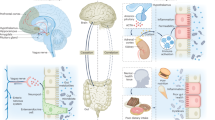
Abstract
Major depressive disorder is a debilitating mental illness that seriously endangers human health. Its pathogenesis is highly complex, and traditional treatments face substantial challenges. A growing body of preclinical and clinical findings highlight the important role of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis of depression and its potential as a diagnostic and therapeutic target. A deeper understanding of how the gut microbiome regulates depression will greatly enhance its clinical application, improve diagnostic and treatment strategies, and pave the way for microbiota-based precision medicine for depression. In this review, we summarize the depression-associated compositional and functional microbial alterations, delineate their mechanistic contributions to disease pathogenesis, and evaluate their potentiality as novel diagnostic biomarkers and treatment targets. Finally, we consider the future potential of utilizing the gut microbiome to advance precision medicine approaches for depression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mayer EA, Craske M, Naliboff BD. Depression, anxiety, and the gastrointestinal system. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62:28–36.
Diaz Heijtz R, Wang S, Anuar F, Qian Y, Björkholm B, Samuelsson A, et al. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:3047–52.
Neufeld KM, Kang N, Bienenstock J, Foster JA. Reduced anxiety-like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ-free mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011;23:255–64.e119.
Bercik P, Denou E, Collins J, Jackson W, Lu J, Jury J, et al. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:599–609. 609.e1-3
Cryan JF, Dinan TG. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:701–12.
Gheorghe CE, Cryan JF, Clarke G. Debugging the gut-brain axis in depression. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30:281–3.
Jiang H, Ling Z, Zhang Y, Mao H, Ma Z, Yin Y, et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav Immun. 2015;48:186–94.
Zheng P, Zeng B, Zhou C, Liu M, Fang Z, Xu X, et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:786–96.
Kelly JR, Borre Y, O’ Brien C, Patterson E, El Aidy S, Deane J, et al. Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;82:109–18.
Bosch JA, Nieuwdorp M, Zwinderman AH, Deschasaux M, Radjabzadeh D, Kraaij R, et al. The gut microbiota and depressive symptoms across ethnic groups. Nat Commun. 2022;13:7129.
Zhernakova A, Kurilshikov A, Bonder MJ, Tigchelaar EF, Schirmer M, Vatanen T, et al. Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity. Science. 2016;352:565–9.
Yang J, Zheng P, Li Y, Wu J, Tan X, Zhou J, et al. Landscapes of bacterial and metabolic signatures and their interaction in major depressive disorders. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eaba8555.
Valles-Colomer M, Falony G, Darzi Y, Tigchelaar EF, Wang J, Tito RY, et al. The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4:623–32.
Radjabzadeh D, Bosch JA, Uitterlinden AG, Zwinderman AH, Ikram MA, van Meurs JBJ, et al. Gut microbiome-wide association study of depressive symptoms. Nat Commun. 2022;13:7128.
Van Hul M, Cani PD, Petitfils C, De Vos WM, Tilg H, El-Omar EM. What defines a healthy gut microbiome? Gut. 2024;73:1893–908.
Joos R, Boucher K, Lavelle A, Arumugam M, Blaser MJ, Claesson MJ, et al. Examining the healthy human microbiome concept. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2025;23:192–205.
Liu L, Wang H, Zhang H, Chen X, Zhang Y, Wu J, et al. Toward a deeper understanding of gut microbiome in depression: the promise of clinical applicability. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9:e2203707.
Liu L, Wang H, Chen X, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Xie P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: from pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine. 2023;90:104527.
Simpson CA, Diaz-Arteche C, Eliby D, Schwartz OS, Simmons JG, Cowan CSM. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression - A systematic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;83:101943.
Nikolova VL, Smith MRB, Hall LJ, Cleare AJ, Stone JM, Young AH. Perturbations in Gut Microbiota Composition in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:1343–54.
Mirzayi C, Renson A, Zohra F, Elsafoury S, Geistlinger L, Kasselman LJ, et al. Reporting guidelines for human microbiome research: the STORMS checklist. Nat Med. 2021;27:1885–92.
Li D, Liu R, Wang M, Peng R, Fu S, Fu A, et al. 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase expressed by gut microbes degrades testosterone and is linked to depression in males. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30:329–339.e5.
Li D, Sun T, Tong Y, Le J, Yao Q, Tao J, et al. Gut-microbiome-expressed 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase degrades estradiol and is linked to depression in premenopausal females. Cell Metab. 2023;35:685–694.e5.
Qin Y, Havulinna AS, Liu Y, Jousilahti P, Ritchie SC, Tokolyi A, et al. Combined effects of host genetics and diet on human gut microbiota and incident disease in a single population cohort. Nat Genet. 2022;54:134–42.
Bang S, Shin YH, Park SM, Deng L, Williamson RT, Graham DB, et al. Unusual phospholipids from morganella morganii linked to depression. J Am Chem Soc. 2025;147:2998–3002.
