Abstract
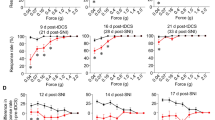
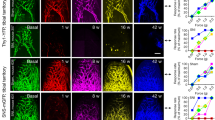
Neuropathic pain caused by nerve injury presents with severe spontaneous pain and a variety of comorbidities, including deficits in higher executive functions. None of these clinical problems are adequately treated with current analgesics. Targeting of the mitogen-activated protein kinase-interacting kinase (MNK1/2) and its phosphorylation target, the mRNA cap binding protein eIF4E, attenuates many types of nociceptive plasticity induced by inflammatory mediators and chemotherapeutic drugs but inhibiting this pathway does not alter nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia. We used genetic manipulations and pharmacology to inhibit MNK-eIF4E activity in animals with spared nerve injury, a model of peripheral nerve injury (PNI)-induced neuropathic pain. We assessed the presence of spontaneous pain using conditioned place preference. We also tested performance in a medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)-dependent rule-shifting task. WT neuropathic animals showed signs of spontaneous pain and were significantly impaired in the rule-shifting task while genetic and pharmacological inhibition of the MNK-eIF4E signaling axis protected against and reversed spontaneous pain and PNI-mediated cognitive impairment. Additionally, pharmacological and genetic inhibition of MNK-eIF4E signaling completely blocked and reversed maladaptive shortening in the length of axon initial segments (AIS) in the mPFC of PNI mice. Surprisingly, these striking positive outcomes on neuropathic pain occurred in the absence of any effect on mechanical allodynia, a standard test for neuropathic pain efficacy. Our results illustrate new testing paradigms for determining preclinical neuropathic pain efficacy and point to the MNK inhibitor tomivosertib (eFT508) as an important drug candidate for neuropathic pain treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Eccleston C. Chronic pain and distraction: an experimental investigation into the role of sustained and shifting attention in the processing of chronic persistent pain. Behav Res Ther. 1995;33:391–405.
Dick B, Eccleston C, Crombez G. Attentional functioning in fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and musculoskeletal pain patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;47:639–44.
Karp JF, Reynolds CF 3rd, Butters MA, Dew MA, Mazumdar S, Begley AE, et al. The relationship between pain and mental flexibility in older adult pain clinic patients. Pain Med. 2006;7:444–52.
Povedano M, Gascon J, Galvez R, Ruiz M, Rejas J. Cognitive function impairment in patients with neuropathic pain under standard conditions of care. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2007;33:78–89.
Schiltenwolf M, Akbar M, Hug A, Pfuller U, Gantz S, Neubauer E, et al. Evidence of specific cognitive deficits in patients with chronic low back pain under long-term substitution treatment of opioids. Pain Physician. 2014;17:9–20.
Shiers S, Pradhan G, Mwirigi J, Mejia G, Ahmad A, Kroener S, et al. Neuropathic pain creates an enduring prefrontal cortex dysfunction corrected by the type II diabetic drug metformin but not by gabapentin. J Neurosci. 2018;38:7337–50.
Attridge N, Pickering J, Inglis M, Keogh E, Eccleston C. People in pain make poorer decisions. Pain. 2019;160:1662–69.
Dick BD, Rashiq S. Disruption of attention and working memory traces in individuals with chronic pain. Anesth Analg. 2007;104:1223–9.
Galvez R, Marsal C, Vidal J, Ruiz M, Rejas J. Cross-sectional evaluation of patient functioning and health-related quality of life in patients with neuropathic pain under standard care conditions. Eur J Pain. 2007;11:244–55.
Melemedjian OK, Asiedu MN, Tillu DV, Sanoja R, Yan J, Lark A, et al. Targeting adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in preclinical models reveals a potential mechanism for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 2011;7:70.
Moy JK, Khoutorsky A, Asiedu MN, Black BJ, Kuhn JL, Barragan-Iglesias P, et al. The MNK-eIF4E signaling axis contributes to injury-induced nociceptive plasticity and the development of chronic pain. J Neurosci. 2017;37:7481–99.
Moy JK, Kuhn JL, Szabo-Pardi TA, Pradhan G, Price TJ. eIF4E phosphorylation regulates ongoing pain, independently of inflammation, and hyperalgesic priming in the mouse CFA model. Neurobiol Pain. 2018;4:45–50.
Inyang KE, Szabo-Pardi T, Wentworth E, McDougal TA, Dussor G, Burton MD, et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin prevents and reverses neuropathic pain and spinal cord microglial activation in male but not female mice. Pharmacol Res. 2019;139:1–16.
Megat S, Ray PR, Moy JK, Lou TF, Barragan-Iglesias P, Li Y, et al. Nociceptor translational profiling reveals the ragulator-Rag GTPase complex as a critical generator of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 2019;39:393–411.
Yang Q, Wu Z, Hadden JK, Odem MA, Zuo Y, Crook RJ, et al. Persistent pain after spinal cord injury is maintained by primary afferent activity. J Neurosci. 2014;34:10765–9.
