Abstract
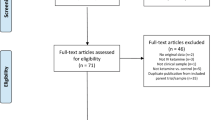
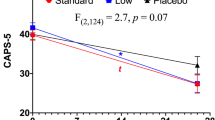
Evidence supporting specific therapies for late-life treatment-resistant depression (LL-TRD) is necessary. This study used Bayesian adaptive randomization to determine the optimal dose for the probability of treatment response (≥50% improvement from baseline on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale) 7 days after a 40 min intravenous (IV) infusion of ketamine 0.1 mg/kg (KET 0.1), 0.25 mg/kg (KET 0.25), or 0.5 mg/kg (KET 0.5), compared to midazolam 0.03 mg/kg (MID) as an active placebo. The goal of this study was to identify the best dose to carry forward into a larger clinical trial. Response durability at day 28, safety and tolerability, and effects on cortical excitation/inhibition (E/I) ratio using resting electroencephalography gamma and alpha power, were also determined. Thirty-three medication-free US military veterans (mean age 62; range: 55–72; 10 female) with LL-TRD were randomized double-blind. The trial was terminated when dose superiority was established. All interventions were safe and well-tolerated. Pre-specified decision rules terminated KET 0.1 (N = 4) and KET 0.25 (N = 5) for inferiority. Posterior probability was 0.89 that day-seven treatment response was superior for KET 0.5 (N = 11; response rate = 70%) compared to MID (N = 13; response rate = 46%). Persistent treatment response at day 28 was superior for KET 0.5 (response rate = 82%) compared to MID (response rate = 37%). KET 0.5 had high posterior probability of increased frontal gamma power (posterior probability = 0.99) and decreased posterior alpha power (0.89) during infusion, suggesting an acute increase in E/I ratio. These results suggest that 0.5 mg/kg is an effective initial IV ketamine dose in LL-TRD, although further studies in individuals older than 75 are required.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Warden D, Ritz L, et al. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: implications for clinical practice. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:28–40.
Nelson JC, Delucchi K, Schneider LS. Efficacy of second generation antidepressants in late-life depression: a meta-analysis of the evidence. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008;16:558–67.
Zanardi R, Cusin C, Rossini D, De Ronchi D, Serretti A. Comparison of response to fluvoxamine in nondemented elderly compared to younger patients affected by major depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2003;23:535–9.
Tedeschini E, Levkovitz Y, Iovieno N, Ameral VE, Nelson JC, Papakostas GI. Efficacy of antidepressants for late-life depression: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of placebo-controlled randomized trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72:1660–8.
Beekman ATF, Copeland J, Prince MJ. Review of community prevalence of depression in later life. Br J Psychiatry. 1999;174:307–11.
Heo M, Murphy CF, Fontaine KR, Bruce ML, Alexopoulos GS. Population projection of US adults with lifetime experience of depressive disorder by age and sex from year 2005 to 2050. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008;23:1266–70.
Kishimoto T, Chawla JM, Hagi K, Zarate CA, Kane JM, Bauer M, et al. Single-dose infusion ketamine and non-ketamine N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists for unipolar and bipolar depression: a meta-analysis of efficacy, safety and time trajectories. Psychol Med. 2016;46:1459–72.
Abdallah CG, Sanacora G, Duman RS, Krystal JH. The neurobiology of depression, ketamine and rapid-acting antidepressants: Is it glutamate inhibition or activation? Pharmacol Ther. 2018;190:148–58.
Abdallah CG, De Feyter HM, Averill LA, Jiang L, Averill CL, Chowdhury GMI, et al. The effects of ketamine on prefrontal glutamate neurotransmission in healthy and depressed subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018;43:2154–60.
Abdallah CG, Jackowski A, Salas R, Gupta S, Sato JR, Mao X, et al. The nucleus accumbens and ketamine treatment in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017;42:1739–46.
Gilbert JR, Zarate CA. Electrophysiological biomarkers of antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant depression: gamma power and long-term potentiation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020;189:172856.
Fagerholm ED, Leech R, Williams S, Zarate CA, Moran RJ, Gilbert JR. Fine-tuning neural excitation/inhibition for tailored ketamine use in treatment-resistant depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:335.
Buzsáki G, Wang X-J. Mechanisms of gamma oscillations. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:203–25.