Ahmed H, Leyrolle Q, Koistinen V, Kärkkäinen O, Layé S, Delzenne N, et al. Microbiota-derived metabolites as drivers of gut-brain communication. Gut Microbes. 2022;14:2102878.
Averina OV, Zorkina YA, Yunes RA, Kovtun AS, Ushakova VM, Morozova AY, et al. Bacterial metabolites of human gut microbiota correlating with depression. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:9234.
Cheng J, Hu H, Ju Y, Liu J, Wang M, Liu B, et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and depression: deep insight into biological mechanisms and potential applications. Gen Psychiatr. 2024;37:e101374.
Skonieczna-Żydecka K, Grochans E, Maciejewska D, Szkup M, Schneider-Matyka D, Jurczak A, et al. Faecal short chain fatty acids profile is changed in polish depressive women. Nutrients. 2018;10:1939.
Louis P, Duncan SH, Sheridan PO, Walker AW, Flint HJ. Microbial lactate utilisation and the stability of the gut microbiome. Gut Microbiome. 2022;3:e3.
Zhang K, Fujita Y, Chang L, Qu Y, Pu Y, Wang S, et al. Abnormal composition of gut microbiota is associated with resilience versus susceptibility to inescapable electric stress. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9:231.
Ernst J, Hock A, Henning A, Seifritz E, Boeker H, Grimm S. Increased pregenual anterior cingulate glucose and lactate concentrations in major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:113–9.
Bai S, Xie J, Bai H, Tian T, Zou T, Chen JJ. Gut microbiota-derived inflammation-related serum metabolites as potential biomarkers for major depressive disorder. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:3755–66.
MahmoudianDehkordi S, Bhattacharyya S, Brydges CR, Jia W, Fiehn O, Rush AJ, et al. Gut microbiome-linked metabolites in the pathobiology of major depression with or without Anxiety-A role for bile acids. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:937906.
Lin X, Liang W, Li L, Xiong Q, He S, Zhao J, et al. The accumulation of gut microbiome-derived indoxyl sulfate and P-Cresyl sulfate in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Ren Nutr. 2022;32:578–86.
Wang G, Fan Y, Zhang G, Cai S, Ma Y, Yang L, et al. Microbiota-derived indoles alleviate intestinal inflammation and modulate microbiome by microbial cross-feeding. Microbiome. 2024;12:59.
Brydges CR, Fiehn O, Mayberg HS, Schreiber H, Dehkordi SM, Bhattacharyya S, et al. Indoxyl sulfate, a gut microbiome-derived uremic toxin, is associated with psychic anxiety and its functional magnetic resonance imaging-based neurologic signature. Sci Rep. 2021;11:21011.
Chevalier G, Siopi E, Guenin-Macé L, Pascal M, Laval T, Rifflet A, et al. Effect of gut microbiota on depressive-like behaviors in mice is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6363.
Minichino A, Jackson MA, Francesconi M, Steves CJ, Menni C, Burnet PWJ, et al. Endocannabinoid system mediates the association between gut-microbial diversity and anhedonia/amotivation in a general population cohort. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:6269–76.
Yang B, Lin L, Bazinet RP, Chien YC, Chang JP, Satyanarayanan SK, et al. Clinical efficacy and biological regulations of ω-3 PUFA-Derived endocannabinoids in major depressive disorder. Psychother Psychosom. 2019;88:215–24.
Caspani G, Kennedy S, Foster JA, Swann J. Gut microbial metabolites in depression: understanding the biochemical mechanisms. Microb Cell. 2019;6:454–81.
Aburto MR, Cryan JF. Gastrointestinal and brain barriers: unlocking gates of communication across the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;21:222–47.
Parker A, Fonseca S, Carding SR. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes. 2020;11:135–57.
Mann ER, Lam YK, Uhlig HH. Short-chain fatty acids: linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024;24:577–95.
Braniste V, Al-Asmakh M, Kowal C, Anuar F, Abbaspour A, Tóth M, et al. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:263ra158.
Geng S, Yang L, Cheng F, Zhang Z, Li J, Liu W, et al. Gut microbiota are associated with psychological stress-induced defections in intestinal and blood-brain barriers. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:3067.
Wu H, Wang J, Teng T, Yin B, He Y, Jiang Y, et al. Biomarkers of intestinal permeability and blood-brain barrier permeability in adolescents with major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. 2023;323:659–66.
Stevens BR, Goel R, Seungbum K, Richards EM, Holbert RC, Pepine CJ, et al. Increased human intestinal barrier permeability plasma biomarkers zonulin and FABP2 correlated with plasma LPS and altered gut microbiome in anxiety or depression. Gut. 2018;67:1555–7.
Martín-Hernández D, Caso JR, Bris ÁG, Maus SR, Madrigal JL, García-Bueno B, et al. Bacterial translocation affects intracellular neuroinflammatory pathways in a depression-like model in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2016;103:122–33.
Kronsten VT, Tranah TH, Pariante C, Shawcross DL. Gut-derived systemic inflammation as a driver of depression in chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2022;76:665–80.
