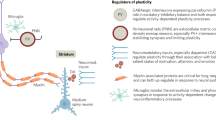
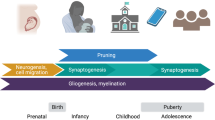
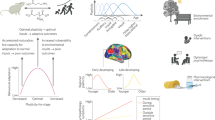
Abstract
Identifying when periods of enhanced neurobiological plasticity occur throughout the human cortex is foundational to understanding when different neural circuits and the psychological processes that they support will be most impacted by adverse and enriching environments. Animal research has identified “critical periods” of plasticity that occur in primary cortices and enable profound environment-dependent sculpting of sensory function early in life. Recent evidence suggests that critical periods may additionally occur in the human brain during childhood and adolescence, where they are hypothesized to unfold hierarchically across sensorimotor and association cortical regions. In this article, we consider neural, environmental, and behavioral evidence for hierarchical critical periods in human development. We review neuroimaging studies that have characterized the development of in vivo correlates of critical period plasticity and synthesize research that has explored when lower-order and higher-order cortical regions exhibit differential environmental sensitivity. We outline how the field is well-positioned to further investigate the precise nature, timing, and consequences of putative critical periods and summarize approaches to making progress in this area. We end by describing the relevance of critical periods for understanding youth psychiatric risk and for informing age-specific environmental enrichment interventions capable of supporting healthy development by fostering resiliency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 13 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $19.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larsen B, Sydnor VJ, Keller AS, Yeo BTT, Satterthwaite TD. A critical period plasticity framework for the sensorimotor–association axis of cortical neurodevelopment. Trends Neurosci. 2023;46:847–62.
Reh RK, Dias BG, Nelson CA, Kaufer D, Werker JF, Kolb B, et al. Critical period regulation across multiple timescales. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:23242–51.
Takesian AE, Hensch TK. Balancing plasticity/stability across brain development. In: Merzenich MM, Nahum M, Van Vleet TM, editors. Progress in brain research, Vol. 207, Elsevier; 2013. p. 3–34.
Herzberg MP, Nielsen AN, Luby J, Sylvester CM. Measuring neuroplasticity in human development: the potential to inform the type and timing of mental health interventions. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024;50:124–36.
Gabard-Durnam L, McLaughlin KA. Sensitive periods in human development: charting a course for the future. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2020;36:120–8.
Hensch TK. Critical period plasticity in local cortical circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:877–88.
Larsen B, Luna B. Adolescence as a neurobiological critical period for the development of higher-order cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;94:179–95.
Lee HHC, Bernard C, Ye Z, Acampora D, Simeone A, Prochiantz A, et al. Genetic Otx2 mis-localization delays critical period plasticity across brain regions. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:680–8.
Kalish BT, Barkat TR, Diel EE, Zhang EJ, Greenberg ME, Hensch TK. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing of mouse auditory cortex reveals critical period triggers and brakes. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2020;117:11744–52.
Sydnor VJ, Larsen B, Bassett DS, Alexander-Bloch A, Fair DA, Liston C, et al. Neurodevelopment of the association cortices: patterns, mechanisms, and implications for psychopathology. Neuron. 2021;109:2820–46.
Nelson CA, Gabard-Durnam L. Early adversity and critical periods: neurodevelopmental consequences of violating the expectable environment. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43:133–43.
Sisk LM, Gee DG. Stress and adolescence: vulnerability and opportunity during a sensitive window of development. Current Opin Psychol. 2022;44:286–92.
Gervain J, Vines BW, Chen LM, Seo RJ, Hensch TK, Werker JF, et al. Valproate reopens critical-period learning of absolute pitch. Front Syst Neurosci. 2013;7:102.
Luby JL, Herzberg MP, Hoyniak C, Tillman R, Lean RE, Brady R, et al. Basic environmental supports for positive brain and cognitive development in the first year of life. JAMA Pediatr. 2024;178:465–72.
Luby J, Baram TZ, Rogers C, Barch DM. Neurodevelopmental optimization after early life adversity: cross species studies to elucidate sensitive periods and brain mechanisms to inform early intervention. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43:744–51.
Vanderwert RE, Marshall PJ, Nelson CA, Zeanah CH, Fox NA. Timing of intervention affects brain electrical activity in children exposed to severe psychosocial neglect. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11415.
Nelson CA, Fox NA, Zeanah CH. Romania’s abandoned children: the effects of early profound psychosocial deprivation on the course of human development. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2023;32:515–21.
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN. The period of susceptibility to the physiological effects of unilateral eye closure in kittens. J Physiol. 1970;206:419–36.
Werker JF, Hensch TK. Critical periods in speech perception: new directions. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66:173–96.
Hübener M, Bonhoeffer T. Neuronal plasticity: beyond the critical period. Cell. 2014;159:727–37.
Dehorter N, Del Pino I. Shifting developmental trajectories during critical periods of brain formation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:283.
Hensch TK, Quinlan EM. Critical periods in amblyopia. Visual Neurosci. 2018;35:E014.
