Abstract
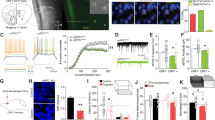
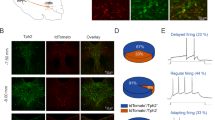
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) signaling via limbic NPY1 and 2 receptors (NPY1R and NPY2R, respectively) is known to modulate binge-like ethanol consumption in rodents. However, the role of NPY signaling in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), which provides top-down modulation of the limbic system, is unknown. Here, we used “drinking-in-the-dark” (DID) procedures in C57BL/6J mice to address this gap in the literature. First, the impact of DID on NPY immunoreactivity (IR) was assessed in the mPFC. Next, the role of NPY1R and NPY2R signaling in the mPFC on ethanol consumption was evaluated through site-directed pharmacology. Chemogenetic inhibition of NPY1R+ neurons in the mPFC was performed to further evaluate the role of this population. To determine the potential role of NPY1R+ neurons projecting from the mPFC to the basolateral amygdala (BLA) this efferent population was selectively silenced. Three, 4-day cycles of DID reduced NPY IR in the mPFC. Intra-mPFC activation of NPY1R and antagonism of NPY2R resulted in decreased binge-like ethanol intake. Silencing of mPFC NPY1R+ neurons overall, and specifically NPY1R+ neurons projecting to the BLA, significantly reduced binge-like ethanol intake. We provide novel evidence that (1) binge-like ethanol intake reduces NPY levels in the mPFC; (2) activation of NPY1R or blockade of NPY2R reduces binge-like ethanol intake; and (3) chemogenetic inhibition of NPY1R+ neurons in the mPFC and NPY1R+ mPFC neurons projecting to the BLA blunts binge-like drinking. These observations provide the first direct evidence that NPY signaling in the mPFC modulates binge-like ethanol consumption.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
NIAAA. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Council approves definition of binge drinking. NIAAA Newsletter. 2004.
Fan AZ, Russell M, Stranges S, Dorn J, Trevisan M. Association of lifetime alcohol drinking trajectories with cardiometabolic risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:154–61. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-1395
Hingson R, Heeren T, Winter M, Wechsler H. Magnitude of alcohol-related mortality and morbidity among U.S. college students ages 18-24: changes from 1998 to 2001. Annu Rev Public Health. 2005;26:259–79. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.26.021304.144652
Miller JW, Naimi TS, Brewer RD, Jones SE. Binge drinking and associated health risk behaviors among high school students. Pediatrics. 2007;119:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-1517
Miller P, Plant M. Spreading out or concentrating weekly consumption: alcohol problems and other consequences within a UK population sample. Alcohol Alcohol. 2005;40:461–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agh169
Sprow GM, Thiele TE. The neurobiology of binge-like ethanol drinking: evidence from rodent models. Physiol Behav. 2012;106:325–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.12.026
Rhodes JS, Best K, Belknap JK, Finn DA, Crabbe JC. Evaluation of a simple model of ethanol drinking to intoxication in C57BL/6J mice. Physiol Behav. 2005;84:53–63.
