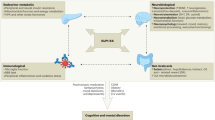
Abstract
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a chronic and disabling psychiatric illness characterized by complex pathophysiological mechanisms. Traditional treatments often fail to address these multidimensional processes, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic strategies. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), widely used for metabolic disorders, have emerged as promising candidates for a range of neuropsychiatric conditions due to their broad neurobiological effects. This narrative review synthesizes preclinical, clinical, and real-world evidence evaluating the therapeutic potential of GLP-1RAs in BD. These agents modulate neurotransmission, reduce neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, enhance mitochondrial and neurotrophic function, and improve insulin sensitivity and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis regulation. These mechanisms are implicated in the neurobiology of BD, and preliminary findings suggest benefits across core psychopathological domains and common comorbidities, including depression, anxiety, mania, cognitive dysfunction, weight gain, and substance use disorders. While human data—particularly in BD populations—remain limited, evidence points to potential adjunctive benefits, especially in individuals with metabolic or cognitive vulnerabilities. Given their pleiotropic actions and established safety profile, GLP-1RAs represent compelling candidates for drug repurposing in BD. Well-powered, controlled trials are needed to confirm efficacy and safety, identify optimal subgroups, and evaluate long-term outcomes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McIntyre RS, Berk M, Brietzke E, Goldstein BI, López-Jaramillo C, Kessing LV, et al. Bipolar disorders. Lancet. 2020;396:1841–56.
Oliva V, Fico G, De Prisco M, Gonda X, Rosa AR, Vieta E. Bipolar disorders: an update on critical aspects. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024;48:101135.
Léda-Rêgo G, Studart-Bottó P, Abbade P, Rabelo-Da-Ponte FD, Casqueiro JS, Sarmento S, et al. Lifetime prevalence of psychiatric comorbidities in patients with bipolar disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2024;337:115953.
Liu YK, Ling S, Lui LMW, Ceban F, Vinberg M, Kessing LV, et al. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, impaired fasting glucose, general obesity, and abdominal obesity in patients with bipolar disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2022;300:449–61.
Jawad MY, Meshkat S, Tabassum A, McKenzie A, Di Vincenzo JD, Guo Z, et al. The bidirectional association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 2023;28:541–60.
McIntyre RS, Alda M, Baldessarini RJ, Bauer M, Berk M, Correll CU, et al. The clinical characterization of the adult patient with bipolar disorder aimed at personalization of management. World Psychiatry. 2022;21:364–87.
Robinson N, Bergen SE. Environmental risk factors for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder and their relationship to genetic risk: current knowledge and future directions. Front Genet. 2021;12:686666.
Poletti S, Mazza MG, Benedetti F. Inflammatory mediators in major depression and bipolar disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2024;14:247.
Giménez-Palomo A, Guitart-Mampel M, Meseguer A, Borràs R, García-García FJ, Tobías E, et al. Reduced mitochondrial respiratory capacity in patients with acute episodes of bipolar disorder: could bipolar disorder be a state-dependent mitochondrial disease? Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2024;149:52–64.
Belvederi Murri M, Prestia D, Mondelli V, Pariante C, Patti S, Olivieri B, et al. The HPA axis in bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016;63:327–42.
Calkin CV. Insulin resistance takes center stage: a new paradigm in the progression of bipolar disorder. Ann Med. 2019;51:281.
Nierenberg AA, Agustini B, Köhler-Forsberg O, Cusin C, Katz D, Sylvia LG, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder: a review. JAMA. 2023;330:1370–80.
McIntyre RS, Kwan ATH, Rosenblat JD, Teopiz KM, Mansur RB. Psychotropic drug–related weight gain and its treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 2024;181:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.20230922.
Drucker DJ. The GLP-1 journey: from discovery science to therapeutic impact. J Clin Invest. 2024;134:e175634.
Committee ADAPP, ElSayed NA, McCoy RG, Aleppo G, Bajaj M, Balapattabi K, et al. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of care in diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care. 2025;48:S181–S206.
McIntyre RS, Rasgon N, Goldberg JF, Wong S, Le GH, Mansur RB, et al. The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists on neurogenesis, differentiation, and plasticity (Neuro-GDP): potential mechanistically informed therapeutics in the treatment and prevention of mental disorders. CNS Spectr. 2025;30:e23.
Gejl M, Gjedde A, Egefjord L, Møller A, Hansen SB, Vang K, et al. In Alzheimer’s disease, 6-month treatment with GLP-1 analog prevents decline of brain glucose metabolism: randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016;8:108.
Javed D, Jajja FA, Javed A. GLP-1 receptor agonists: a revolution in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease? Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024;86:11–12.
Lee JM, Sharifi M, Oshman L, Griauzde DH, Chua KP. Dispensing of glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists to adolescents and young adults, 2020–2023. JAMA. 2024;331:2041–3.
Detka J, Głombik K. Insights into a possible role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of depression. Pharmacol Rep. 2021;73:1020–32.
Chen X, Zhao P, Wang W, Guo L, Pan Q. The antidepressant effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2024;32:117–27.
Levy B, Manove E. Functional outcome in bipolar disorder: the big picture. Depress Res Treat. 2012;2012:12.
Mcelroy SL, Guerdjikova AI, Blom TJ, Mori N, Romo-Nava F. Liraglutide in obese or overweight individuals with stable bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2024;44:89–95.
Mansur RB, Ahmed J, Cha DS, Woldeyohannes HO, Subramaniapillai M, Lovshin J, et al. Liraglutide promotes improvements in objective measures of cognitive dysfunction in individuals with mood disorders: a pilot, open-label study. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:114–20.
Cuomo A, Bolognesi S, Goracci A, Ciuoli C, Crescenzi BB, Maina G, et al. Feasibility, adherence and efficacy of liraglutide treatment in a sample of individuals with mood disorders and obesity. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:432154.
Lee SE, Lee NY, Kim SH, Kim KA, Kim YS. Effect of liraglutide 3.0 mg treatment on weight reduction in obese antipsychotic-treated patients. Psychiatry Res. 2021;299:113830.
Magioncalda P, Martino M. A unified model of the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;27:202–11.
Sandoval DA, D’Alessio DA. Physiology of proglucagon peptides: role ofglucagon and GLP-1 in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2015;95:513–48.
Cork SC, Richards JE, Holt MK, Gribble FM, Reimann F, Trapp S. Distribution and characterisation of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expressing cells in the mouse brain. Mol Metab. 2015;4:718–31.
Alvarez E, Martínez MD, Roncero I, Chowen JA, García-Cuartero B, Gispert JD, et al. The expression of GLP-1 receptor mRNA and protein allows the effect of GLP-1 on glucose metabolism in the human hypothalamus and brainstem. J Neurochem. 2005;92:798–806.
Hsu TM, Hahn JD, Konanur VR, Lam A, Kanoski SE. Hippocampal GLP-1 receptors influence food intake, meal size, and effort-based responding for food through volume transmission. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;40:327.
Zeng N, Cutts EJ, Lopez CB, Kaur S, Duran M, Virkus SA, et al. Anatomical and functional characterization of central amygdala Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expressing neurons. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021;15:724030.
van Bloemendaal L, ten Kulve JS, La Fleur SE, Ijzerman RG, Diamant M. Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 on appetite and body weight: focus on the CNS. J Endocrinol. 2014;221:T1–T16.
