Abstract
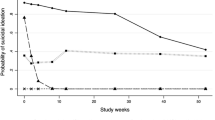
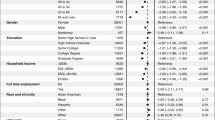
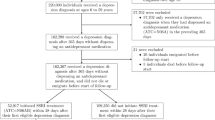
Irritability in pediatric samples is associated with higher rates of subsequent suicide-related outcomes. No study, to date, has evaluated the longitudinal association between irritability and suicidal ideation (SI) in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD). This report evaluated whether irritability is associated with SI at the same visit (i.e., concurrently) and whether early changes in irritability with antidepressant treatment predict subsequent levels of SI. Participants of Combining Medications to Enhance Depression Outcomes (CO-MED, n = 665), Establishing Moderators and Biosignatures of Antidepressant Response in Clinical Care (EMBARC, n = 296), and Suicide Assessment Methodology Study (SAMS, n = 266) were included. Repeated-measures mixed model analyses evaluated concurrent association throughout the trial between irritability (five-item irritability domain of Concise Associated Symptom Tracking scale) and SI (three-item suicidal thoughts factor of Concise Health Risk Tracking scale) after controlling for overall depression (excluding suicidality-related item), and predicted subsequent levels of SI (repeated observations from week-2-to-week-8) based on early (baseline-to-week-2) changes in irritability after controlling for early changes in overall depression. Higher irritability was associated with higher SI concurrently; estimates (standard error) were 0.18 (0.02, p < 0.0001), 0.64 (0.02, p < 0.0001), and 0.26 (0.04, p < 0.0001) in CO-MED, EMBARC, and SAMS respectively. Greater baseline-to-week-2 reductions in irritability predicted lower levels of subsequent SI; estimates (standard errors) were −0.08 (0.03, p = 0.023), −0.50 (0.05, p < 0.0001), and −0.12 (0.05, p = 0.024) in CO-MED, EMBARC, and SAMS, respectively. Controlling for anxiety or insomnia produced similar results. In conclusion, irritability and SI were consistently linked in adults with MDD. These findings support careful assessment of irritability in suicide risk assessment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Curtin S, Hedegaard H. Suicide rates for females and males by race and ethnicity: United States, 1999 and 2017. NCHS Health E-Stat; 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/suicide/rates_1999_2017.pdf. Accessed 11 Mar 2020.
Brown GK, Beck AT, Steer RA, Grisham JR. Risk factors for suicide in psychiatric outpatients: a 20-year prospective study. J Consul Clin Psychol. 2000;68:371–7.
Hawton K, Casanas ICC, Haw C, Saunders K. Risk factors for suicide in individuals with depression: a systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2013;147:17–28.
Hawton K, Sutton L, Haw C, Sinclair J, Harriss L. Suicide and attempted suicide in bipolar disorder: a systematic review of risk factors. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66:693–704.
Orri M, Perret LC, Turecki G, Geoffroy MC. Association between irritability and suicide-related outcomes across the life-course. Systematic review of both community and clinical studies. J Affect Disord. 2018;239:220–33.
Conner KR, Meldrum S, Wieczorek WF, Duberstein PR, Welte JW. The association of irritability and impulsivity with suicidal ideation among 15- to 20-year-old males. Suicide Life-Threat Behav. 2004;34:363–73.
Orri M, Galera C, Turecki G, et al. Association of childhood irritability and depressive/anxious mood profiles with adolescent suicidal ideation and attempts. JAMA Psychiatry 2018;75:465–73.
Pickles A, Aglan A, Collishaw S, Messer J, Rutter M, Maughan B. Predictors of suicidality across the life span: The Isle of Wight study. Psychological Med 2009;40:1453–66.
Kuba T, Yakushi T, Fukuhara H, et al. Suicide-related events among child and adolescent patients during short-term antidepressant therapy. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;65:239–45.
Berk L, Hallam KT, Venugopal K, et al. Impact of irritability: a 2-year observational study of outpatients with bipolar I or schizoaffective disorder. Bipolar Disord 2017;19:184–97.
Melhem NM, Porta G, Oquendo MA, et al. Severity and variability of depression symptoms predicting suicide attempt in high-risk individuals. JAMA Psychiatry 2019;76:603–13.
Boudreaux ED, Larkin C, Kini N, et al. Predictive utility of an emergency department decision support tool in patients with active suicidal ideation. Psychol Serv. 2018;15:270–8.
McGarry A, McDermott MP, Kieburtz K, et al. Risk factors for suicidality in Huntington disease: An analysis of the 2CARE clinical trial. Neurology 2019;92:e1643–e1651.