Tian P, Zhu H, Qian X, Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhao J, et al. Consumption of butylated starch alleviates the chronic restraint stress-induced neurobehavioral and gut barrier deficits through reshaping the gut microbiota. Front Immunol. 2021;12:755481.
Liu L, Wang H, Rao X, Yu Y, Li W, Zheng P, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the lysine acetylome and succinylome in the hippocampus of gut microbiota-dysbiosis mice. J Adv Res. 2021;30:27–38.
Wang HY, Liu LX, Chen XY, Zhang YD, Li WX, Li WW, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the gut microbiome and post-translational modifications elucidates the route involved in microbiota-host interactions. Zool Res. 2024;45:95–107.
Zheng P, Wu J, Zhang H, Perry SW, Yin B, Tan X, et al. The gut microbiome modulates gut-brain axis glycerophospholipid metabolism in a region-specific manner in a nonhuman primate model of depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:2380–92.
Deng Y, Zhou M, Wang J, Yao J, Yu J, Liu W, et al. Involvement of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in chronic restraint stress: disturbances of the kynurenine metabolic pathway in both the gut and brain. Gut Microbes. 2021;13:1–16.
Mayneris-Perxachs J, Castells-Nobau A, Arnoriaga-Rodríguez M, Martin M, de la Vega-Correa L, Zapata C, et al. Microbiota alterations in proline metabolism impact depression. Cell Metab. 2022;34:681–701.e10.
Amin N, Liu J, Bonnechere B, MahmoudianDehkordi S, Arnold M, Batra R, et al. Interplay of metabolome and gut microbiome in individuals with major depressive disorder vs control individuals. JAMA Psychiatry. 2023;80:597–609.
Sudo N. Biogenic amines: signals between commensal microbiota and gut physiology. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:504.
González-Arancibia C, Urrutia-Piñones J, Illanes-González J, Martinez-Pinto J, Sotomayor-Zárate R, Julio-Pieper M, et al. Do your gut microbes affect your brain dopamine? Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019;236:1611–22.
Yang HL, Li MM, Zhou MF, Xu HS, Huan F, Liu N, et al. Links between gut dysbiosis and neurotransmitter disturbance in chronic restraint stress-induced depressive behaviours: the role of inflammation. Inflammation. 2021;44:2448–62.
Siopi E, Galerne M, Rivagorda M, Saha S, Moigneu C, Moriceau S, et al. Gut microbiota changes require vagus nerve integrity to promote depressive-like behaviors in mice. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:3002–12.
Zhang ZW, Gao CS, Zhang H, Yang J, Wang YP, Pan LB, et al. Morinda officinalis oligosaccharides increase serotonin in the brain and ameliorate depression via promoting 5-hydroxytryptophan production in the gut microbiota. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12:3298–312.
Zhou M, Fan Y, Xu L, Yu Z, Wang S, Xu H, et al. Microbiome and tryptophan metabolomics analysis in adolescent depression: roles of the gut microbiota in the regulation of tryptophan-derived neurotransmitters and behaviors in human and mice. Microbiome. 2023;11:145.
Zhao M, Ren Z, Zhao A, Tang Y, Kuang J, Li M, et al. Gut bacteria-driven homovanillic acid alleviates depression by modulating synaptic integrity. Cell Metab. 2024;36:1000–1012.e6.
Tian P, Zou R, Wang L, Chen Y, Qian X, Zhao J, et al. Multi-Probiotics ameliorate Major depressive disorder and accompanying gastrointestinal syndromes via serotonergic system regulation. J Adv Res. 2023;45:117–25.
Strandwitz P, Kim KH, Terekhova D, Liu JK, Sharma A, Levering J, et al. GABA-modulating bacteria of the human gut microbiota. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4:396–403.
Lach G, Schellekens H, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Anxiety, depression, and the microbiome: a role for gut peptides. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15:36–59.
Worthington JJ, Reimann F, Gribble FM. Enteroendocrine cells-sensory sentinels of the intestinal environment and orchestrators of mucosal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2018;11:3–20.
Yu L, Li Y. Involvement of intestinal enteroendocrine cells in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Biomedicines. 2022;10:2577.
Joo MK, Lee JW, Woo JH, Kim HJ, Kim DH, Choi JH. Regulation of colonic neuropeptide Y expression by the gut microbiome in patients with ulcerative colitis and its association with anxiety- and depression-like behavior in mice. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2319844.
Keller J, Gomez R, Williams G, Lembke A, Lazzeroni L, Murphy GM Jr., et al. HPA axis in major depression: cortisol, clinical symptomatology and genetic variation predict cognition. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:527–36.
Vodička M, Ergang P, Hrnčíř T, Mikulecká A, Kvapilová P, Vagnerová K, et al. Microbiota affects the expression of genes involved in HPA axis regulation and local metabolism of glucocorticoids in chronic psychosocial stress. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;73:615–24.
