Abstract
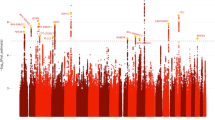
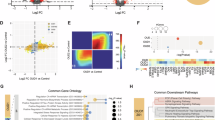
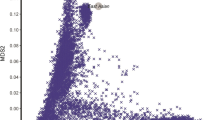
Substance use disorders commonly co-occur with one another and with other psychiatric disorders. They share common features including high impulsivity, negative affect, and lower executive function. We tested whether a common genetic factor undergirds liability to problematic alcohol use (PAU), problematic tobacco use (PTU), cannabis use disorder (CUD), and opioid use disorder (OUD) by applying genomic structural equation modeling to genome-wide association study summary statistics for individuals of European ancestry (Total N = 1,019,521; substance-specific Ns range: 82,707–435,563) while adjusting for the genetics of substance use (Ns = 184,765−632,802). We also tested whether shared liability across SUDs is associated with behavioral constructs (risk-taking, executive function, neuroticism; Ns = 328,339−427,037) and non-substance use psychopathology (psychotic, compulsive, and early neurodevelopmental disorders). Shared genetic liability to PAU, PTU, CUD, and OUD was characterized by a unidimensional addiction risk factor (termed The Addiction-Risk-Factor, independent of substance use. OUD and CUD demonstrated the largest loadings, while problematic tobacco use showed the lowest loading. The Addiction-Risk-Factor was associated with risk-taking, neuroticism, executive function, and non-substance psychopathology, but retained specific variance before and after accounting for the genetics of substance use. Thus, a common genetic factor partly explains susceptibility for alcohol, tobacco, cannabis, and opioid use disorder. The Addiction-Risk-Factor has a unique genetic architecture that is not shared with normative substance use or non-substance psychopathology, suggesting that addiction is not the linear combination of substance use and psychopathology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Degenhardt L, Charlson F, Ferrari A, Santomauro D, Erskine H, Mantilla-Herrara A, et al. The global burden of disease attributable to alcohol and drug use in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5:987–1012.
Bhalla IP, Stefanovics EA, Rosenheck RA. Clinical epidemiology of single versus multiple substance use disorders. Med Care. 2017;55:S24–S32.
Merikangas KR, Kalaydjian A. Magnitude and impact of comorbidity of mental disorders from epidemiologic surveys. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2007;20:353–8.
Palmer RH, Button TM, Rhee SH, Corley RP, Young SE, Stallings MC, et al. Genetic etiology of the common liability to drug dependence: evidence of common and specific mechanisms for DSM-IV dependence symptoms. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012;123 Suppl:S24–32.
Zhou H, Rentsch CT, Cheng Z, Kember RL, Nunez YZ, Sherva RM, et al. Association of OPRM1 functional coding variant with opioid use disorder: a genome-wide association study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.1206.
Sanchez-Roige S, Palmer AA, Clarke TK. Recent efforts to dissect the genetic basis of alcohol use and abuse. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;87:609–18.
Johnson EC, Demontis D, Thorgeirsson TE, Walters RK, Polimanti R, Hatoum AS, et al. A large-scale genome-wide association study meta-analysis of cannabis use disorder. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;0:1032–45.
Polimanti R, Walters RK, Johnson EC, McClintick JN, Adkins AE, Adkins DE, et al. Leveraging genome-wide data to investigate differences between opioid use vs. opioid dependence in 41,176 individuals from the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25:1673–87.
Kranzler HR, Zhou H, Kember RL, Vickers Smith R, Justice AC, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and use disorder in 274,424 individuals from multiple populations. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1499.
Sanchez-Roige S, Palmer AA, Fontanillas P, Elson SL, Research Team, the Substance Use Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics C., Adams MJ, et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis of the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT) in two population-based cohorts. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:107–18.
Walters RK, Polimanti R, Johnson EC, McClintick JN, Adams MJ, Adkins AE, et al. Transancestral GWAS of alcohol dependence reveals common genetic underpinnings with psychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1656–69.
Mallard TT, Savage JE, Johnson EC, Huang Y, Edwards AC, Hottenga JJ, et al. Item-level genome-wide association study of the alcohol use disorders identification test in three population-based cohorts. Am J Psychiatry. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1176/APPI.AJP.2020.20091390.