Murphy N, Ramakrishnan N, Vo-Le B, Vo-Le B, Smith MA, Iqbal T, et al. A randomized cross-over trial to define neurophysiological correlates of AV-101 N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade in healthy veterans. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021;46:820–7.
Lozano-Soldevilla D. On the physiological modulation and potential mechanisms underlying parieto-occipital alpha oscillations. Front Comput Neurosci. 2018;12:23.
Szymkowicz SM, Finnegan N, Dale RM. Failed response to repeat intravenous ketamine infusions in geriatric patients with major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014;34:285–6.
Lipsitz O, Di Vincenzo JD, Rodrigues NB, Cha DS, Lee Y, Greenberg D, et al. Safety, tolerability, and real-world effectiveness of intravenous ketamine in older adults with treatment-resistant depression: a case series. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2021:S1064748121000026.
George D, Gálvez V, Martin D, Kumar D, Leyden J, Hadzi-Pavlovic D, et al. Pilot randomized controlled trial of titrated subcutaneous ketamine in older patients with treatment-resistant depression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2017;25:1199–209.
Ochs-Ross R, Daly EJ, Zhang Y, Lane R, Lim P, Morrison RL, et al. Efficacy and safety of esketamine nasal spray plus an oral antidepressant in elderly patients with treatment-resistant depression-TRANSFORM-3. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2020;28:121–41.
Magnusson KR, Brim BL, Das SR. Selective vulnerabilities of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors during brain aging. Front Aging Neurosci. 2010;2:11.
Boyce RD, Handler SM, Karp JF, Hanlon JT. Age-related changes in antidepressant pharmacokinetics and potential drug-drug interactions: a comparison of evidence-based literature and package insert information. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2012;10:139–50.
Holper L. Optimal doses of antidepressants in dependence on age: combined covariate actions in Bayesian network meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;18:100219.
May Lee K, Lee JJ. Evaluating Bayesian adaptive randomization procedures with adaptive clip methods for multi-arm trials. Stat Methods Med Res. 2021;30:1273–87.
Berry DA. Bayesian clinical trials. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:27–36.
O’Brien B, Green CE, Al-Jurdi R, Chang L, Lijffijt M, Iqbal S, et al. Bayesian adaptive randomization trial of intravenous ketamine for veterans with late-life, treatment-resistant depression. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2019;16:100432.
Chandler GM, Iosifescu DV, Pollack MH, Targum SD, Fava M. Validation of the Massachusetts General Hospital Antidepressant Treatment History Questionnaire (ATRQ). CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010;16:322–5.
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Ibrahim HM, Carmody TJ, Arnow B, Klein DN, et al. The 16-Item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS), clinician rating (QIDS-C), and self-report (QIDS-SR): a psychometric evaluation in patients with chronic major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:573–83.
Guy W. ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare Public Health Service Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration; 1976.
Posner K, Brown GK, Stanley B, Brent DA, Yershova KV, Oquendo MA, et al. The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale: initial validity and internal consistency findings from three multisite studies with adolescents and adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168:1266–77.
Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Putman FW, Southwick SM, Marmar CR, Charney DS, et al. Measurement of dissociative states with the Clinican-Administered Dissociative States Scale (CADSS). J Trauma Stress. 1998;11:125–36.
Overall JE, Gorham DR. The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep. 1962;10:799–812.
Rush AJ, O’Neal BL. Patient Rated Inventory of Side Effects (PRISE): unpublished rating scale. Dallas: University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center; 1999.
Murphy N, Lijffijt M, Ramakrishnan N, Vo-Le B, Vo-Le B, Iqbal S, et al. Does mismatch negativity have utility for NMDA receptor drug development in depression? Braz J Psychiatry. 2021. In press. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-4446-2020-1685.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2019.
Nugent AC, Ballard ED, Gould TD, Park LT, Moaddel R, Brutsche NE, et al. Ketamine has distinct electrophysiological and behavioral effects in depressed and healthy subjects. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:1040–52.
Fava M, Freeman MP, Flynn M, Judge H, Hoeppner BB, Cusin C, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial of intravenous ketamine as adjunctive therapy in treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Mol Psychiatry. 2018;25:1592–603.
Sullivan EM, Timi P, Hong LE, O’Donnell P. Reverse translation of clinical electrophysiological biomarkers in behaving rodents under acute and chronic NMDA receptor antagonism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:719–27.