Kuti D, Winkler Z, Horváth K, Juhász B, Paholcsek M, Stágel A, et al. Gastrointestinal (non-systemic) antibiotic rifaximin differentially affects chronic stress-induced changes in colon microbiome and gut permeability without effect on behavior. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;84:218–28.
Xu C, Lee SK, Zhang D, Frenette PS. The gut microbiome regulates psychological-stress-induced inflammation. Immunity. 2020;53:417–428.e4.
Schneider KM, Blank N, Alvarez Y, Thum K, Lundgren P, Litichevskiy L, et al. The enteric nervous system relays psychological stress to intestinal inflammation. Cell. 2023;186:2823–2838.e20.
Agirman G, Yu KB, Hsiao EY. Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis. Science. 2021;374:1087–92.
Medina-Rodriguez EM, Watson J, Reyes J, Trivedi M, Beurel E. Th17 cells sense microbiome to promote depressive-like behaviors. Microbiome. 2023;11:92.
Zhu X, Sakamoto S, Ishii C, Smith MD, Ito K, Obayashi M, et al. Dectin-1 signaling on colonic γδ T cells promotes psychosocial stress responses. Nat Immunol. 2023;24:625–36.
Westfall S, Caracci F, Zhao D, Wu QL, Frolinger T, Simon J, et al. Microbiota metabolites modulate the T helper 17 to regulatory T cell (Th17/Treg) imbalance promoting resilience to stress-induced anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;91:350–68.
Yao H, Zhang D, Yu H, Yuan H, Shen H, Lan X, et al. Gut microbiota regulates chronic ethanol exposure-induced depressive-like behavior through hippocampal NLRP3-mediated neuroinflammation. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:919–30.
Liu P, Liu Z, Wang J, Wang J, Gao M, Zhang Y, et al. Immunoregulatory role of the gut microbiota in inflammatory depression. Nat Commun. 2024;15:3003.
Huang Y, Wu J, Zhang H, Li Y, Wen L, Tan X, et al. The gut microbiome modulates the transformation of microglial subtypes. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:1611–21.
Yirmiya R, Rimmerman N, Reshef R. Depression as a microglial disease. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38:637–58.
Hao W, Ma Q, Wang L, Yuan N, Gan H, He L, et al. Gut dysbiosis induces the development of depression-like behavior through abnormal synapse pruning in microglia-mediated by complement C3. Microbiome. 2024;12:34.
He H, He H, Mo L, You Z, Zhang J. Priming of microglia with dysfunctional gut microbiota impairs hippocampal neurogenesis and fosters stress vulnerability of mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2024;115:280–94.
Wu J, Li Y, Huang Y, Liu L, Zhang H, Nagy C, et al. Integrating spatial and single-nucleus transcriptomic data elucidates microglial-specific responses in female cynomolgus macaques with depressive-like behaviors. Nat Neurosci. 2023;26:1352–64.
Agirman G, Hsiao EY. SnapShot: the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Cell. 2021;184:2524–2524.e1.
Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH, Mazmanian SK. The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell. 2016;167:915–32.
Wang S, Harvey L, Martin R, van der Beek EM, Knol J, Cryan JF, et al. Targeting the gut microbiota to influence brain development and function in early life. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;95:191–201.
Borre YE, O’Keeffe GW, Clarke G, Stanton C, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol Med. 2014;20:509–18.
Liu G, Yu Q, Tan B, Ke X, Zhang C, Li H, et al. Gut dysbiosis impairs hippocampal plasticity and behaviors by remodeling serum metabolome. Gut Microbes. 2022;14:2104089.
Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Sandhu K, Peterson V, Dinan TG. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:179–94.
Lynch CMK, Cowan CSM, Bastiaanssen TFS, Moloney GM, Theune N, van de Wouw M, et al. Critical windows of early-life microbiota disruption on behaviour, neuroimmune function, and neurodevelopment. Brain Behav Immun. 2023;108:309–27.
Keogh CE, Kim DHJ, Pusceddu MM, Knotts TA, Rabasa G, Sladek JA, et al. Myelin as a regulator of development of the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;91:437–50.
Hagan CC, Graham JM, Wilkinson PO, Midgley N, Suckling J, Sahakian BJ, et al. Neurodevelopment and ages of onset in depressive disorders. Lancet Psychiatry. 2015;2:1112–6.
Liu L, Wang H, Chen X, Zhang Y, Li W, Rao X, et al. Integrative analysis of long Non-coding RNAs, Messenger RNAs, and MicroRNAs indicates the neurodevelopmental dysfunction in the hippocampus of gut microbiota-dysbiosis mice. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:745437.
De Santa F, Strimpakos G, Marchetti N, Gargari G, Torcinaro A, Arioli S, et al. Effect of a multi-strain probiotic mixture consumption on anxiety and depression symptoms induced in adult mice by postnatal maternal separation. Microbiome. 2024;12:29.
Lu J, Zhang Z, Yin X, Tang Y, Ji R, Chen H, et al. An entorhinal-visual cortical circuit regulates depression-like behaviors. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:3807–20.