Sanchez-Roige S, Cox NJ, Johnson EO, Hancock DB, Davis LK. Alcohol and cigarette smoking consumption as genetic proxies for alcohol misuse and nicotine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021;221:108612.
Lee PH, Anttila V, Won H, Feng Y-CA, Rosenthal J, Zhu Z, et al. Genomic relationships, novel loci, and pleiotropic mechanisms across eight psychiatric disorders. Cell. 2019;179:1469–1482.e11.
Carey CE, Agrawal A, Bucholz KK, Hartz SM, Lynskey MT, Nelson EC, et al. Associations between polygenic risk for psychiatric disorders and substance involvement. Front Genet. 2016;7:149.
Karlsson Linnér R, Mallard TT, Barr PB, Sanchez-Roige S, Madole JW, et al. Multivariate analysis of 1.5 million people identifies genetic associations with traits related to self-regulation and addiction. Nat. Neurosci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00908-3.
Abdellaoui A, Smit DJA, van den Brink W, Denys D, Verweij KJH. Genomic relationships across psychiatric disorders including substance use disorders. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021;220:108535.
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND. Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159:1642–52.
Nagel M, Watanabe K, Stringer S, Posthuma D, van der Sluis S. Item-level analyses reveal genetic heterogeneity in neuroticism. Nat Commun. 2018;9:905.
Koob GF, Volkow ND. Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3:760–73.
Zhou H, Sealock JM, Sanchez-Roige S, Clarke TK, Levey DF, Cheng Z, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of problematic alcohol use in 435,563 individuals yields insights into biology and relationships with other traits. Nat Neurosci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-0643-5.
Hatoum A, Mitchell E, Morrison C, Evans L, Keller M, Friedman N, et al. GWAS of over 427,000 individuals establishes GABAergic and synaptic molecular pathways as key for cognitive executive functions. Preprint at bioRxiv (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/674515.
Grotzinger AD, Rhemtulla M, de Vlaming R, Ritchie SJ, Mallard TT, Hill WD, et al. Genomic structural equation modelling provides insights into the multivariate genetic architecture of complex traits. Nat Hum Behav. 2019;3:513–25.
Hancock DB, Guo Y, Reginsson GW, Gaddis NC, Lutz SM, Sherva R, et al. Genome-wide association study across European and African American ancestries identifies a SNP in DNMT3B contributing to nicotine dependence. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1–9.
Liu M, Jiang Y, Wedow R, Li Y, Brazel DM, Chen F, et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use. Nat Genet. 2019;51:237–44.
Pasman JA, Verweij K, Gerring Z, Stringer S, Sanchez-Roige S, Treur JL, et al. GWAS of lifetime cannabis use reveals new risk loci, genetic overlap with psychiatric traits, and a causal influence of schizophrenia. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1161–70.
Edenberg HJ, McClintick JN. Alcohol dehydrogenases, aldehyde dehydrogenases, and alcohol use disorders: a critical review. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2018;42:2281–97.
Bulik-Sullivan BK, Loh PR, Finucane HK, Ripke S, Yang J, Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics C, et al. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2015;47:291–5.
Zhou H, Sealock JM, Sanchez-Roige S, Clarke TK, Levey DF, Cheng Z, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of problematic alcohol use in 435,563 individuals yields insights into biology and relationships with other traits. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:809–18.
Turley P, Walters RK, Maghzian O, Okbay A, Lee JJ, Fontana MA, et al. Multi-trait analysis of genome-wide association summary statistics using MTAG. Nat Genet. 2018;50:229–37.
Liu M, Jiang Y, Wedow R, Li Y, Brazel DM, Chen F, et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use. Nat Genet. 2019;51:237–44.
Strawbridge RJ, Ward J, Lyall LM, Tunbridge EM, Cullen B, Graham N, et al. Genetics of self-reported risk-taking behaviour, trans-ethnic consistency and relevance to brain gene expression. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8:178.
Volkow ND, Koob GF, McLellan AT. Neurobiologic advances from the brain disease model of addiction. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:363–71.
Bondy E, Baranger DA, Balbona JV, Sputo K, Paul SE, Oltmanns T, et al. Neuroticism and reward-related ventral striatum activity: probing vulnerability to stress-related depression. Preprint at bioRxiv (2020). https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/5wd3k.
Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature. 2014;511:421–7.