Perlis RH, Fava M, Trivedi MH, et al. Irritability is associated with anxiety and greater severity, but not bipolar spectrum features, in major depressive disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2009;119:282–9.
Pendse B, Westrin A, Engstrom G. Temperament traits in seasonal affective disorder, suicide attempters with non-seasonal major depression and healthy controls. J Affect Disord. 1999;54:55–65.
Azorin JM, Kaladjian A, Besnier N, et al. Suicidal behaviour in a French Cohort of major depressive patients: characteristics of attempters and nonattempters. J Affect Disord. 2010;123:87–94.
Akiskal HS, Benazzi F. Does the FDA proposed list of possible correlates of suicidality associated with antidepressants apply to an adult private practice population? J Affect Disord. 2006;94:105–10.
Brotman MA, Kircanski K, Stringaris A, Pine DS, Leibenluft E. Irritability in youths: a translational model. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174:520–32.
AP Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Pub; Arlington, VA, 2013.
Fava M, Hwang I, Rush AJ, Sampson N, Walters EE, Kessler RC. The importance of irritability as a symptom of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry 2010;15:856.
Perlis RH, Uher R, Ostacher M, et al. Association between bipolar spectrum features and treatment outcomes in outpatients with major depressive disorderbipolar spectrum features and treatment outcomes in MDD. JAMA Psychiatry 2011;68:351–60.
Jha MK, Minhajuddin A, South C, Rush AJ, Trivedi MH. Irritability and its clinical utility in major depressive disorder: prediction of individual-level acute-phase outcomes using early changes in irritability and depression severity. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:358–66.
Pine DanielS. Heterogeneity in major depressive disorder: lessons from developmental research on irritability. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:331–2.
Jha MK, Grannemann BD, Trombello JM, et al. A structured approach to detecting and treating depression in primary care: VitalSign6 Project. Ann Fam Med. 2019;17:326–35.
Kircanski K, White LK, Tseng WL, et al. A latent variable approach to differentiating neural mechanisms of irritability and anxiety in youth. JAMA Psychiatry 2018;75:631–9.
McCall WV, Benca RM, Rosenquist PB, et al. Reducing Suicidal Ideation Through Insomnia Treatment (REST-IT): a randomized clinical trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:957–65.
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Stewart JW, et al. Combining medications to enhance depression outcomes (CO-MED): acute and long-term outcomes of a single-blind randomized study. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168:689–701.
Trivedi MH, McGrath PJ, Fava M, et al. Establishing moderators and biosignatures of antidepressant response in clinical care (EMBARC): Rationale and design. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;78:11–23.
Trivedi MH, South C, Jha MK, et al. A novel strategy to identify placebo responders: prediction index of clinical and biological markers in the EMBARC Trial. Psychother Psychosom. 2018;87:285–95.
Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Morris DW, et al. Concise health risk tracking scale: a brief self-report and clinician rating of suicidal risk. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72:757–64.
Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Morris DW, et al. Concise associated symptoms tracking scale: a brief self-report and clinician rating of symptoms associated with suicidality. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72:765–74.
Jha MK, Minhajuddin A, South C, Rush AJ, Trivedi MH. Worsening anxiety, irritability, insomnia, or panic predicts poorer antidepressant treatment outcomes: clinical utility and validation of the Concise Associated Symptom Tracking (CAST) Scale. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018;21:325–32.
Minhajuddin A, Jha MK, Chin Fatt C, Trivedi MH. Psychometric properties of Concise Associated Symptom Tracking (CAST) scale and validation of its clinical utility in patients with major depressive disorder: findings from the EMBARC study. Psychiatr Res Clin Pract. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.prcp.20190041.
Williams JB. A structured interview guide for the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988;45:742–7.
Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960;23:56–62.
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Ibrahim HM, et al. The 16-Item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS), clinician rating (QIDS-C), and self-report (QIDS-SR): a psychometric evaluation in patients with chronic major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2003;54:573–83.
Vittengl JR, Clark LA, Kraft D, Jarrett RB. Multiple measures, methods, and moments: a factor-analytic investigation of change in depressive symptoms during acute-phase cognitive therapy for depression. Psychol Med. 2005;35:693–704.
Trombello JM, Killian MO, Grannemann BD, et al. The Concise Health Risk Tracking-Self Report: Psychometrics within a placebo-controlled antidepressant trial among depressed outpatients. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33:185–93.
Jha MK, Minhajuddin A, Greer TL, Carmody T, Rush AJ, Trivedi MH. Early improvement in psychosocial function predicts longer-term symptomatic remission in depressed patients. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0167901.
Jang JM, Park JI, Oh KY, et al. Predictors of suicidal ideation in a community sample: roles of anger, self-esteem, and depression. Psychiatry Res. 2014;216:74–81.