Li XY, Zhang SY, Hong YZ, Chen ZG, Long Y, Yuan DH, et al. TGR5-mediated lateral hypothalamus-dCA3-dorsolateral septum circuit regulates depressive-like behavior in male mice. Neuron. 2024;112:1795–1814.e10.
Yuan Z, Qi Z, Wang R, Cui Y, An S, Wu G, et al. A corticoamygdalar pathway controls reward devaluation and depression using dynamic inhibition code. Neuron. 2023;111:3837–3853.e5.
Zheng Z, Guo C, Li M, Yang L, Liu P, Zhang X, et al. Hypothalamus-habenula potentiation encodes chronic stress experience and drives depression onset. Neuron. 2022;110:1400–1415.e6.
Schaub AC, Schneider E, Vazquez-Castellanos JF, Schweinfurth N, Kettelhack C, Doll JPK, et al. Clinical, gut microbial and neural effects of a probiotic add-on therapy in depressed patients: a randomized controlled trial. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12:227.
Yamanbaeva G, Schaub AC, Schneider E, Schweinfurth N, Kettelhack C, Doll JPK, et al. Effects of a probiotic add-on treatment on fronto-limbic brain structure, function, and perfusion in depression: secondary neuroimaging findings of a randomized controlled trial. J Affect Disord. 2023;324:529–38.
Pinto-Sanchez MI, Hall GB, Ghajar K, Nardelli A, Bolino C, Lau JT, et al. Probiotic bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 reduces depression scores and alters brain activity: a pilot study in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:448–459.e8.
Kaelberer MM, Buchanan KL, Klein ME, Barth BB, Montoya MM, Shen X, et al. A gut-brain neural circuit for nutrient sensory transduction. Science. 2018;361:eaat5236.
Kaelberer MM, Rupprecht LE, Liu WW, Weng P, Bohórquez DV. Neuropod cells: the emerging biology of gut-brain sensory transduction. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2020;43:337–53.
Sahasrabudhe A, Rupprecht LE, Orguc S, Khudiyev T, Tanaka T, Sands J, et al. Multifunctional microelectronic fibers enable wireless modulation of gut and brain neural circuits. Nat Biotechnol. 2024;42:892–904.
Han W, Tellez LA, Perkins MH, Perez IO, Qu T, Ferreira J, et al. A neural circuit for gut-induced reward. Cell. 2018;175:665–678.e23.
Zheng P, Yang J, Li Y, Wu J, Liang W, Yin B, et al. Gut microbial signatures can discriminate unipolar from bipolar depression. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7:1902862.
Zhao H, Jin K, Jiang C, Pan F, Wu J, Luan H, et al. A pilot exploration of multi-omics research of gut microbiome in major depressive disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12:8.
Xie P, Zhou X, Li Y, Wu J, Zhang H, Huang Y, et al. Gut microbial CAZymes markers for depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2024;14:135.
Gihawi A, Ge Y, Lu J, Puiu D, Xu A, Cooper CS, et al. Major data analysis errors invalidate cancer microbiome findings. mBio. 2023;14:e0160723.
Hoffmann DE, von Rosenvinge EC, Roghmann MC, Palumbo FB, McDonald D, Ravel J. The DTC microbiome testing industry needs more regulation. Science. 2024;383:1176–9.
Porcari S, Mullish BH, Asnicar F, Ng SC, Zhao L, Hansen R, et al. International consensus statement on microbiome testing in clinical practice. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;10:154–67.
Wang Y, Zhang S, Borody TJ, Zhang F. Encyclopedia of fecal microbiota transplantation: a review of effectiveness in the treatment of 85 diseases. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135:1927–39.
Lin H, Guo Q, Wen Z, Tan S, Chen J, Lin L, et al. The multiple effects of fecal microbiota transplantation on diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) patients with anxiety and depression behaviors. Microb Cell Fact. 2021;20:233.
Guo Q, Lin H, Chen P, Tan S, Wen Z, Lin L, et al. Dynamic changes of intestinal flora in patients with irritable bowel syndrome combined with anxiety and depression after oral administration of enterobacteria capsules. Bioengineered. 2021;12:11885–97.
Green JE, Berk M, Mohebbi M, Loughman A, McGuinness AJ, Castle D, et al. Feasibility, acceptability, and safety of faecal microbiota transplantation in the treatment of major depressive disorder: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Can J Psychiatry. 2023;68:315–26.
Yu Y, Wang W, Zhang F. The next generation fecal microbiota transplantation: to transplant bacteria or virome. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10:e2301097.
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11:506–14.
Akkasheh G, Kashani-Poor Z, Tajabadi-Ebrahimi M, Jafari P, Akbari H, Taghizadeh M, et al. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in patients with major depressive disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition. 2016;32:315–20.
Kazemi A, Noorbala AA, Azam K, Eskandari MH, Djafarian K. Effect of probiotic and prebiotic vs placebo on psychological outcomes in patients with major depressive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr. 2019;38:522–8.