Kalra S, Bhattacharya S, Kapoor N. Contemporary classification of Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1RAs). Diabetes Ther. 2021;12:2133.
West J, Li M, Wong S, Le GH, Teopiz KM, Valentino K, et al. Are Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists Central Nervous System (CNS) penetrant: a narrative review. Neurol Ther. 2025;14:1157–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40120-025-00724-Y.
Hunter K, Hölscher C. Drugs developed to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci. 2012;13:33.
Au HCT, Zheng YJ, Le GH, Wong S, Teopiz KM, Kwan ATH, et al. Association of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and neurogenesis: a systematic review. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2025;37:e50.
Trujillo PharmD J, Jennifer Trujillo C. Safety and tolerability of once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020;45:43–60.
Lee JG, Woo YS, Park SW, Seog DH, Seo MK, Bahk WM. Neuromolecular etiology of bipolar disorder: possible therapeutic targets of mood stabilizers. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2022;20:228.
Owji AA, Khoshdel Z, Sanea F, Panjehshahin MR, Shojaee Fard M, Smith DM, et al. Effects of intracerebroventricular injection of glucagon like peptide-1 and its related peptides on serotonin metabolism and on levels of amino acids in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 2002;929:70–75.
Korol SV, Jin Z, Babateen O, Birnir B. GLP-1 and exendin-4 transiently enhance GABAA receptor–mediated synaptic and tonic currents in rat hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. Diabetes. 2015;64:79–89.
Rebosio C, Balbi M, Passalacqua M, Ricciarelli R, Fedele E. Presynaptic GLP-1 receptors enhance the depolarization-evoked release of glutamate and GABA in the mouse cortex and hippocampus. Biofactors. 2018;44:148–57.
Hernandez NS, Weir VR, Ragnini K, Merkel R, Zhang Y, Mace K, et al. GLP-1 receptor signaling in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus attenuates cocaine seeking by activating GABAergic circuits that project to the VTA. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:4394–408.
Anderberg RH, Anefors C, Bergquist F, Nissbrandt H, Skibicka KP. Dopamine signaling in the amygdala, increased by food ingestion and GLP-1, regulates feeding behavior. Physiol Behav. 2014;136:135–44.
Reddy IA, Pino JA, Weikop P, Osses N, Sørensen G, Bering T, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor activation regulates cocaine actions and dopamine homeostasis in the lateral septum by decreasing arachidonic acid levels. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6:809.
Fortin SM, Roitman MF. Central GLP-1 receptor activation modulates cocaine-evoked phasic dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens core. Physiol Behav. 2017;176:17–25.
Hayes MR, Schmidt HD. GLP-1 influences food and drug reward. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2016;9:66–70.
Wang XF, Liu JJ, Xia J, Liu J, Mirabella V, Pang ZP. Endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 suppresses high-fat food intake by reducing synaptic drive onto mesolimbic dopamine neurons. Cell Rep. 2015;12:726–33.
Rosenblat JD, McIntyre RS. Bipolar disorder and immune dysfunction: epidemiological findings, proposed pathophysiology and clinical implications. Brain Sci. 2017;7:144.
Sayana P, Colpo GD, Simões LR, Giridharan VV, Teixeira AL, Quevedo J, et al. A systematic review of evidence for the role of inflammatory biomarkers in bipolar patients. J Psychiatr Res. 2017;92:160–82.
Wong CK, McLean BA, Baggio LL, Koehler JA, Hammoud R, Rittig N, et al. Central glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor activation inhibits toll-like receptor agonist-induced inflammation. Cell Metab. 2024;36:130–143.e5.
Velmurugan K, Balamurugan AN, Loganathan G, Ahmad A, Hering BJ, Pugazhenthi S. Antiapoptotic actions of Exendin-4 against hypoxia and cytokines are augmented by CREB. Endocrinology. 2012;153:1116–28.
Yoon G, Kim YK, Song J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 suppresses neuroinflammation and improves neural structure. Pharmacol Res. 2020;152:104615.
Mcclean PL, Parthsarathy V, Faivre E, Holscher C. The diabetes drug liraglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2011;31:6587–94.
Alharbi SH. Anti-inflammatory role of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and its clinical implications. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024;15:20420188231222370.
Ventorp F, Bay-Richter C, Nagendra AS, Janelidze S, Matsson VS, Lipton J, et al. Exendin-4 treatment improves LPS-induced depressive-like behavior without affecting pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017;7:263–73.
Andreazza AC, Duong A, Young LT. Bipolar disorder as a mitochondrial disease. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;83:720–1.
Morris G, Walder K, Mcgee SL, Dean OM, Tye SJ, Maes M, et al. A model of the mitochondrial basis of bipolar disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017;74:1–20.
Andreazza AC, Kauer-Sant’Anna M, Frey BN, Bond DJ, Kapczinski F, Young LT, et al. Oxidative stress markers in bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2008;111:135–44.
Lichtstein D, Ilani A, Rosen H, Horesh N, Singh SV, Buzaglo N, et al. Na+, K+-ATPase signaling and bipolar disorder. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:2314.
Todorova V, Blokland A. Mitochondria and synaptic plasticity in the mature and aging nervous system. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;15:166–73.
González-García I, Gruber T, García-Cáceres C. Insulin action on astrocytes: from energy homeostasis to behaviour. J Neuroendocrinol. 2021;33:e12953.
Reiner DJ, Mietlicki-Baase EG, McGrath LE, Zimmer DJ, Bence KK, Sousa GL, et al. Astrocytes regulate GLP-1 receptor-mediated effects on energy balance. J Neurosci. 2016;36:3531–40.
Timper K, del Río-Martín A, Cremer AL, Bremser S, Alber J, Giavalisco P, et al. GLP-1 Receptor signaling in astrocytes regulates fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial integrity, and function. Cell Metab. 2020;31:1189–1205.e13.
Wang RF, Xue GF, Hölscher C, Tian MJ, Feng P, Zheng JY, et al. Post-treatment with the GLP-1 analogue liraglutide alleviate chronic inflammation and mitochondrial stress induced by status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2018;142:45–52.
He W, Wang H, Zhao C, Tian X, Li L, Wang H. Role of liraglutide in brain repair promotion through Sirt1-mediated mitochondrial improvement in stroke. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:2986–3001.
Hayes JD, Dinkova-Kostova AT. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014;39:199–218.
Thompson Ray M, Cynthia, Weickert S, Wyatt E, Webster MJ, Ray T, et al. Decreased BDNF, trkB-TK+ and GAD67 mRNA expression in the hippocampus of individuals with schizophrenia and mood disorders. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2011;36:195–203.
Huang TL, Hung YY, Te Lee C, Chen RF. Serum protein levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tropomyosin-related Kinase B in bipolar disorder: effects of mood stabilizers. Neuropsychobiology. 2012;65:65–69.
Craddock N, O’Donovan MC, Owen MJ. The genetics of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: dissecting psychosis. J Med Genet. 2005;42:193.