Thiele TE, Crabbe JC, Boehm SL. “Drinking in the Dark” (DID): a simple mouse model of binge-like alcohol intake. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2014;68:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142301.ns0949s68. 9.49
Koob GF. Alcoholism: allostasis and beyond. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:232–43. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ALC.0000057122.36127.C2
Koob GF, Le Moal M. Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2001;24:97–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00195-0
Gilpin NW. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the extended amygdala is recruited during the transition to alcohol dependence. Neuropeptides. 2012;46:253–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2012.08.001
Sparrow AM, Lowery-Gionta EG, Pleil KE, Li C, Sprow GM, Cox BR, et al. Central neuropeptide Y modulates binge-like ethanol drinking in C57BL/6J mice via Y1 and Y2 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37:1409–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.327
Pleil KE, Lowery-Gionta EG, Crowley NA, Li C, Marcinkiewcz CA, Rose JH, et al. Effects of chronic ethanol exposure on neuronal function in the prefrontal cortex and extended amygdala. Neuropharmacology. 2015;99:735–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.06.017
Lowery-Gionta EG, Navarro M, Li C, Pleil KE, Rinker JA, Cox BR, et al. Corticotropin releasing factor signaling in the central amygdala is recruited during binge-like ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. J Neurosci. 2012;32:3405–13. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6256-11.2012
Likhtik E, Paz R. Amygdala-prefrontal interactions in (mal)adaptive learning. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38:158–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2014.12.007
Likhtik E, Pelletier JG, Paz R, Pare D. Prefrontal control of the amygdala. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7429–37. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2314-05.2005
Lei K, Wegner SA, Yu JH, Mototake A, Hu B, Hopf FW. Nucleus accumbens shell and mPFC but not insula orexin-1 receptors promote excessive alcohol drinking. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:400 https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00400
Haun HL, Griffin WC, Lopez MF, Solomon MG, Mulholland PJ, Woodward JJ, et al. Increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in medial prefrontal cortex selectively reduces excessive drinking in ethanol dependent mice. Neuropharmacology. 2018;140:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.07.031
Holmes A, Fitzgerald PJ, MacPherson KP, DeBrouse L, Colacicco G, Flynn SM, et al. Chronic alcohol remodels prefrontal neurons and disrupts NMDAR-mediated fear extinction encoding. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:1359–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3204
Lalumiere RT. Optogenetic dissection of amygdala functioning. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014;8:107 https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00107
Little JP, Carter AG. Synaptic mechanisms underlying strong reciprocal connectivity between the medial prefrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci. 2013;33:15333–42. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2385-13.2013
Mcdonald AJ, Mascagni F, Guo L. Projections of the medial and lateral prefrontal cortices to the amygdala: a Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin study in the rat. Neuroscience. 1996;71:55–75.
Pinard CR, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ. Medial prefrontal cortical innervation of the intercalated nuclear region of the amygdala. Neuroscience. 2012;205:112–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.036
Robinson SL, Thiele TE. The role of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in alcohol and drug abuse disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017;136:177–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2017.06.005
Palmiter RD, Erickson JC, Hollopeter G, Baraban SC, Schwartz MW. Life without neuropeptide Y. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1998;53:163–99.
Kubota Y, Shigematsu N, Karube F, Sekigawa A, Kato S, Yamaguchi N, et al. Selective coexpression of multiple chemical markers defines discrete populations of neocortical GABAergic neurons. Cereb Cortex. 2011;21:1803–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhq252
Carballedo A, Scheuerecker J, Meisenzahl E, Schoepf V, Bokde A, Möller HJ, et al. Functional connectivity of emotional processing in depression. J Affect Disord. 2011;134:272–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2011.06.021
Gilabert-Juan J, Castillo-Gomez E, Guirado R, Moltó MD, Nacher J. Chronic stress alters inhibitory networks in the medial prefrontal cortex of adult mice. Brain Struct Funct. 2013;218:1591–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0479-1
Ehlers CL, Li TK, Lumeng L, Hwang BH, Somes C, Jimenez P, et al. Neuropeptide Y levels in ethanol-naive alcohol-preferring and nonpreferring rats and in Wistar rats after ethanol exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:1778–82.
Padilla SL, Qiu J, Soden ME, Sanz E, Nestor CC, Barker FD, et al. Agouti-related peptide neural circuits mediate adaptive behaviors in the starved state. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19:734–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4274
Marshall SA, McKnight KH, Blose AK, Lysle DT, Thiele TE. Modulation of binge-like ethanol consumption by IL-10 signaling in the basolateral amygdala. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-016-9709-2
Pleil KE, Rinker JA, Lowery-Gionta EG, Mazzone CM, McCall NM, Kendra AM, et al. NPY signaling inhibits extended amygdala CRF neurons to suppress binge alcohol drinking. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:545–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3972
Finn DA, Snelling C, Fretwell AM, Tanchuck MA, Underwood L, Cole M, et al. Increased drinking during withdrawal from intermittent ethanol exposure is blocked by the CRF receptor antagonist D-Phe-CRF(12-41). Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:939–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00379.x
Brothers SP, Wahlestedt C. Therapeutic potential of neuropeptide Y (NPY) receptor ligands. EMBO Mol Med. 2010;2:429–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201000100
MacLaren DA, Browne RW, Shaw JK, Krishnan Radhakrishnan S, Khare P, España RA, et al. Clozapine N-oxide administration produces behavioral effects in long-evans rats: implications for designing DREADD experiments. eNeuro. 2016;3. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0219-16.2016
Balleine BW, Dickinson A. Goal-directed instrumental action: contingency and incentive learning and their cortical substrates. Neuropharmacology. 1998;37:407–19.