Slykerman RF, Hood F, Wickens K, Thompson JMD, Barthow C, Murphy R, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 in Pregnancy on Postpartum Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety: A Randomised Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. EBioMedicine. 2017;24:159–65.
Tian P, Chen Y, Zhu H, Wang L, Qian X, Zou R, et al. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 attenuates major depression disorder via regulating gut microbiome and tryptophan metabolism: A randomized clinical trial. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;100:233–41.
Zhang X, Chen S, Zhang M, Ren F, Ren Y, Li Y, et al. Effects of fermented milk containing lacticaseibacillus paracasei strain shirota on constipation in patients with depression: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients. 2021;13:2238.
Kreuzer K, Reiter A, Birkl-Töglhofer AM, Dalkner N, Mörkl S, Mairinger M, et al. The PROVIT study-effects of multispecies probiotic add-on treatment on metabolomics in major depressive disorder-a randomized, Placebo-controlled trial. Metabolites. 2022;12:770.
Bambling M, Edwards SC, Hall S, Vitetta L. A combination of probiotics and magnesium orotate attenuate depression in a small SSRI resistant cohort: an intestinal anti-inflammatory response is suggested. Inflammopharmacology. 2017;25:271–4.
Nikolova VL, Cleare AJ, Young AH, Stone JM. Acceptability, tolerability, and estimates of putative treatment effects of probiotics as adjunctive treatment in patients with depression: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2023;80:842–7.
Miyaoka T, Kanayama M, Wake R, Hashioka S, Hayashida M, Nagahama M, et al. Clostridium butyricum MIYAIRI 588 as adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder: a prospective open-label trial. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2018;41:151–5.
Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:491–502.
Burokas A, Arboleya S, Moloney RD, Peterson VL, Murphy K, Clarke G, et al. Targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis: prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82:472–87.
Chi L, Khan I, Lin Z, Zhang J, Lee MYS, Leong W, et al. Fructo-oligosaccharides from Morinda officinalis remodeled gut microbiota and alleviated depression features in a stress rat model. Phytomedicine. 2020;67:153157.
Liu Z, Li L, Ma S, Ye J, Zhang H, Li Y, et al. High-Dietary fiber intake alleviates antenatal obesity-induced postpartum depression: roles of gut microbiota and microbial metabolite short-chain fatty acid involved. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68:13697–710.
Heidarzadeh-Rad N, Gökmen-Özel H, Kazemi A, Almasi N, Djafarian K. Effects of a psychobiotic supplement on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in depressive patients: a Post Hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;26:486–95.
Alli SR, Gorbovskaya I, Liu JCW, Kolla NJ, Brown L, Müller DJ. The gut microbiome in depression and potential benefit of prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics: a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:4494.
Swanson KS, Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Reimer RA, Reid G, Verbeke K, et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of synbiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17:687–701.
Dinan TG, Stanton C, Long-Smith C, Kennedy P, Cryan JF, Cowan CSM, et al. Feeding melancholic microbes: MyNewGut recommendations on diet and mood. Clin Nutr. 2019;38:1995–2001.
Aslam H, Lotfaliany M, So D, Berding K, Berk M, Rocks T, et al. Fiber intake and fiber intervention in depression and anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev 2023, https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuad143.
Salminen S, Collado MC, Endo A, Hill C, Lebeer S, Quigley EMM, et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:649–67.
Zhang K, Chen L, Yang J, Liu J, Li J, Liu Y, et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids ameliorate methamphetamine-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in a Sigmar-1 receptor-dependent manner. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13:4801–22.
Chen Y, Tian P, Wang Z, Pan R, Shang K, Wang G, et al. Indole Acetic Acid Exerts Anti-Depressive Effects on an Animal Model of Chronic Mild Stress. Nutrients. 2022;14:5019.
Cheng L, Wu H, Cai X, Zhang Y, Yu S, Hou Y, et al. A Gpr35-tuned gut microbe-brain metabolic axis regulates depressive-like behavior. Cell Host Microbe. 2024;32:227–243.e6.
Braga JD, Thongngam M, Kumrungsee T. Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a potential postbiotic mediator in the gut-brain axis. NPJ Sci Food. 2024;8:16.
Yu M, Jia HM, Qin LL, Zou ZM. Gut microbiota and gut tissue metabolites involved in development and prevention of depression. J Affect Disord. 2022;297:8–17.
Meng C, Feng S, Hao Z, Dong C, Liu H. Antibiotics exposure attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced anxiety-like and depression-like behavior. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2022;136:105620.
Wong ML, Inserra A, Lewis MD, Mastronardi CA, Leong L, Choo J, et al. Inflammasome signaling affects anxiety- and depressive-like behavior and gut microbiome composition. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:797–805.
Schmidtner AK, Slattery DA, Gläsner J, Hiergeist A, Gryksa K, Malik VA, et al. Minocycline alters behavior, microglia and the gut microbiome in a trait-anxiety-dependent manner. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9:223.
Lee J, Park SJ, Choi S, Chang J, Park YJ, Jeong S, et al. Antibiotic exposure and depression incidence: a cohort study of the Korean population. Psychiatry Res. 2024;339:115992.