Stahl EA, Breen G, Forstner AJ, McQuillin A, Ripke S, Trubetskoy V, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat Genet 2019;51:793–803.
Howard DM, Adams MJ, Clarke TK, Hafferty JD, Gibson J, Shirali M, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:343–52.
Demontis D, Walters RK, Martin J, Mattheisen M, Als TD, Agerbo E, et al. Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:63–75.
Arnold PD, Askland KD, Barlassina C, Bellodi L, Bienvenu OJ, Black D, et al. Revealing the complex genetic architecture of obsessive-compulsive disorder using meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1181–8.
Watson HJ, Yilmaz Z, Thornton LM, Hübel C, Coleman J, Gaspar HA, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight risk loci and implicates metabo-psychiatric origins for anorexia nervosa. Nat Genet. 2019;51:1207–14.
Yu D, Sul JH, Tsetsos F, Nawaz MS, Huang AY, Zelaya I, et al. Interrogating the genetic determinants of Tourette’s syndrome and other tiC disorders through genome-wide association studies. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:217–27.
Grove J, Ripke S, Als TD, Mattheisen M, Walters RK, Won H, et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:431–44.
Grotzinger AD, Rhemtulla M, de Vlaming R, Ritchie SJ, Mallard TT, Hill WD, et al. Genomic SEM provides insights into the multivariate genetic architecture of complex traits. Preprint at bioRxiv (2018). https://doi.org/10.1101/305029.
Grotzinger AD, Mallard TT, Akingbuwa WA, Ip HF, Adams MJ, Lewis CM, et al. Genetic architecture of 11 major psychiatric disorders at biobehavioral, functional genomic, and molecular genetic levels of analysis. medRxiv. 2020;18:18–19.
Agrawal A, Scherrer JF, Pergadia ML, Lynskey MT, Madden PA, Sartor CE, et al. A latent class analysis of DSM-IV and fagerström (FTND) criteria for nicotine dependence. Nicotine Tob Res. 2011;13:972–81.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge our contributing studies and the participants in those studies without whom this effort would not be possible. The MVP summary statistics were obtained via an approved dbGaP application (phs001672.v4.p1). The authors thank Million Veteran Program (MVP) staff, researchers, and volunteers, who have contributed to MVP, and especially participants who previously served their country in the military and now generously agreed to enroll in the study. (For details, see https://www.research.va.gov/mvp/ and Gaziano, J.M. et al. Million Veteran Program: A mega-biobank to study genetic influences on health and disease. J Clin Epidemiol 70, 214–23 (2016)). This research is based on data from the Million Veteran Program, Office of Research and Development, Veterans Health Administration, and was supported by the Veterans Administration (VA) Cooperative Studies Program (CSP) award #G002. This study included summary statistics of a genetic study on cannabis use (Pasman et al, 2018 Nature Neuroscience). We would like to acknowledge all participating groups of the International Cannabis Consortium, and in particular the members of the working group including Joelle Pasman, Karin Verweij, Nathan Gillespie, Eske Derks, and Jacqueline Vink. Pasman et al, (2018) included data from the UK Biobank resource under application numbers 9905, 16406, and 25331.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ASH conducted the analysis and wrote the manuscript. ECJ, SMC assisted with the analysis and creation of the figures. RP, HZ, RW, JG, HE, RB, and AA, provided critical commentary on the manuscript and argumentation. RB and AA oversaw all analysis. ASH had access to all data and takes responsibility for the analysis herein.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatoum, A.S., Johnson, E.C., Colbert, S.M.C. et al. The addiction risk factor: A unitary genetic vulnerability characterizes substance use disorders and their associations with common correlates. Neuropsychopharmacol. 47, 1739–1745 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01209-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01209-w
This article is cited by
-
The genetics of cannabis lifetime use
Neuropsychopharmacology (2026)
-
Genome-wide meta-analyses of cross substance use disorders in diverse populations
Molecular Psychiatry (2026)
-
Post-COVID-19 Epidemiology of Substance Use and Affective Concerns
Current Addiction Reports (2026)
-
Risk of substance use disorders in the adult children of parents with severe alcohol use disorder: a nationwide cohort study
BMC Public Health (2025)
-
Whole-exome sequencing study of opioid dependence offers novel insights into the contributions of exome variants
Translational Psychiatry (2025)