Valvassori SS, Resende WR, Budni J, Dal-Pont GC, Bavaresco DV, Reus GZ, et al. Sodium butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, reverses behavioral and mitochondrial alterations in animal models of depression induced by Early- or Late-life stress. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2015;12:312–20.
Jornada LK, Moretti M, Valvassori SS, Ferreira CL, Padilha PT, Arent CO, et al. Effects of mood stabilizers on hippocampus and amygdala BDNF levels in an animal model of mania induced by ouabain. J Psychiatr Res. 2010;44:506–10.
Valvassori SS, Mariot E, Varela RB, Bavaresco DV, Dal-Pont GC, Ferreira CL, et al. The role of neurotrophic factors in manic-, anxious- and depressive-like behaviors induced by amphetamine sensitization: implications to the animal model of bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. 2019;245:1106–13.
Varela RB, Valvassori SS, Lopes-Borges J, Mariot E, Dal-Pont GC, Amboni RT, et al. Sodium butyrate and mood stabilizers block ouabain-induced hyperlocomotion and increase BDNF, NGF and GDNF levels in brain of Wistar rats. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;61:114–21.
Bomba M, Granzotto A, Castelli V, Massetti N, Silvestri E, Canzoniero LMT, et al. Exenatide exerts cognitive effects by modulating the BDNF-TrkB neurotrophic axis in adult mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2018;64:33–43.
Gumuslu E, Mutlu O, Celikyurt IK, Ulak G, Akar F, Erden F, et al. Exenatide enhances cognitive performance and upregulates neurotrophic factor gene expression levels in diabetic mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2016;30:376–84.
Ji C, Xue GF, Lijun C, Feng P, Li D, Li L, et al. A novel dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist is neuroprotective in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson′s disease by increasing expression of BNDF. Brain Res. 2016;1634:1–11.
Park SW, Mansur RB, Lee Y, Lee JH, Seo MK, Choi AJ, et al. Liraglutide activates mTORC1 signaling and AMPA receptors in rat hippocampal neurons under toxic conditions. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:417341.
Bertilsson G, Patrone C, Zachrisson O, Andersson A, Dannaeus K, Heidrich J, et al. Peptide hormone exendin-4 stimulates subventricular zone neurogenesis in the adult rodent brain and induces recovery in an animal model of parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res. 2008;86:326–38.
Hamilton A, Patterson S, Porter D, Gault VA, Holscher C. Novel GLP-1 mimetics developed to treat type 2 diabetes promote progenitor cell proliferation in the brain. J Neurosci Res. 2011;89:481–9.
Song Y, Yang J, Chang M, Wei Y, Yin Z, Zhu Y, et al. Shared and distinct functional connectivity of hippocampal subregions in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:993356.
Perry A, Roberts G, Mitchell PB, Breakspear M. Connectomics of bipolar disorder: a critical review, and evidence for dynamic instabilities within interoceptive networks. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:1296–318.
Syan SK, Smith M, Frey BN, Remtulla R, Kapczinski F, Hall GBC, et al. Resting-state functional connectivity in individuals with bipolar disorder during clinical remission: a systematic review. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2018;43:298.
Au HCT, Zheng YJ, Le GH, Wong S, Phan L, Teopiz KM, et al. A systematic review in effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) mono-agonists on functional connectivity: target engagement and rationale for the development in mental disorders. J Affect Disord. 2025;370:321–7.
Watson KT, Wroolie TE, Tong G, Foland-Ross LC, Frangou S, Singh M, et al. Neural correlates of liraglutide effects in persons at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2019;356:271–8.
Juruena MF, Cleare AJ, Young AH. Neuroendocrine stress system in bipolar disorder. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2021;48:149–71.
Daban C, Vieta E, Mackin P, Young AH. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and bipolar disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2005;28:469–80.
Diz-Chaves Y, Mastoor Z, Spuch C, González-Matías LC, Mallo F. Anti-inflammatory effects of GLP-1 receptor activation in the brain in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:9583.
Gil-Lozano M, Pérez-Tilve D, Alvarez-Crespo M, Martís A, Fernandez AM, Catalina PAF, et al. GLP-1(7-36)-amide and Exendin-4 stimulate the HPA axis in rodents and humans. Endocrinology. 2010;151:2629–40.
Gil-Lozano M, Romani-́Pérez M, Outeiriño-Iglesias V, Vigo E, González-Matías LC, Brubaker PL, et al. Corticotropin-releasing hormone and the sympathoadrenal system are major mediators in the effects of peripherally administered Exendin-4 on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis of male rats. Endocrinology. 2014;155:2511–23.
Winzeler B, Da Conceição I, Refardt J, Sailer CO, Dutilh G, Christ-Crain M. Effects of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis in healthy volunteers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:202–8.
Charles EF, Lambert CG, Kerner B. Bipolar disorder and diabetes mellitus: evidence for disease-modifying effects and treatment implications. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2016;4:13.
Steardo L, Fabrazzo M, Sampogna G, Monteleone AM, D’Agostino G, Monteleone P, et al. Impaired glucose metabolism in bipolar patients and response to mood stabilizer treatments. J Affect Disord. 2019;245:174–9.
Hajek T, Calkin C, Blagdon R, Slaney C, Uher R, Alda M. Insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, and brain structure in bipolar disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39:2910–8.
Mansur RB, Delgado-Peraza F, Subramaniapillai M, Lee Y, Iacobucci M, Nasri F, et al. Exploring brain insulin resistance in adults with bipolar depression using extracellular vesicles of neuronal origin. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;133:82–92.
Van Der Heide LP, Kamal A, Artola A, Gispen WH, Ramakers GMJ. Insulin modulates hippocampal activity-dependent synaptic plasticity in a N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase-dependent manner. J Neurochem. 2005;94:1158–66.
Shah S, Iqbal M, Karam J, Salifu M, McFarlane SI. Oxidative stress, glucose metabolism, and the prevention of type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological insights. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007;9:911–29.
Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Mechanisms of disease: endothelial dysfunction in insulin resistance and diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3:46–56.
Bomfim TR, Forny-Germano L, Sathler LB, Brito-Moreira J, Houzel JC, Decker H, et al. An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease-associated Aβ oligomers. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1339–53.
Long-Smith CM, Manning S, McClean PL, Coakley MF, O’Halloran DJ, Holscher C, et al. The diabetes drug liraglutide ameliorates aberrant insulin receptor localisation and signalling in parallel with decreasing both amyloid-β plaque and glial pathology in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med. 2013;15:102–14.
Talbot K, Wang HY. The nature, significance, and glucagon-like peptide-1 analog treatment of brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 2014;10:S12–S25.
Daniele G, Iozzo P, Molina-Carrion M, Lancaster J, Ciociaro D, Cersosimo E, et al. Exenatide regulates cerebral glucose metabolism in brain areas associated with glucose homeostasis and reward system. Diabetes. 2015;64:3406–12.
Vieta E, Valentí M. Pharmacological management of bipolar depression: acute treatment, maintenance, and prophylaxis. CNS Drugs. 2013;27:515–29.
De Giorgi R, Ghenciulescu A, Dziwisz O, Taquet M, Adler AI, Koychev I, et al. An analysis on the role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in cognitive and mental health disorders. Nat Mental Health. 2025;2025:1–20.