Korotkova T, Fuchs EC, Ponomarenko A, von Engelhardt J, Monyer H. NMDA receptor ablation on parvalbumin-positive interneurons impairs hippocampal synchrony, spatial representations, and working memory. Neuron. 2010;68:557–69.
Kocsis B. Differential role of NR2A and NR2B subunits in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist-induced aberrant cortical gamma oscillations. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;71:987–95.
Ramakrishnan N, Lijffijt M, Green CE, Balderston NL, Murphy N, Grillon C, et al. Neurophysiological and clinical effects of the NMDA receptor antagonist lanicemine (BHV-5500) in PTSD: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Depress Anxiety. 2021;38:1108–19.
Chaumon M, Busch NA. Prestimulus neural oscillations inhibit visual perception via modulation of response gain. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014;26:2514–29.
Iemi L, Chaumon M, Crouzet SM, Busch NA. Spontaneous neural oscillations bias perception by modulating baseline excitability. J Neurosci. 2017;37:807–19.
Banerjee P, Donello JE, Hare B, Duman RS. Rapastinel, an NMDAR positive modulator, produces distinct behavioral, sleep, and EEG profiles compared with ketamine. Behav Brain Res. 2020;391:112706.
Schumacher J, Thomas AJ, Peraza LR, Firbank M, Cromarty R, Hamilton CA, et al. EEG alpha reactivity and cholinergic system integrity in Lewy body dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020;12:46.
Fogaça MV, Duman RS. Cortical GABAergic dysfunction in stress and depression: new insights for therapeutic interventions. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:87.
Lissemore JI, Bhandari A, Mulsant BH, Lenze EJ, Reynolds CF, Karp JF, et al. Reduced GABAergic cortical inhibition in aging and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018;43:2277–84.
Farmer CA, Gilbert JR, Moaddel R, George J, Adeojo L, Lovett J, et al. Ketamine metabolites, clinical response, and gamma power in a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial for treatment-resistant major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020;45:1398–404.
Acknowledgements
The opinions expressed reflect those of the authors and not necessarily those of the Department of Veterans Affairs, or the U.S. government. This work is supported by a Department of Veterans Affairs Merit Award (Grant # CX-001205-01AI), and by facilities and resources of the Michael E DeBakey VA Medical Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was conceptualized by SJM, RAJ, ACS, CEG, and ML. Study procedures and data collection were performed by SI, LCC, TI, ML, SJM, ACS, LH, and DAF. Data pre-processing and analysis was performed by CG, NM, CNH, and NR. Interpretation of the data was performed by SJM, CEG, ML, NM, and CNH. The first draft of the article was written by ML, NM, and SJM. All authors contributed to the drafting and revising of the manuscript. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
SJM has served as a consultant to Allergan, Alkermes, Axsome Therapeutics, BioXcel Therapeutics, Clexio Biosciences, Eleusis, EMA Wellness, Engrail Therapeutics, Greenwich Biosciences, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Levo Therapeutics, Perception Neurosciences, Neurocrine, Relmada Therapeutics, Sage Therapeutics, Seelos Therapeutics, and Signant Health. He has served as an investigator for studies funded by Janssen, Merck, NeuroRx, and Sage Therapeutics, and has received research support from Biohaven Pharmaceuticals and VistaGen Therapeutics. RKA has served on the Janssen advisory and speaker board. ML has served as principal investigator for trials funded by NeuroRx and VistaGen Therapeutics. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lijffijt, M., Murphy, N., Iqbal, S. et al. Identification of an optimal dose of intravenous ketamine for late-life treatment-resistant depression: a Bayesian adaptive randomization trial. Neuropsychopharmacol. 47, 1088–1095 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01242-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01242-9
This article is cited by
-
A randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial of ketamine in Rett syndrome
Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (2025)
-
Neurophysiological correlates of ketamine-induced dissociative state in bipolar disorder: insights from real-world clinical settings
Molecular Psychiatry (2025)
-
Non-improvement predicts subsequent non-response to repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for depression: a re-analysis of a 2-week open-label study in patients with unipolar and bipolar depression
Translational Psychiatry (2024)
-
Treating intrusive memories after trauma in healthcare workers: a Bayesian adaptive randomised trial developing an imagery-competing task intervention
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Neural complexity EEG biomarkers of rapid and post-rapid ketamine effects in late-life treatment-resistant depression: a randomized control trial
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)