Zhang W, Ding H, Su P, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for attempted suicide in the elderly: a cross-sectional study in Shanghai, China. Int Psychogeriatr. 2017;29:709–15.
Wilks CR, Morland LA, Dillon KH, et al. Anger, social support, and suicide risk in U.S. military veterans. J Psychiatr Res. 2019;109:139–44.
Racine M, Sanchez-Rodriguez E, Galan S, et al. Factors associated with suicidal ideation in patients with chronic non-cancer pain. Pain Med. 2017;18:283–93.
Kampfer N, Staufenbiel S, Wegener I, et al. Suicidality in patients with somatoform disorder-the speechless expression of anger? Psychiatry Res. 2016;246:485–91.
Stringer B, van Meijel B, Eikelenboom M, et al. Recurrent suicide attempts in patients with depressive and anxiety disorders: the role of borderline personality traits. J Affect Disord. 2013;151:23–30.
Hogstedt C, Forsell Y, Hemmingsson T, Lundberg I, Lundin A. Psychological symptoms in late adolescence and long-term risk of suicide and suicide attempt. Suicide Life-Threat Behav. 2018;48:315–27.
Start AR, Allard Y, Adler A, Toblin R. Predicting suicide ideation in the military: the independent role of aggression. Suicide Life-Threat Behav. 2019;49:444–54.
Ducasse D, Jaussent I, Guillaume S, et al. Affect lability predicts occurrence of suicidal ideation in bipolar patients: a two-year prospective study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2017;135:460–9.
Leibenluft E. Irritability in children: what we know and what we need to learn. World Psychiatry. 2017;16:100–1.
Brotman MA, Kircanski K, Leibenluft E. Irritability in children and adolescents. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2017;13:317–41.
Hartley CM, Pettit JW, Castellanos D. Reactive aggression and suicide-related behaviors in children and adolescents: a review and preliminary meta-analysis. Suicide Life-Threat Behav. 2018;48:38–51.
Toohey MJ, DiGiuseppe R. Defining and measuring irritability: construct clarification and differentiation. Clin Psychol Rev. 2017;53:93–108.
Stanley IH, Rogers ML, Hanson JE, Gutierrez PM, Joiner TE. PTSD symptom clusters and suicide attempts among high-risk military service members: a three-month prospective investigation. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2019;87:67–78.
Dolsen MR, Cheng P, Arnedt JT, et al. Neurophysiological correlates of suicidal ideation in major depressive disorder: Hyperarousal during sleep. J Affect Disord. 2017;212:160–6.
Trivedi MH, Jha MK, Kahalnik F, et al. VitalSign(6): a primary care first (PCP-First) model for universal screening and measurement-based care for depression. Pharmaceuticals. 2019;12:71. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020071.
Friedman RA. Antidepressants’ black-box warning-10 years later. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1666–8.
Towbin K, Vidal-Ribas P, Brotman MA, et al. A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of citalopram adjunctive to stimulant medication in youth with chronic severe irritability. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;59:350–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design: MHT. Obtained funding: MT. Data acquisition: MKJ and MT. Data analysis: AM. Data interpretation: MKJ, AM, CCF, KK, AS, EL, and MT. Drafting of the work: MKJ. Revising paper critically for important intellectual content: MKJ, AM, CCF, KK, AS, Leibenluft, MT. Final approval: MKJ, AM, CCF, KK, AS, EL, and MT. The design of CO-MED, EMBARC and SAMS was led by MT. MKJ and MT contributed substantially to the acquisition of data. AM completed the data analysis. MKJ, AM, CCF, KK, AS, EL, and MT contributed to the interpretation of data. MKJ drafted the initial paper and all authors revised paper critically for important intellectual content. All authors provided the final approval to the submitted version and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Findings of this report were presented in part at the 2019 Annual Meeting of American College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, M.K., Minhajuddin, A., Chin Fatt, C. et al. Association between irritability and suicidal ideation in three clinical trials of adults with major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol. 45, 2147–2154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-0769-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-0769-x
This article is cited by
-
Towards treatments targeting the gut to improve behavioural outcomes in autism spectrum disorder
Journal of Neural Transmission (2026)
-
The relationship between irritability and suicidal ideation: the chain mediating effects of rumination and distress tolerance
BMC Psychiatry (2025)
-
Association between overt aggression and suicidal ideation in patients with major depressive disorder: the mediational role of cognitive symptoms
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2025)
-
Prevalence and correlates of irritability among U.S. adults
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
The Presentation of Depression in Depressed Autistic Individuals: A Systematic Review
Review Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders (2024)