Turan I, Sayan Ozacmak H, Ozacmak VH, Ergenc M, Bayraktaroğlu T. The effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (exenatide) on memory impairment, and anxiety- and depression-like behavior induced by REM sleep deprivation. Brain Res Bull. 2021;174:194–202.
Krass M, Volke A, Rünkorg K, Wegener G, Lund S, Abildgaard A, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists have a sustained stimulatory effect on corticosterone release after chronic treatment. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2014;27:25–32.
Weina H, Yuhu N, Christian H, Birong L, Feiyu S, Le W. Liraglutide attenuates the depressive- and anxiety-like behaviour in the corticosterone induced depression model via improving hippocampal neural plasticity. Brain Res. 2018;1694:55–62.
Bertelli PR, Mocelin R, Marcon M, Sachett A, Gomez R, Rosa AR, et al. Anti-stress effects of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide in zebrafish. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021;111:110388.
Anderberg RH, Richard JE, Hansson C, Nissbrandt H, Bergquist F, Skibicka KP. GLP-1 is both anxiogenic and antidepressant; divergent effects of acute and chronic GLP-1 on emotionality. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016;65:54–66.
Seo MK, Jeong S, Seog DH, Lee JA, Lee JH, Lee Y, et al. Effects of liraglutide on depressive behavior in a mouse depression model and cognition in the probe trial of Morris water maze test. J Affect Disord. 2023;324:8–15.
Sağlam C, Turan İ, Özaçmak HS. The effect of glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonist on behavioral despair and anxiety-like behavior in ovariectomized rats: modulation of BDNF/CREB, Nrf2 and lipocalin 2. Behav Brain Res. 2022;435:114053.
Darwish AB, El Sayed NS, Salama AAA, Saad MA. Dulaglutide impedes depressive-like behavior persuaded by chronic social defeat stress model in male C57BL/6 mice: Implications on GLP-1R and cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in the hippocampus. Life Sci. 2023;320:121546.
Ren G, Xue P, Wu B, Yang F, Wu X. Intranasal treatment of lixisenatide attenuated emotional and olfactory symptoms via CREB-mediated adult neurogenesis in mouse depression model. Aging. 2021;13:3896–908.
Aygun H. Exendin-4 increases absence-like seizures and anxiety–depression-like behaviors in WAG/Rij rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2021;123:108246.
de Souza AG, Chaves Filho AJM, Souza Oliveira JV, de Souza DAA, Lopes IS, de Carvalho MAJ, et al. Prevention of pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling and behavioral comorbidities in mice by levetiracetam combined with the GLP-1 agonist liraglutide: involvement of brain antioxidant and BDNF upregulating properties. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:429–39.
Yang F, Wang X, Qi J, Zhang K, Jiang Y, Feng B, et al. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 receptor activation inhibits microglial pyroptosis via promoting mitophagy to alleviate depression-like behaviors in diabetic mice. Nutrients. 2022;15:38.
Mansur RB, Fries GR, Trevizol AP, Subramaniapillai M, Lovshin J, Lin K, et al. The effect of body mass index on glucagon-like peptide receptor gene expression in the post mortem brain from individuals with mood and psychotic disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29:137–46.
Pozzi M, Mazhar F, Peeters GGAM, Vantaggiato C, Nobile M, Clementi E, et al. A systematic review of the antidepressant effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) functional agonists: further link between metabolism and psychopathology: special Section on “Translational and Neuroscience Studies in Affective Disorders”. J Affect Disord. 2019;257:774–8.
Bode BW, Testa MA, Magwire M, Hale PM, Hammer M, Blonde L, et al. Patient-reported outcomes following treatment with the human GLP-1 analogue liraglutide or glimepiride in monotherapy: results from a randomized controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12:604–12.
De Wit HM, Vervoort GMM, Jansen HJ, De Grauw WJC, De Galan BE, Tack CJ. Liraglutide reverses pronounced insulin-associated weight gain, improves glycaemic control and decreases insulin dose in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 26 week, randomised clinical trial (ELEGANT). Diabetologia. 2014;57:1812–9.
O’Neil PM, Aroda VR, Astrup A, Kushner R, Lau DCW, Wadden TA, et al. Neuropsychiatric safety with liraglutide 3.0 mg for weight management: results from randomized controlled phase 2 and 3a trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1529–36.
Kahal H, Kilpatrick E, Rigby A, Coady A, Atkin S. The effects of treatment with liraglutide on quality of life and depression in young obese women with PCOS and controls. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2019;35:142–5.
de Wit HM, Vervoort GM, Jansen HJ, de Galan BE, Tack CJ. Durable efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and pronounced insulin-associated weight gain: 52-week results from the Effect of Liraglutide on insulin-associated wEight GAiN in patients with Type 2 diabetes’ (ELEGANT) randomized controlled trial. J Intern Med. 2016;279:283–92.
Idris I, Abdulla H, Tilbrook S, Dean R, Ali N. Exenatide improves excessive daytime sleepiness and wakefulness in obese patients with type 2 diabetes without obstructive sleep apnoea. J Sleep Res. 2013;22:70–75.
Moulton CD, Pickup JC, Amiel SA, Winkley K, Ismail K. Investigating incretin-based therapies as a novel treatment for depression in type 2 diabetes: findings from the South London Diabetes (SOUL-D) Study. Prim Care Diabetes. 2016;10:156–9.
Tasci I, Naharci MI, Bozoglu E, Safer U, Aydogdu A, Yilmaz BF, et al. Cognitive and functional influences of vildagliptin, a DPP-4 Inhibitor, added to ongoing metformin therapy in elderly with type 2 diabetes. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2013;13:256–63.
Grant P, Lipscomb D, Quin J. Psychological and quality of life changes in patients using GLP-1 analogues. J Diabetes Complications. 2011;25:244–6.
Athauda D, Maclagan K, Skene SS, Bajwa-Joseph M, Letchford D, Chowdhury K, et al. Exenatide once weekly versus placebo in Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;390:1664–75.
Miras AD, Pérez-Pevida B, Aldhwayan M, Kamocka A, McGlone ER, Al-Najim W, et al. Adjunctive liraglutide treatment in patients with persistent or recurrent type 2 diabetes after metabolic surgery (GRAVITAS): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:549–59.
Best JH, Rubin RR, Peyrot M, Li Y, Yan P, Malloy J, et al. Weight-related quality of life, health utility, psychological well-being, and satisfaction with exenatide once weekly compared with sitagliptin or pioglitazone after 26 weeks of treatment. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:314–9.
Reaney M, Mathieu C, Östenson CG, Matthaei S, Krarup T, Kiljański J, et al. Patient-reported outcomes among patients using exenatide twice daily or insulin in clinical practice in six European countries: the CHOICE prospective observational study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013;11:217.
Gonzalez JS, Bebu I, Krause-Steinrauf H, Hoogendoorn CJ, Crespo-Ramos G, Presley C, et al. Differential effects of type 2 diabetes treatment regimens on diabetes distress and depressive symptoms in the glycemia reduction approaches in diabetes: a Comparative Effectiveness Study (GRADE). Diabetes Care. 2024;47:610–9.