Fishbein SRS, Mahmud B, Dantas G. Antibiotic perturbations to the gut microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;21:772–88.
Gómez-Ochoa SA, Pitton M, Valente LG, Sosa Vesga CD, Largo J, Quiroga-Centeno AC, et al. Efficacy of phage therapy in preclinical models of bacterial infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe. 2022;3:e956–e968.
Federici S, Kredo-Russo S, Valdés-Mas R, Kviatcovsky D, Weinstock E, Matiuhin Y, et al. Targeted suppression of human IBD-associated gut microbiota commensals by phage consortia for treatment of intestinal inflammation. Cell. 2022;185:2879–2898.e24.
Pirnay JP, Djebara S, Steurs G, Griselain J, Cochez C, De Soir S, et al. Personalized bacteriophage therapy outcomes for 100 consecutive cases: a multicentre, multinational, retrospective observational study. Nat Microbiol. 2024;9:1434–53.
Li Y, Zhu F, Li Y, Pan S, Wang H, Yang Z, et al. Bacteriophages allow selective depletion of gut bacteria to produce a targeted-bacterium-depleted mouse model. Cell Rep Methods. 2022;2:100324.
Drevets WC, Wittenberg GM, Bullmore ET, Manji HK. Immune targets for therapeutic development in depression: towards precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;21:224–44.
Zuo Z, Zhao F. Gut microbiota-targeted interventions: from conventional approaches to genetic engineering. Sci Bull (Beijing). 2023;68:1231–4.
Riglar DT, Silver PA. Engineering bacteria for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018;16:214–25.
Sanmarco LM, Rone JM, Polonio CM, Fernandez Lahore G, Giovannoni F, Ferrara K, et al. Lactate limits CNS autoimmunity by stabilizing HIF-1α in dendritic cells. Nature. 2023;620:881–9.
Wang S, Zhou X, Ma Y, Zhang S, Gong X, Zhang B, et al. Gut-to-brain neuromodulation by synthetic butyrate-producing commensal bacteria. The Innovation Life. 2024;2:100082.
McCoubrey LE, Elbadawi M, Basit AW. Current clinical translation of microbiome medicines. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43:281–92.
Luo Y, Kataoka Y, Ostinelli EG, Cipriani A, Furukawa TA. National prescription patterns of antidepressants in the treatment of adults with major depression in the US between 1996 and 2015: a population representative survey based analysis. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:35.
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1905–17.
Minichino A, Preston T, Fanshawe JB, Fusar-Poli P, McGuire P, Burnet PWJ, et al. Psycho-Pharmacomicrobiomics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry. 2024;95:611–28.
Brown LC, Bobo WV, Gall CA, Müller DJ, Bousman CA. Pharmacomicrobiomics of antidepressants in depression: a systematic review. J Pers Med. 2023;13:1086.
Xu F, Xie Q, Kuang W, Dong Z. Interactions between antidepressants and intestinal microbiota. Neurotherapeutics. 2023;20:359–71.
Michaelis L, Berg L, Maier L. Confounder or Confederate? the interactions between drugs and the gut microbiome in psychiatric and neurological diseases. Biol Psychiatry. 2024;95:361–9.
Yang Y, Zhao S, Yang X, Li W, Si J, Yang X. The antidepressant potential of lactobacillus casei in the postpartum depression rat model mediated by the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neurosci Lett. 2022;774:136474.
Li Q, Li L, Niu X, Tang C, Wang H, Gao J, et al. Probiotics alleviate depressive behavior in chronic unpredictable mild stress rat models by remodeling intestinal flora. Neuroreport. 2021;32:686–93.
Huang M, He Y, Tian L, Yu L, Cheng Q, Li Z, et al. Gut microbiota-SCFAs-brain axis associated with the antidepressant activity of berberine in CUMS rats. J Affect Disord. 2023;325:141–50.
Zhou Z, Wang Y, Sun S, Zhang K, Wang L, Zhao H, et al. Paeonia lactiflora Pall. Polysaccharide alleviates depression in CUMS mice by inhibiting the NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 signaling pathway and affecting the composition of their intestinal flora. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;316:116716.
Zhang M, Li A, Yang Q, Li J, Zheng L, Wang G, et al. Matrine alleviates depressive-like behaviors via modulating microbiota-gut-brain axis in CUMS-induced mice. J Transl Med. 2023;21:145.
Ait Chait Y, Mottawea W, Tompkins TA, Hammami R. Unravelling the antimicrobial action of antidepressants on gut commensal microbes. Sci Rep. 2020;10:17878.
Rukavishnikov G, Leonova L, Kasyanov E, Leonov V, Neznanov N, Mazo G. Antimicrobial activity of antidepressants on normal gut microbiota: Results of the in vitro study. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023;17:1132127.
Klünemann M, Andrejev S, Blasche S, Mateus A, Phapale P, Devendran S, et al. Bioaccumulation of therapeutic drugs by human gut bacteria. Nature. 2021;597:533–8.