Cowie AM, Moehring F, O'Hara C, Stucky CL. Optogenetic inhibition of CGRPalpha sensory neurons reveals their distinct roles in neuropathic and incisional pain. J Neurosci. 2018;38:5807–25.
North RY, Li Y, Ray P, Rhines LD, Tatsui CE, Rao G, et al. Electrophysiological and transcriptomic correlates of neuropathic pain in human dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain. 2019;142:1215–26.
Khoutorsky A, Price TJ. Translational control mechanisms in persistent pain. Trends Neurosci. 2018;41:100–14.
Uttam S, Wong C, Price TJ, Khoutorsky A. eIF4E-dependent translational control: a central mechanism for regulation of pain plasticity. Front Genet. 2018;9:470.
Furic L, Rong L, Larsson O, Koumakpayi IH, Yoshida K, Brueschke A, et al. eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:14134–9.
Gkogkas CG, Khoutorsky A, Cao R, Jafarnejad SM, Prager-Khoutorsky M, Giannakas N, et al. Pharmacogenetic inhibition of eIF4E-dependent Mmp9 mRNA translation reverses fragile X syndrome-like phenotypes. Cell Rep. 2014;9:1742–55.
Amorim IS, Kedia S, Kouloulia S, Simbriger K, Gantois I, Jafarnejad SM, et al. Loss of eIF4E phosphorylation engenders depression-like behaviors via selective mRNA translation. J Neurosci. 2018;38:2118–33.
Moy JK, Khoutorsky A, Asiedu MN, Dussor G, Price TJ. eIF4E phosphorylation influences Bdnf mRNA translation in mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:29.
Ueda T, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fukuyama H, Nagata S, Fukunaga R. Mnk2 and Mnk1 are essential for constitutive and inducible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E but not for cell growth or development. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:6539–49.
Jackson-Laboratory. Body Weight Information for C57BL/6J. 2019.
Decosterd I, Woolf CJ. Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain. 2000;87:149–58.
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994;53:55–63.
Angoa-Perez M, Kane MJ, Briggs DI, Francescutti DM, Kuhn DM. Marble burying and nestlet shredding as tests of repetitive, compulsive-like behaviors in mice. J Vis Exp. 2013;82:50978.
Black BJ, Atmaramani R, Kumaraju R, Plagens S, Romero-Ortega M, Dussor G, et al. Adult mouse sensory neurons on microelectrode arrays exhibit increased spontaneous and stimulus-evoked activity in the presence of interleukin-6. J Neurophysiol. 2018;120:1374–85.
King T, Vera-Portocarrero L, Gutierrez T, Vanderah TW, Dussor G, Lai J, et al. Unmasking the tonic-aversive state in neuropathic pain. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:1364–6.
Reich SH, Sprengeler PA, Chiang GG, Appleman JR, Chen J, Clarine J, et al. Structure-based design of pyridone-aminal eFT508 targeting dysregulated translation by selective mitogen-activated protein kinase interacting kinases 1 and 2 (MNK1/2) inhibition. J Med Chem. 2018;61:3516–40.
Grubb MS, Burrone J. Activity-dependent relocation of the axon initial segment fine-tunes neuronal excitability. Nature. 2010;465:1070–4.
Kuba H, Oichi Y, Ohmori H. Presynaptic activity regulates Na(+) channel distribution at the axon initial segment. Nature. 2010;465:1075–8.
Grubb MS, Shu Y, Kuba H, Rasband MN, Wimmer VC, Bender KJ. Short- and long-term plasticity at the axon initial segment. J Neurosci. 2011;31:16049–55.
Richards GC, Lluka LJ, Smith MT, Haslam C, Moore B, OʼCallaghan J, et al. Effects of long-term opioid analgesics on cognitive performance and plasma cytokine concentrations in patients with chronic low back pain: a cross-sectional pilot study. Pain Rep. 2018;3:e669.
APF. (American Pain Foundation, 2006).
Apkarian AV, Sosa Y, Sonty S, Levy RM, Harden RN, Parrish TB, et al. Chronic back pain is associated with decreased prefrontal and thalamic gray matter density. J Neurosci. 2004;24:10410–5.
Schmidt-Wilcke T, Leinisch E, Straube A, Kampfe N, Draganski B, Diener HC, et al. Gray matter decrease in patients with chronic tension type headache. Neurology. 2005;65:1483–6.
Davis KD, Pope G, Chen J, Kwan CL, Crawley AP, Diamant NE. Cortical thinning in IBS: implications for homeostatic, attention, and pain processing. Neurology. 2008;70:153–4.
Kuchinad A, Schweinhardt P, Seminowicz DA, Wood PB, Chizh BA, Bushnell MC. Accelerated brain gray matter loss in fibromyalgia patients: premature aging of the brain? J Neurosci. 2007;27:4004–7.