Battini V, Van Manen RP, Gringeri M, Mosini G, Guarnieri G, Bombelli A, et al. The potential antidepressant effect of antidiabetic agents: new insights from a pharmacovigilance study based on data from the reporting system databases FAERS and VigiBase. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1128387.
Tsai WH, Sung FC, Chiu LT, Shih YH, Tsai MC, Wu SI. Decreased risk of anxiety in diabetic patients receiving Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist: a Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:765446.
Moulton CD, Hopkins CWP, Ismail K, Stahl D. Repositioning of diabetes treatments for depressive symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018;94:91–103.
Spoorthy MS, Chakrabarti S, Grover S. Comorbidity of bipolar and anxiety disorders: an overview of trends in research. World J Psychiatry. 2019;9:7.
Kinzig KP, D’Alessio DA, Herman JP, Sakai RR, Vahl TP, Figueredo HF, et al. CNS Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptors mediate endocrine and anxiety responses to interoceptive and psychogenic stressors. J Neurosci. 2003;23:6163–70.
Maclusky NJ, Cook S, Scrocchi L, Shin J, Kim J, Vaccarino F, et al. Neuroendocrine function and response to stress in mice with complete disruption of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor signaling. Endocrinology. 2000;141:752–62.
Grillon C, Levenson J, Pine DS. A single dose of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram exacerbates anxiety in humans: a Fear-Potentiated Startle Study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007;32:225–31.
Strawn JR, D’Alessio DA, Keck PE, Seeley RJ. Failure of glucagon-like peptide-1 to induce panic attacks or anxiety in patients with panic disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42:787–9.
Eren-Yazicioglu CY, Kara B, Sancak S, Uysal SP, Yazici D, Okuroglu N, et al. Effect of exenatide use on cognitive and affective functioning in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: exenatide use mediates depressive scores through increased perceived stress levels. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2021;41:428–35.
Miller A, Joyce B, Bartelt K, Deckert J. Most GLP-1 medications correlated with a lower likelihood of anxiety and depression diagnoses. Epic Research. 2024 Feb 6 [cited 2025 Jan 24]. Available from: https://www.epicresearch.org/articles/most-glp-1-medications-correlated-with-a-lower-likelihood-of-anxiety-and-depression-diagnoses.
Kunz M, Gama CS, Andreazza AC, Salvador M, Ceresér KM, Gomes FA, et al. Elevated serum superoxide dismutase and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances in different phases of bipolar disorder and in schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32:1677–81.
de Sousa RT, Zarate CA, Zanetti MV, Costa AC, Talib LL, Gattaz WF, et al. Oxidative stress in early stage Bipolar Disorder and the association with response to lithium. J Psychiatr Res. 2014;50:36–41.
Luca A, Calandra C, Luca M. Gsk3 signalling and redox status in bipolar disorder: evidence from lithium efficacy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:3030547.
Niciu MJ, Ionescu DF, Mathews DC, Richards EM, Zarate CA. Second messenger/signal transduction pathways in major mood disorders: moving from membrane to mechanism of action, part II: bipolar disorder. CNS Spectr. 2013;18:242–51.
Beurel E, Grieco SF, Jope RS. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;148:114–31.
Chaves Filho AJM, Cunha NL, de Souza AG, Soares MVR, Jucá PM, de Queiroz T, et al. The GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide reverses mania-like alterations and memory deficits induced by D-amphetamine and augments lithium effects in mice: relevance for bipolar disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020;99:109872.
Çiçekli MN, Tiryaki ES, Altun A, Günaydın C. GLP-1 agonist liraglutide improves ouabain-induced mania and depressive state via GSK-3β pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct. 2022;42:486–94.
Gualtieri CT, Morgan DW. The frequency of cognitive impairment in patients with anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder: an unaccounted source of variance in clinical trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008;69:1122–30.
Miskowiak KW, Carvalho AF, Vieta E, Kessing LV. Cognitive enhancement treatments for bipolar disorder: a systematic review and methodological recommendations. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;26:1541–61.
Bora E, McIntyre RS, Ozerdem A. Neurococognitive and neuroimaging correlates of obesity and components of metabolic syndrome in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Psychol Med. 2019;49:738–49.
During MJ, Cao L, Zuzga DS, Francis JS, Fitzsimons HL, Jiao X, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is involved in learning and neuroprotection. Nat Med. 2003;9:1173–9.
Taati M, Barzegar PEF, Raisi A. Exercise improves spatial learning and memory performance through the Central GLP-1 receptors. Behav Neurol. 2022;2022:2900628.
Porter DW, Kerr BD, Flatt PR, Holscher C, Gault VA. Four weeks administration of Liraglutide improves memory and learning as well as glycaemic control in mice with high fat dietary-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12:891–9.
Iwai T, Suzuki M, Kobayashi K, Mori K, Mogi Y, Oka JI. The influences of juvenile diabetes on memory and hippocampal plasticity in rats: improving effects of glucagon-like peptide-1. Neurosci Res. 2009;64:67–74.
Lennox R, Flatt PR, Gault VA. Lixisenatide improves recognition memory and exerts neuroprotective actions in high-fat fed mice. Peptides (NY). 2014;61:38–47.
McIntyre RS, Powell AM, Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Soczynska JK, Alsuwaidan M, Woldeyohannes HO, et al. The neuroprotective effects of GLP-1: possible treatments for cognitive deficits in individuals with mood disorders. Behav Brain Res. 2013;237:164–71.
Erbil D, Eren CY, Demirel C, Küçüker MU, Solaroğlu I, Eser HY. GLP-1’s role in neuroprotection: a systematic review. Brain Inj. 2019;33:734–819.
Reich N, Hölscher C. The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an in-depth review. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:970925.
Kellar D, Craft S. Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:758–66.
Luan S, Cheng W, Wang C, Gong J, Zhou J. Impact of glucagon-like peptide 1 analogs on cognitive function among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta−analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1047883.
Nørgaard CH, Friedrich S, Hansen CT, Gerds T, Ballard C, Møller DV, et al. Treatment with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and incidence of dementia: data from pooled double-blind randomized controlled trials and nationwide disease and prescription registers. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2022;8:e12268.
Tang H, Shao H, Shaaban CE, Yang K, Brown J, Anton S, et al. Newer glucose-lowering drugs and risk of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71:2096–106.
Dei Cas A, Micheli MM, Aldigeri R, Gardini S, Ferrari-Pellegrini F, Perini M, et al. Long-acting exenatide does not prevent cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024;47:2339–49.
Ishøy PL, Fagerlund B, Broberg BV, Bak N, Knop FK, Glenthøj BY, et al. No cognitive-enhancing effect of GLP-1 receptor agonism in antipsychotic-treated, obese patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;136:52–62.
Mansur RB, Zugman A, Ahmed J, Cha DS, Subramaniapillai M, Lee Y, et al. Treatment with a GLP-1R agonist over four weeks promotes weight loss-moderated changes in frontal-striatal brain structures in individuals with mood disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;27:1153–62.
Edge MD, Johnson SL, Ng T, Carver CS. Iowa gambling task performance in euthymic bipolar i disorder: a meta-analysis and empirical study. J Affect Disord. 2013;150:115–22.
