali M. A simple method to scale the macromolecular pool size ratio for computing the g-ratio in vivo. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM. Singapore: ISMRM annual Meeting; 2016. pp 3369.
Mohammadi S, Carey D, Dick F, Diedrichsen J, Sereno MI, Reisert M, et al. Whole-Brain in-vivo measurements of the Axonal G-ratio in a group of 37 healthy volunteers. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:441.
Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 2007;8:118–27.
Fortin JP, Parker D, Tunc B, Watanabe T, Elliott MA, Ruparel K, et al. Harmonization of multi-site diffusion tensor imaging data. NeuroImage. 2017;161:149–70.
Sui YV, McKenna F, Bertisch H, Storey P, Anthopolos R, Goff DC, et al. Decreased basal ganglia and thalamic iron in early psychotic spectrum disorders are associated with increased psychotic and schizotypal symptoms. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:5144–53.
Winkler AM, Kochunov P, Blangero J, Almasy L, Zilles K, Fox PT, et al. Cortical thickness or grey matter volume? The importance of selecting the phenotype for imaging genetics studies. NeuroImage. 2010;53:1135–46.
Smith SM, Nichols TE. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage. 2009;44:83–98.
Mori S, Wakana S, Van Zijl PC, Nagae-Poetscher L. MRI atlas of human white matter. Elsevier; 2005.
Flynn SW, Lang DJ, Mackay AL, Goghari V, Vavasour IM, Whittall KP, et al. Abnormalities of myelination in schizophrenia detected in vivo with MRI, and post-mortem with analysis of oligodendrocyte proteins. Mol Psychiatry. 2003;8:811–20.
Vanes LD, Mouchlianitis E, Barry E, Patel K, Wong K, Shergill SS. Cognitive correlates of abnormal myelination in psychosis. Sci Rep. 2019;9:5162.
Karlsgodt KH, van Erp TG, Poldrack RA, Bearden CE, Nuechterlein KH, Cannon TD. Diffusion tensor imaging of the superior longitudinal fasciculus and working memory in recent-onset schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:512–8.
Abi-Dargham A. Schizophrenia: overview and dopamine dysfunction. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75:e31.
Fields RD. A new mechanism of nervous system plasticity: activity-dependent myelination. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015;16:756–67.
Kaiser T, Allen HM, Kwon O, Barak B, Wang J, He Z, et al. MyelTracer: a semi-automated software for myelin g-ratio quantification. eNeuro 2021;8:ENEURO.0558-20.2021.
Grier MD, West KL, Kelm ND, Fu C, Does MD, Parker B, et al. Loss of mTORC2 signaling in oligodendrocyte precursor cells delays myelination. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0188417.
Golestani AM, Miles L, Babb J, Castellanos FX, Malaspina D, Lazar M. Constrained by our connections: white matter’s key role in interindividual variability in visual working memory capacity. J Neurosci. 2014;34:14913–8.
Paus T, Toro R. Could sex differences in white matter be explained by g ratio? Front Neuroanat. 2009;3:14.
Basu K, Appukuttan S, Manchanda R, Sik A. Difference in axon diameter and myelin thickness between excitatory and inhibitory callosally projecting axons in mice. Cereb Cortex. 2023;33:4101–15.
Son S, Kubota M, Miyata J, Fukuyama H, Aso T, Urayama S, et al. Creativity and positive symptoms in schizophrenia revisited: structural connectivity analysis with diffusion tensor imaging. Schizophr Res. 2015;164:221–6.
Kochunov P, Hong LE, Dennis EL, Morey RA, Tate DF, Wilde EA, et al. ENIGMA-DTI: translating reproducible white matter deficits into personalized vulnerability metrics in cross-diagnostic psychiatric research. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022;43:194–206.
Zeng B, Ardekani BA, Tang Y, Zhang T, Zhao S, Cui H, et al. Abnormal white matter microstructure in drug-naive first episode schizophrenia patients before and after eight weeks of antipsychotic treatment. Schizophr Res. 2016;172:1–8.
Tomyshev AS, Lebedeva IS, Akhadov TA, Omelchenko MA, Rumyantsev AO, Kaleda VG. Alterations in white matter microstructure and cortical thickness in individuals at ultra-high risk of psychosis: a multimodal tractography and surface-based morphometry study. Psychiatry Res: Neuroimaging. 2019;289:26–36.
Cropley VL, Klauser P, Lenroot RK, Bruggemann J, Sundram S, Bousman C, et al. Accelerated gray and white matter deterioration with age in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174:286–95.
Gouvea-Junqueira D, Falvella ACB, Antunes A, Seabra G, Brandao-Teles C, Martins-de-Souza D, et al. Novel treatment strategies targeting myelin and oligodendrocyte dysfunction in schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:379.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01MH108962 to ML and R01EB027087 to AS) and the Radiology Department at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine. We acknowledge Dr. Pippa Storey for providing the magnetization transfer imaging sequence for this study. We thank Research Match and NAMI for supporting our recruitment efforts, and we extend our sincere gratitude to our participants for their contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was conceptualized by YVS and ML. Recruitment of participants and clinical assessment were conducted with the help of HB and DCG. AS provided expertise in MRI pulse sequence and quantitative parametric mapping. Imaging data acquisition and processing, and statistical analysis were performed by YVS and ML. YVS drafted the original manuscript, with all coauthors involved in manuscript review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the NYU Grossman School of Medicine. All participants provided written informed consent and were given a full explanation of the research protocol before being enrolled in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sui, Y.V., Bertisch, H., Goff, D.C. et al. Quantitative magnetization transfer and g-ratio imaging of white matter myelin in early psychotic spectrum disorders. Mol Psychiatry 30, 2739–2747 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-024-02883-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-024-02883-0