Wilson TJ, Blackledge MS, Vigueira PA. Resensitization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by amoxapine, an FDA-approved antidepressant. Heliyon. 2018;4:e00501.
Ye X, Wang D, Zhu H, Wang D, Li J, Tang Y, et al. Gut microbiota changes in patients with major depressive disorder treated with vortioxetine. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:641491.
Lee SM, Dong TS, Krause-Sorio B, Siddarth P, Milillo MM, Lagishetty V, et al. The intestinal microbiota as a predictor for antidepressant treatment outcome in geriatric depression: a prospective pilot study. Int Psychogeriatr. 2022;34:33–45.
Zhang L, Liu YX, Wang Z, Wang XQ, Zhang JJ, Jiang RH, et al. Clinical characteristic and fecal microbiota responses to probiotic or antidepressant in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome with depression comorbidity: a pilot study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132:346–51.
Wang Y, Zhou J, Ye J, Sun Z, He Y, Zhao Y, et al. Multi-omics reveal microbial determinants impacting the treatment outcome of antidepressants in major depressive disorder. Microbiome. 2023;11:195.
Shen Y, Yang X, Li G, Gao J, Liang Y. The change of gut microbiota in MDD patients under SSRIs treatment. Sci Rep. 2021;11:14918.
Tomizawa Y, Kurokawa S, Ishii D, Miyaho K, Ishii C, Sanada K, et al. Effects of psychotropics on the microbiome in patients with depression and anxiety: considerations in a naturalistic clinical setting. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021;24:97–107.
Wang Y, Yu Z, Ding P, Lu J, Mao L, Ngiam L, et al. Antidepressants can induce mutation and enhance persistence toward multiple antibiotics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2023;120:e2208344120.
Hategan A, Bourgeois JA. Proposed antidepressant-associated antimicrobial resistance: a function of the illness, its treatment, or both? J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2023;43:392–3.
Dong Z, Shen X, Hao Y, Li J, Xu H, Yin L, et al. Gut microbiome: a potential indicator for predicting treatment outcomes in major depressive disorder. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:813075.
Clark AM, Clinton RT, Baker JK, Hufford CD. Demethylation of imipramine by enteric bacteria. J Pharm Sci. 1983;72:1288–90.
Zimmermann M, Zimmermann-Kogadeeva M, Wegmann R, Goodman AL. Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019;570:462–7.
Javdan B, Lopez JG, Chankhamjon P, Lee YJ, Hull R, Wu Q, et al. Personalized mapping of drug metabolism by the human gut microbiome. Cell. 2020;181:1661–1679.e22.
Zhu B, Xu Y, Zhao P, Yiu SM, Yu H, Shi JY. NNAN: nearest neighbor attention network to predict drug-microbe associations. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:846915.
Selwyn FP, Cui JY, Klaassen CD. RNA-Seq quantification of hepatic drug processing genes in germ-free mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015;43:1572–80.
Chen L, Wang D, Garmaeva S, Kurilshikov A, Vich Vila A, Gacesa R, et al. The long-term genetic stability and individual specificity of the human gut microbiome. Cell. 2021;184:2302–2315.e12.
Ratiner K, Ciocan D, Abdeen SK, Elinav E. Utilization of the microbiome in personalized medicine. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024;22:291–308.
Zhao Q, Chen Y, Huang W, Zhou H, Zhang W. Drug-microbiota interactions: an emerging priority for precision medicine. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:386.
Poirot MG, Ruhe HG, Mutsaerts HMM, Maximov II, Groote IR, Bjørnerud A, et al. Treatment Response Prediction in Major Depressive Disorder Using Multimodal MRI and Clinical Data: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2024;181:223–33.
Gaisser KD, Skloss SN, Brettner LM, Paleologu L, Roco CM, Rosenberg AB, et al. High-throughput single-cell transcriptomics of bacteria using combinatorial barcoding. Nat Protoc 2024, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-024-01007-w.
Lan F, Saba J, Ross TD, Zhou Z, Krauska K, Anantharaman K, et al. Massively parallel single-cell sequencing of diverse microbial populations. Nat Methods. 2024;21:228–35.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation Project of China (82201683, 82401814 and 82401789), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTB2024NSCQ-MSX0649), and the Joint Project of Chongqing Municipal Science and Technology Bureau and Chongqing Health Commission (2023CCXM003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LXL, HYW, and PX conceived the idea for the review. SFL, LW, XLM, QSC, and RX searched the literature and extracted relevant information. LXL, YMD, and DH designed and prepared the figures and tables. LXL and HYW originally drafted the manuscript. SYG and HPZ reviewed the original draft and provided feedback to further improve the manuscript. LXL, HYW, HPZ, and PX acquired the funding. All authors reviewed the final version of the manuscript and approved the submission in its present form.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Wang, H., Guo, S. et al. The emerging role of the gut microbiome in depression: implications for precision medicine. Mol Psychiatry 30, 5901–5913 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03191-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03191-x