Adida M, Jollant F, Clark L, Besnier N, Guillaume S, Kaladjian A, et al. Trait-related decision-making impairment in the three phases of bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70:357–65.
Pouchon A, Vinckier F, Dondé C, Gueguen MC, Polosan M, Bastin J. Reward and punishment learning deficits among bipolar disorder subtypes. J Affect Disord. 2023;340:694–702.
Jiménez E, Solé B, Arias B, Mitjans M, Varo C, Reinares M, et al. Characterizing decision-making and reward processing in bipolar disorder: a cluster analysis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018;28:863–74.
Badulescu S, Tabassum A, Le GH, Wong S, Phan L, Gill H, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 agonist and effects on reward behaviour: a systematic review. Physiol Behav. 2024;283:114622.
Blundell J, Finlayson G, Axelsen M, Flint A, Gibbons C, Kvist T, et al. Effects of once-weekly semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food preference and body weight in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1242–51.
Yammine L, Green CE, Kosten TR, de Dios C, Suchting R, Lane SD, et al. Exenatide adjunct to nicotine patch facilitates smoking cessation and may reduce post-cessation weight gain: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Nicotine Tob Res. 2021;23:1682–90.
Bae JH, Choi HJ, Cho KIK, Kim LK, Kwon JS, Cho YM. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonist differentially affects brain activation in response to visual food cues in lean and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J. 2019;44:248–59.
Van Bloemendaal L, IJzerman RG, Ten Kulve JS, Barkhof F, Konrad RJ, Drent ML, et al. GLP-1 receptor activation modulates appetite- and reward-related brain areas in humans. Diabetes. 2014;63:4186–96.
Hanssen R, Rigoux L, Kuzmanovic B, Iglesias S, Kretschmer AC, Schlamann M, et al. Liraglutide restores impaired associative learning in individuals with obesity. Nat Metab. 2023;5:1352–63.
Gold AK, Otto MW, Deckersbach T, Sylvia LG, Nierenberg AA, Kinrys G. Substance use comorbidity in bipolar disorder: a qualitative review of treatment strategies and outcomes. Am J Addict. 2018;27:188–201.
Lalli M, Brouillette K, Kapczinski F, de Azevedo Cardoso T. Substance use as a risk factor for bipolar disorder: a systematic review. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;144:285–95.
Albanese MJ, Pies R. The bipolar patient with comorbid substance use disorder: recognition and management. CNS Drugs. 2004;18:585–96.
Richardson T, Garavan H. Relationships between substance use and hypomanic symptoms in a non-clinical sample. Ment Health Subst Use. 2011;4:211–21.
González-Pinto A, Goikolea JM, Zorrilla I, Bernardo M, Arrojo M, Cunill R, et al. Clinical practice guideline on pharmacological and psychological management of adult patients with bipolar disorder and comorbid substance use. Adicciones. 2022;34:142–56.
Volkow ND. Personalizing the treatment of substance use disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177:113–6. https://doi.org/10.1176/AppiAjp201919121284
Facal F, Costas J. Genomic evidence of GLP-1 receptor as target for the treatment of substance use disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2025;92:48–49.
Zheng YJ, Soegiharto C, Au HCT, Valentino K, Le GH, Wong S, et al. A systematic review on the role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on alcohol-related behaviors: potential therapeutic strategy for alcohol use disorder. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2025;37:e51.
Kruse Klausen M, Thomsen M, Wortwein G, Fink-Jensen A. The role of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in addictive disorders. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179:625–41.
Merkel R, Hernandez NS, Weir V, Zhang Y, Caffrey A, Rich MT, et al. An endogenous GLP-1 circuit engages VTA GABA neurons to regulate mesolimbic dopamine neurons and attenuate cocaine seeking. Sci Adv. 2025;11:eadr5051.
Tuesta LM, Chen Z, Duncan A, Fowler CD, Ishikawa M, Lee BR, et al. GLP-1 acts on habenular avoidance circuits to control nicotine intake. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20:708–16.
Aranäs C, Edvardsson CE, Shevchouk OT, Zhang Q, Witley S, Blid Sköldheden S, et al. Semaglutide reduces alcohol intake and relapse-like drinking in male and female rats. EBioMedicine. 2023;93:104642.
Thomsen M, Holst JJ, Molander A, Linnet K, Ptito M, Fink-Jensen A. Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 analogs on alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring vervet monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019;236:603–11.
Sirohi S, Schurdak JD, Seeley RJ, Benoit SC, Davis JF. Central & peripheral glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signaling differentially regulate addictive behaviors. Physiol Behav. 2016;161:140–4.
Volkow ND, Xu R. GLP-1R agonist medications for addiction treatment. Addiction. 2025;120:198–200.
Butelman ER, Goldstein RZ, Nwaneshiudu CA, Girdhar K, Roussos P, Russo SJ, et al. Neuroimmune mechanisms of opioid use disorder and recovery: translatability to human studies, and future research directions. Neuroscience. 2023;528:102–16.
Martinelli S, Mazzotta A, Longaroni M, Petrucciani N. Potential role of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists in substance use disorder: a systematic review of randomized trials. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2024;264:112424.
Probst L, Monnerat S, Vogt DR, Lengsfeld S, Burkard T, Meienberg A, et al. Effects of dulaglutide on alcohol consumption during smoking cessation. JCI Insight. 2023;8:e170419.
Klausen MK, Jensen ME, Møller M, Le Dous N, Jensen AMØ, Zeeman VA, et al. Exenatide once weekly for alcohol use disorder investigated in a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. JCI Insight. 2022;7:e159863.
Angarita GA, Matuskey D, Pittman B, Costeines JL, Potenza MN, Jastreboff AM, et al. Testing the effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide on cocaine self-administration and subjective responses in humans with cocaine use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021;221:108614.
Lengsfeld S, Burkard T, Meienberg A, Jeanloz N, Vukajlovic T, Bologna K, et al. Effect of dulaglutide in promoting abstinence during smoking cessation: a single-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2023;57:101865.
Wang W, Volkow ND, Berger NA, Davis PB, Kaelber DC, Xu R. Associations of semaglutide with incidence and recurrence of alcohol use disorder in real-world population. Nat Commun. 2024;15:5177.
Lähteenvuo M, Tiihonen J, Solismaa A, Tanskanen A, Mittendorfer-Rutz E, Taipale H. Repurposing semaglutide and liraglutide for alcohol use disorder. JAMA Psychiatry. 2025;82:94–98.
Wang W, Volkow ND, Berger NA, Davis PB, Kaelber DC, Xu R. Association of semaglutide with reduced incidence and relapse of cannabis use disorder in real-world populations: a Retrospective Cohort study. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;29:2587–98.
Sletved KSO, Ziersen SC, Andersen PK, Vinberg M, Kessing LV. Socio-economic functioning in patients with bipolar disorder and their unaffected siblings – results from a nation-wide population-based longitudinal study. Psychol Med. 2023;53:706–13.
Dayabandara M, Hanwella R, Ratnatunga S, Seneviratne S, Suraweera C, de Silva VA. Antipsychotic-associated weight gain: management strategies and impact on treatment adherence. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017;13:2231.