Luciana M, Collins P.F. Is adolescence a sensitive period for the development of incentive-reward motivation? In: Andersen S.L., editor. Sensitive periods of brain development and preventive interventions. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022. p. 79–99.
Hensch TK. Critical period regulation. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:549–79.
Stern EA, Maravall M, Svoboda K. Rapid development and plasticity of layer 2/3 maps in rat barrel cortex in vivo. Neuron. 2001;31:305–15.
Lendvai B, Stern EA, Chen B, Svoboda K. Experience-dependent plasticity of dendritic spines in the developing rat barrel cortex in vivo. Nature. 2000;404:876–81.
Han YK, Köver H, Insanally MN, Semerdjian JH, Bao S. Early experience impairs perceptual discrimination. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1191–7.
de Villers-Sidani E, Chang EF, Bao S, Merzenich MM. Critical period window for spectral tuning defined in the primary auditory cortex (A1) in the rat. J Neurosci. 2007;27:180–9.
Fagiolini M, Hensch TK. Inhibitory threshold for critical-period activation in primary visual cortex. Nature. 2000;404:183–6.
Fagiolini M, Pizzorusso T, Berardi N, Domenici L, Maffei L. Functional postnatal development of the rat primary visual cortex and the role of visual experience: dark rearing and monocular deprivation. Vision Res. 1994;34:709–20.
Di Cristo G, Chattopadhyaya B, Kuhlman SJ, Fu Y, Bélanger M-C, Wu CZ, et al. Activity-dependent PSA expression regulates inhibitory maturation and onset of critical period plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1569–77.
Chattopadhyaya B, Cristo GD, Higashiyama H, Knott GW, Kuhlman SJ, Welker E, et al. Experience and activity-dependent maturation of perisomatic GABAergic innervation in primary visual cortex during a postnatal critical period. J Neurosci. 2004;24:9598–611.
Fagiolini M, Fritschy J-M, Löw K, Möhler H, Rudolph U, Hensch TK. Specific GABAA circuits for visual cortical plasticity. Science. 2004;303:1681–3.
Harauzov A, Spolidoro M, DiCristo G, Pasquale RD, Cancedda L, Pizzorusso T, et al. Reducing intracortical inhibition in the adult visual cortex promotes ocular dominance plasticity. J Neurosci. 2010;30:361–71.
Cisneros-Franco JM, Villers-Sidani É, de. Reactivation of critical period plasticity in adult auditory cortex through chemogenetic silencing of parvalbumin-positive interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019;116:26329–31.
Sale A, Maya Vetencourt JF, Medini P, Cenni MC, Baroncelli L, De Pasquale R, et al. Environmental enrichment in adulthood promotes amblyopia recovery through a reduction of intracortical inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:679–81.
Gu Y, Tran T, Murase S, Borrell A, Kirkwood A, Quinlan EM. Neuregulin-dependent regulation of fast-spiking interneuron excitability controls the timing of the critical period. J Neurosci. 2016;36:10285–95.
Moissidis M, Abbasova L, Alis R, Bernard C, Domínguez Y, Qin S, et al. A postnatal molecular switch drives the activity-dependent maturation of parvalbumin interneurons. [Preprint] 2024. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.08.588555.
Lensjø KK, Lepperød ME, Dick G, Hafting T, Fyhn M. Removal of perineuronal nets unlocks juvenile plasticity through network mechanisms of decreased inhibition and increased gamma activity. J Neurosci. 2017;37:1269–83.
Faini G, Aguirre A, Landi S, Lamers D, Pizzorusso T, Ratto GM, et al. Perineuronal nets control visual input via thalamic recruitment of cortical PV interneurons. eLife. 2018;7:e41520.
Rochefort NL, Garaschuk O, Milos R-I, Narushima M, Marandi N, Pichler B, et al. Sparsification of neuronal activity in the visual cortex at eye-opening. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:15049–54.
Frye CG, MacLean JN. Spontaneous activations follow a common developmental course across primary sensory areas in mouse neocortex. J Neurophysiol. 2016;116:431–7.
Nakazawa S, Iwasato T. Spatial organization and transitions of spontaneous neuronal activities in the developing sensory cortex. Dev Growth Differ. 2021;63:323–39.
Nakazawa S, Yoshimura Y, Takagi M, Mizuno H, Iwasato T. Developmental phase transitions in spatial organization of spontaneous activity in postnatal barrel cortex layer 4. J Neurosci. 2020;40:7637–50.
Golshani P, Gonçalves JT, Khoshkhoo S, Mostany R, Smirnakis S, Portera-Cailliau C. Internally mediated developmental desynchronization of neocortical network activity. J Neurosci. 2009;29:10890–9.
Innocenti GM, Price DJ. Exuberance in the development of cortical networks. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:955–65.
Chini M, Pfeffer T, Hanganu-Opatz I. An increase of inhibition drives the developmental decorrelation of neural activity. eLife. 2022;11:e78811.
Chittajallu R, Isaac JTR. Emergence of cortical inhibition by coordinated sensory-driven plasticity at distinct synaptic loci. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:1240–8.