Metz AE, Yau HJ, Centeno MV, Apkarian AV, Martina M. Morphological and functional reorganization of rat medial prefrontal cortex in neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:2423–8.
Seminowicz DA, Laferriere AL, Millecamps M, Yu JS, Coderre TJ, Bushnell MC. MRI structural brain changes associated with sensory and emotional function in a rat model of long-term neuropathic pain. Neuroimage. 2009;47:1007–14.
Ji G, Sun H, Fu Y, Li Z, Pais-Vieira M, Galhardo V, et al. Cognitive impairment in pain through amygdala-driven prefrontal cortical deactivation. J Neurosci. 2010;30:5451–64.
Zhang Z, Gadotti VM, Chen L, Souza IA, Stemkowski PL, Zamponi GW. Role of prelimbic GABAergic circuits in sensory and emotional aspects of neuropathic pain. Cell Rep. 2015;12:752–9.
Kelly CJ, Huang M, Meltzer H, Martina M. Reduced glutamatergic currents and dendritic branching of layer 5 pyramidal cells contribute to medial prefrontal cortex deactivation in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:133.
Cheriyan J, Sheets PL. Altered excitability and local connectivity of mpfc-pag neurons in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 2018;38:4829–39.
Gauriau C, Bernard JF. Pain pathways and parabrachial circuits in the rat. Exp Physiol. 2002;87:251–8.
Goncalves L, Dickenson AH. Asymmetric time-dependent activation of right central amygdala neurones in rats with peripheral neuropathy and pregabalin modulation. Eur J Neurosci. 2012;36:3204–13.
Neugebauer V, Li W, Bird GC, Han JS. The amygdala and persistent pain. Neuroscientist. 2004;10:221–34.
Amorim IS, Lach G, Gkogkas CG. The role of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Genet. 2018;9:561.
Aguilar-Valles A, Haji N, De Gregorio D, Matta-Camacho E, Eslamizade MJ, Popic J, et al. Translational control of depression-like behavior via phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2459.
Abrahamsen B, Zhao J, Asante CO, Cendan CM, Marsh S, Martinez-Barbera JP, et al. The cell and molecular basis of mechanical, cold, and inflammatory pain. Science. 2008;321:702–5.
Knowlton WM, Palkar R, Lippoldt EK, McCoy DD, Baluch F, Chen J, et al. A sensory-labeled line for cold: TRPM8-expressing sensory neurons define the cellular basis for cold, cold pain, and cooling-mediated analgesia. J Neurosci. 2013;33:2837–48.
Price TJ, Prescott SA. Inhibitory regulation of the pain gate and how its failure causes pathological pain. Pain. 2015;156:789–92.
Leterrier C. The axon initial segment: an updated viewpoint. J Neurosci. 2018;38:2135–45.
Kuba H, Yamada R, Ishiguro G, Adachi R. Redistribution of Kv1 and Kv7 enhances neuronal excitability during structural axon initial segment plasticity. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8815.
Mitric M, Seewald A, Moschetti G, Sacerdote P, Ferraguti F, Kummer KK, et al. Layer- and subregion-specific electrophysiological and morphological changes of the medial prefrontal cortex in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9479.
Seminowicz DA, Shpaner M, Keaser ML, Krauthamer GM, Mantegna J, Dumas JA, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy increases prefrontal cortex gray matter in patients with chronic pain. J Pain. 2013;14:1573–84.
Rodriguez-Raecke R, Niemeier A, Ihle K, Ruether W, May A. Brain gray matter decrease in chronic pain is the consequence and not the cause of pain. J Neurosci. 2009;29:13746–50.
Rodriguez-Raecke R, Niemeier A, Ihle K, Ruether W, May A. Structural brain changes in chronic pain reflect probably neither damage nor atrophy. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e54475.
Seminowicz DA, Wideman TH, Naso L, Hatami-Khoroushahi Z, Fallatah S, Ware MA, et al. Effective treatment of chronic low back pain in humans reverses abnormal brain anatomy and function. J Neurosci. 2011;31:7540–50.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant R01NS065926 (TJP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiers, S., Mwirigi, J., Pradhan, G. et al. Reversal of peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain and cognitive dysfunction via genetic and tomivosertib targeting of MNK. Neuropsychopharmacol. 45, 524–533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0537-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0537-y
This article is cited by
-
Distinct roles for MNK1 and MNK2 in social and cognitive behavior through kinase-specific regulation of the synaptic proteome and phosphoproteome
Molecular Psychiatry (2026)
-
Nageotte nodules in human dorsal root ganglia reveal neurodegeneration in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Activation of 5-HT6 Receptors in the Ventrolateral Orbital Cortex Produces Anti-Anxiodepressive Effects in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain
Molecular Neurobiology (2025)
-
Chronic Pain–Related Cognitive Deficits: Preclinical Insights into Molecular, Cellular, and Circuit Mechanisms
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Neuroinflammation in Tinnitus
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports (2022)