Fagiolini A, Kupfer DJ, Houck PR, Novick DM, Frank E. Obesity as a correlate of outcome in patients with bipolar I disorder. Am J Psychiatr. 2003;160:112–7.
Leutner M, Dervic E, Bellach L, Klimek P, Thurner S, Kautzky A. Obesity as pleiotropic risk state for metabolic and mental health throughout life. Transl Psychiatry. 2023;13:175.
Menon T, Lee S, Gong XY, Wong S, Le GH, Kwan ATH, et al. A systematic review on the efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists in mitigating psychotropic drug-related weight gain. CNS Spectr. 2024. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1092852924000531.
Whicher CA, Price HC, Phiri P, Rathod S, Barnard-Kelly K, Ngianga K, et al. The use of liraglutide 3.0 mg daily in the management of overweight and obesity in people with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and first episode psychosis: results of a pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23:1262–71.
Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, Jespersen HR, Jakobsen MI, Svensson CK, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in Clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatr. 2017;74:719–28.
Siskind DJ, Russell AW, Gamble C, Winckel K, Mayfield K, Hollingworth S, et al. Treatment of clozapine-associated obesity and diabetes with exenatide in adults with schizophrenia: a randomized controlled trial (CODEX). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:1050–5.
Ishøy PL, Knop FK, Broberg BV, Bak N, Andersen UB, Jørgensen NR, et al. Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment on body weight in obese antipsychotic-treated patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:162–71.
Shetty R, Basheer FT, Poojari PG, Thunga G, Chandran VP, Acharya LD. Adverse drug reactions of GLP-1 agonists: a systematic review of case reports. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022;16:102427.
Filippatos TD, Panagiotopoulou TV, Elisaf MS. Adverse effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Rev Diabet Stud. 2015;11:202.
Silverii GA, Marinelli C, Mannucci E, Rotella F. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and mental health: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26:2505–8.
Nakhla M, Nair A, Balani P, Ujjawal A, Arun Kumar P, Dasari M, et al. Risk of suicide, hair loss, and aspiration with GLP1-receptor agonists and other diabetic agents: a Real-World Pharmacovigilance Study. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10557-024-07613-W.
Ueda P, Söderling J, Wintzell V, Svanström H, Pazzagli L, Eliasson B, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonist use and risk of suicide death. JAMA Intern Med. 2024;184:1301–12.
Hurtado I, Robles C, Peiró S, García-Sempere A, Sanfélix-Gimeno G. Association of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists with suicidal ideation and self-injury in individuals with diabetes and obesity: a propensity-weighted, population-based cohort study. Diabetologia. 2024;67:2471–80.
Tang H, Lu Y, Donahoo WT, Shao H, Shi L, Fonseca VA, et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists and risk for suicidal ideation and behaviors in U.S. Older adults with type 2 diabetes: a Target Trial Emulation Study. Ann Intern Med. 2024;177:1004–15.
Gamble JM, Chibrikov E, Midodzi WK, Twells LK, Majumdar SR. Examining the risk of depression or self-harm associated with incretin-based therapies used to manage hyperglycaemia in patients with type 2 diabetes: a Cohort Study using the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e023830.
Chen C, Zhou R, Fu F, Xiao J. Postmarket safety profile of suicide/self-injury for GLP-1 receptor agonist: a real-world pharmacovigilance analysis. Eur Psychiatry. 2023;66:e99.
De Giorgi R, Koychev I, Adler AI, Cowen PJ, Harmer CJ, Harrison PJ, et al. 12-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes of semaglutide use for type 2 diabetes: a propensity-score matched Cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. 2024;74:102726.
European Medicines Agency. Association between exposure to GLP-1 receptor agonists and risk of suicide-related and self-harm-related events. HMA-EMA Catalogues of real-world data sources and studies. 2023 [cited 2025 Jan 24]. Available from:https://catalogues.ema.europa.eu/node/3953/methodological-aspects
Kornelius E, Huang JY, Lo SC, Huang CN, Yang YS. The risk of depression, anxiety, and suicidal behavior in patients with obesity on glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy. Sci Rep. 2024;14:24433.
Ruggiero R, Mascolo A, Spezzaferri A, Carpentieri C, Torella D, Sportiello L, et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists and suicidal ideation: analysis of real-word data collected in the European pharmacovigilance database. Pharmaceuticals. 2024;17:147.
Wang W, Volkow ND, Berger NA, Davis PB, Kaelber DC, Xu R. Association of semaglutide with risk of suicidal ideation in a real-world cohort. Nat Med. 2024;30:168–76.
Kerem L, Stokar J. Risk of suicidal ideation or attempts in adolescents with obesity treated with GLP1 receptor agonists. JAMA Pediatr. 2024;178:1307–15.
Nassar M, Misra A, Bloomgarden Z. Impact of treatment with GLP-1RAs on suicide attempts in adults persons with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective comparative effectiveness study based on a global TriNetX health research database. J Diabetes. 2024;16:e13547.
European Medicines Agency. EMA statement on ongoing review of GLP-1 receptor agonists. European Medicines Agency. 2023 Jul 11 [cited 2025 Jan 19]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-statement-ongoing-review-glp-1-receptor-agonists
Fick M. Exclusive: UK probes Novo’s Ozempic, weight-loss drug Saxenda over suicidal, self-harming thoughts. Reuters. 2023 Jul 26 [cited 2025 Jan 19]. Available from: https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/uk-probing-novos-ozempic-weight-loss-drug-saxenda-over-suicidal-self-harming-2023-07-26/
McIntyre RS, Mansur RB, Rosenblat JD, Kwan ATH. The association between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and suicidality: reports to the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2024;23:47–55.
Wang F, Wang S, Zong QQ, Zhang Q, Ng CH, Ungvari GS, et al. Prevalence of comorbid major depressive disorder in Type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of comparative and epidemiological studies. Diabet Med. 2019;36:961–9.
Blasco BV, García-Jiménez J, Bodoano I, Gutiérrez-Rojas L. Obesity and depression: its prevalence and influence as a prognostic factor: a systematic review. Psychiatry Investig. 2020;17:715.
Valentino K, Teopiz KM, Cheung W, Wong S, Le GH, Rosenblat JD, et al. The effect of glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists on measures of suicidality: a systematic review. J Psychiatr Res. 2025;183:112–26.
McIntyre RS. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Suicidality: Association Versus Causation and the Need for Ongoing Surveillance. Am J Psychiatry. 2025:appiajp20241087. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.20241087.
Zhou J, Zheng Y, Xu B, Long S, Zhu LE, Liu Y, et al. Exploration of the potential association between GLP-1 receptor agonists and suicidal or self-injurious behaviors: a pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System database. BMC Med. 2024;22:65.
Schoretsanitis G, Weiler S, Barbui C, Raschi E, Gastaldon C. Disproportionality analysis from world health organization data on semaglutide, liraglutide, and suicidality. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:e2423385–e2423385.
McIntyre RS, Mansur RB, Rosenblat JD, Rhee TG, Cao B, Teopiz KM, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and suicidality: a replication study using reports to the World Health Organization pharmacovigilance database (VigiBase®). J Affect Disord. 2025;369:922–7.