Balleine BW, O’Doherty JP. Human and rodent homologies in action control: corticostriatal determinants of goal-directed and habitual action. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:48–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.131
Mendoza J, Sanio C, Chaudhri N. Inactivating the infralimbic but not prelimbic medial prefrontal cortex facilitates the extinction of appetitive pavlovian conditioning in long-evans rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015;118:198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2014.12.006
Vollmer LL, Schmeltzer S, Schurdak J, Ahlbrand R, Rush J, Dolgas CM, et al. Neuropeptide Y impairs retrieval of extinguished fear and modulates excitability of neurons in the infralimbic prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci. 2016;36:1306–15. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4955-13.2016
Constantinidis C, Williams GV, Goldman-Rakic PS. A role for inhibition in shaping the temporal flow of information in prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:175–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn799
Ghosal S, Hare B, Duman RS. Prefrontal cortex GABAergic deficits and circuit dysfunction in the pathophysiology and treatment of chronic stress and depression. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2017;14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.09.012
Delli Pizzi S, Chiacchiaretta P, Mantini D, Bubbico G, Edden RA, Onofrj M, et al. GABA content within medial prefrontal cortex predicts the variability of fronto-limbic effective connectivity. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1399-x
Abernathy K, Chandler LJ, Woodward JJ. Alcohol and the prefrontal cortex. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010;91:289–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7742(10)91009-X
Cho JH, Deisseroth K, Bolshakov VY. Synaptic encoding of fear extinction in mPFC-amygdala circuits. Neuron. 2013;80:1491–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.09.025
Arruda-Carvalho M, Clem RL. Pathway-selective adjustment of prefrontal-amygdala transmission during fear encoding. J Neurosci. 2014;34:15601–9. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2664-14.2014
Arruda-Carvalho M, Clem RL. Prefrontal-amygdala fear networks come into focus. Front Syst Neurosci. 2015;9:145 https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2015.00145
Christian DT, Alexander NJ, Diaz MR, McCool BA. Thalamic glutamatergic afferents into the rat basolateral amygdala exhibit increased presynaptic glutamate function following withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol. Neuropharmacology. 2013;65:134–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.09.004
Kim MJ, Gee DG, Loucks RA, Davis FC, Whalen PJ. Anxiety dissociates dorsal and ventral medial prefrontal cortex functional connectivity with the amygdala at rest. Cereb Cortex. 2011;21:1667–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhq237
Vertes RP. Differential projections of the infralimbic and prelimbic cortex in the rat. Synapse. 2004;51:32–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.10279
Funding
The authors thank Rhiannon D. Thomas for her technical assistance and Richard Palmiter, PhD for supplying the NPY1R-cre mice. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants AA022048, AA013573, AA015148, and F32AA025811. The authors declare no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, S.L., Marrero, I.M., Perez-Heydrich, C.A. et al. Medial prefrontal cortex neuropeptide Y modulates binge-like ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. 44, 1132–1140 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0310-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0310-7
This article is cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis on the transcriptomic signatures in alcohol use disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2025)
-
Basolateral amygdala neuropeptide Y system modulates binge ethanol consumption
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Patterns of functional connectivity alterations induced by alcohol reflect somatostatin interneuron expression in the human cerebral cortex
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Somatostatin neurons control an alcohol binge drinking prelimbic microcircuit in mice
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)