Hunger JM, Major B, Blodorn A, Miller CT. Weighed down by stigma: how weight-based social identity threat contributes to weight gain and poor health. Soc Personal Psychol Compass. 2015;9:255–68.
McGrath KH, Haller W, Bines JE. Starvation and fasting: biochemical aspects. Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition. 2023;1–4:645–56. Fourth Edition1–4
Montoya A, Bruins R, Katzman MA, Blier P. The noradrenergic paradox: implications in the management of depression and anxiety. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016;12:541–57.
O’Connor DB, Ferguson E, Green JA, O’Carroll RE, O’Connor RC. Cortisol levels and suicidal behavior: a meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016;63:370–9.
Bhatti JA, Nathens AB, Thiruchelvam D, Grantcharov T, Goldstein BI, Redelmeier DA. Self-harm emergencies after bariatric surgery: a Population-Based Cohort Study. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:226–32.
Østergaard SD, Hieronymus F. Psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression. New Eng J Med. 2023;388:e22.
Giurgiuca A, Nemes B, Schipor S, Caragheorgheopol A, Boscaiu V, Cozman D, et al. Cortisol levels and suicide in bipolar I disorder. Acta Endocrinologica (Bucharest). 2017;13:188.
Plans L, Barrot C, Nieto E, Rios J, Schulze TG, Papiol S, et al. Association between completed suicide and bipolar disorder: a systematic review of the literature. J Affect Disord. 2019;242:111–22.
Valvassori SS, Dal-Pont GC, Varela RB, Resende WR, Gava FF, Mina FG, et al. Ouabain induces memory impairment and alter the BDNF signaling pathway in an animal model of bipolar disorder: cognitive and neurochemical alterations in BD model. J Affect Disord. 2021;282:1195–202.
Cooper DH, Ramachandra R, Ceban F, Di Vincenzo JD, Rhee TG, Mansur RB, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists as a protective factor for incident depression in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Psychiatr Res. 2023;164:80–89.
Jalleh RJ, Plummer MP, Marathe CS, Umapathysivam MM, Quast DR, Rayner CK, et al. Clinical consequences of delayed gastric emptying with GLP-1 receptor agonists and tirzepatide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024;110:1–15.
Vieta E. Neuroprogression happens. Psychol Med. 2024;54:3760.
Yatham LN, Schaffer A, Kessing LV, Miskowiak K, Kapczinski F, Vieta E, et al. Early intervention, relapse prevention, and neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: the evidence matters. Bipolar Disord. 2024;26:313–6.
Passos IC, Mwangi B, Vieta E, Berk M, Kapczinski F. Areas of controversy in neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2016;134:91–103.
Grewal S, McKinlay S, Kapczinski F, Pfaffenseller B, Wollenhaupt-Aguiar B. Biomarkers of neuroprogression and late staging in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Aust N Z J Psychiatr. 2023;57:328–43.
Wollenhaupt-Aguiar B, Kapczinski F, Pfaffenseller B. Biological pathways associated with neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Brain Sci. 2021;11:228.
Rodriguez PJ, Zhang V, Gratzl S, Do D, Cartwright BG, Baker C, et al. Discontinuation and reinitiation of dual-labeled GLP-1 receptor agonists among US adults with overweight or obesity. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8:e2457349–e2457349.
Polonsky W, Gamble C, Iyer N, Martin M, Hamersky C. Exploring why people with type 2 diabetes do or do not persist with Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy: a Qualitative Study. Diabetes Spectr. 2021;34:175–83.
Waldrop SW, Johnson VR, Stanford FC. Inequalities in the provision of GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity. Nat Med. 2024;30:22.
Razavi MS, Fathi M, Vahednia E, Ardani AR, Honari S, Akbarzadeh F, et al. Cognitive rehabilitation in bipolar spectrum disorder: a systematic review. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024;16:509–17.
Vieta E, Torrent C. Functional remediation: the pathway from remission to recovery in bipolar disorder. World Psychiatry. 2016;15:288.
Nomoto H, Oba-Yamamoto C, Takahashi Y, Takeuchi J, Nagai S, Yokoyama H, et al. Effects of switching from liraglutide or dulaglutide to subcutaneous semaglutide on glucose metabolism and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes: protocol for a Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label, Blinded-Endpoint, Parallel-Group Comparison Study (The SWITCH-SEMA 1 Study). Diabetes Ther. 2021;12:955–64.
Guglielmi G. The weight-loss drugs being tested in 2025: will they beat ozempic? Nature. 2025;638:591–2.
Acknowledgements
Cristian-Daniel Llach received the support of a fellowship from “la Caixa” Foundation (ID 100010434 - fellowship code LCF/BQ/EU22/11930062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CDLL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Conceptualization. SB: Writing – review & editing. AT: Writing – review & editing. HS: Writing – review & editing. HG: Writing – review & editing. GHL: Writing – review & editing. EV: Writing – review & editing. RSM: Writing – review & editing. JDR: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. RBM: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Cristian-Daniel Llach received financial support from the ‘La Caixa’ Foundation, which provided salary support during the fellowship through its fellowship programs. However, the foundation was not involved in any stage of this manuscript, including its design, writing, revision, or submission. There are no conflicts of interest between the author’s research and the ‘La Caixa’ Foundation. C.L. has also received CME-related honoraria or consulting fees from CASEN Recordati, Organon, Lundbeck, and the Academy for Continuing Medical Education (Akademijazakme), with no financial or other conflicts of interest relevant to the subject of this article. Eduard Vieta has received grants and served as consultant, advisor or CME speaker for the following entities: AB-Biotics, Abbott, AbbVie, Adamed, Alcediag, Angelini, Biogen, Beckley-Psytech, Biohaven, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Casen-Recordati, Celon Pharma, Clariane, Compass, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Esteve, Ethypharm, Ferrer, Gedeon Richter, GH Research, Glaxo-Smith Kline, HMNC, Intra-Cellular therapies, Idorsia, Johnson & Johnson, Lundbeck, Luye Pharma, Medincell, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Newraxpharm, Newron, Novartis, Organon, Orion Corporation, Otsuka, Roche, Rovi, Sage, Sanofi-Aventis, Sunovion, Takeda, Teva, and Viatris, outside the submitted work. Dr. Roger S. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) and the Milken Institute; speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sage, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Neurawell, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Viatris, Abbvie and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. Joshua D Rosenblat has received research grant support from the Canadian Institute of Health Research (CIHR), Physician Services Inc (PSI) Foundation, Labatt Brain Health Network, Brain and Cognition Discovery Foundation (BCDF), Canadian Cancer Society, Canadian Psychiatric Association, Academic Scholars Award, American Psychiatric Association, American Society of Psychopharmacology, University of Toronto, University Health Network Centre for Mental Health, Joseph M. West Family Memorial Fund, Inagene and Timeposters Fellowship and industry funding for speaker/consultation/research fees from iGan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Abbvie, Braxia Health (Canadian Rapid Treatment Centre of Excellence), Braxia Scientific, Janssen, Allergan, Lundbeck, Sunovion and COMPASS.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Llach, CD., Badulescu, S., Tabassum, A. et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists as emerging therapeutics in bipolar disorder: a narrative review of preclinical and clinical evidence. Mol Psychiatry (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03261-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03261-0