Singh SK, Stogsdill JA, Pulimood NS, Dingsdale H, Kim YH, Pilaz L-J, et al. Astrocytes assemble thalamocortical synapses by bridging Nrx1α and NL1 via hevin. Cell. 2016;164:183–96.
Gu Y, Huang S, Chang MC, Worley P, Kirkwood A, Quinlan EM. Obligatory role for the immediate early gene NARP in critical period plasticity. Neuron. 2013;79:335–46.
Cruikshank SJ, Lewis TJ, Connors BW. Synaptic basis for intense thalamocortical activation of feedforward inhibitory cells in neocortex. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:462–8.
Huang ZJ, Kirkwood A, Pizzorusso T, Porciatti V, Morales B, Bear MF, et al. BDNF regulates the maturation of inhibition and the critical period of plasticity in mouse visual cortex. Cell. 1999;98:739–55.
Sugiyama S, Nardo AAD, Aizawa S, Matsuo I, Volovitch M, Prochiantz A, et al. Experience-dependent transfer of Otx2 homeoprotein into the visual cortex activates postnatal plasticity. Cell. 2008;134:508–20.
Gibel-Russo R, Benacom D, Di Nardo AA. Non-cell-autonomous factors implicated in parvalbumin interneuron maturation and critical periods. Front Neural Circuits. 2022;16:875873.
Mataga N, Nagai N, Hensch TK. Permissive proteolytic activity for visual cortical plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2002;99:7717–21.
Westacott LJ, Wilkinson LS. Complement dependent synaptic reorganisation during critical periods of brain development and risk for psychiatric disorder. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:840266.
Coulthard LG, Hawksworth OA, Woodruff TM. Complement: the emerging architect of the developing brain. Trends Neurosci. 2018;41:373–84.
Mataga N, Mizuguchi Y, Hensch TK. Experience-dependent pruning of dendritic spines in visual cortex by tissue plasminogen activator. Neuron. 2004;44:1031–41.
Oray S, Majewska A, Sur M. Dendritic spine dynamics are regulated by monocular deprivation and extracellular matrix degradation. Neuron. 2004;44:1021–30.
Huang X, Stodieck SK, Goetze B, Cui L, Wong MH, Wenzel C, et al. Progressive maturation of silent synapses governs the duration of a critical period. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:E3131–E40.
Dorrn AL, Yuan K, Barker AJ, Schreiner CE, Froemke RC. Developmental sensory experience balances cortical excitation and inhibition. Nature. 2010;465:932–6.
Toyoizumi T, Miyamoto H, Yazaki-Sugiyama Y, Atapour N, Hensch TK, Miller KD. A theory of the transition to critical period plasticity: inhibition selectively suppresses spontaneous activity. Neuron. 2013;80:51–63.
Ribic A, Crair MC, Biederer T. Synapse-selective control of cortical maturation and plasticity by parvalbumin-autonomous action of SynCAM 1. Cell Rep. 2019;26:381–93.e6.
Ribic A, Biederer T. Emerging roles of synapse organizers in the regulation of critical periods. Neural Plast. 2019;2019:1538137.
Pizzorusso T, Medini P, Berardi N, Chierzi S, Fawcett JW, Maffei L. Reactivation of ocular dominance plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science. 2002;298:1248–51.
Tomassy GS, Berger DR, Chen H-H, Kasthuri N, Hayworth KJ, Vercelli A, et al. Distinct profiles of myelin distribution along single axons of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex. Science. 2014;344:319–24.
Stedehouder J, Couey JJ, Brizee D, Hosseini B, Slotman JA, Dirven CMF, et al. Fast-spiking parvalbumin interneurons are frequently myelinated in the cerebral cortex of mice and humans. Cerebral Cortex. 2017;27:5001–13.
McGee AW, Yang Y, Fischer QS, Daw NW, Strittmatter SM. Experience-driven plasticity of visual cortex limited by myelin and Nogo receptor. Science. 2005;309:2222–6.
Xin W, Kaneko M, Roth RH, Zhang A, Nocera S, Ding JB, et al. Oligodendrocytes and myelin limit neuronal plasticity in visual cortex. Nature. 2024;633:856–63.
Zemmar A, Chen C-C, Weinmann O, Kast B, Vajda F, Bozeman J, et al. Oligodendrocyte- and neuron-specific nogo-a restrict dendritic branching and spine density in the adult mouse motor cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2018;28:2109–17.
Raiker SJ, Lee H, Baldwin KT, Duan Y, Shrager P, Giger RJ. Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein and Nogo negatively regulate activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci. 2010;30:12432–45.
Morishita H, Miwa JM, Heintz N, Hensch TK. Lynx1, a cholinergic brake limits plasticity in adult visual cortex. Science. 2010;330:1238–40.
Disney AA, Aoki C, Hawken MJ. Gain modulation by nicotine in macaque V1. Neuron. 2007;56:701–13.
Gil Z, Connors BW, Amitai Y. Differential regulation of neocortical synapses by neuromodulators and activity. Neuron. 1997;19:679–86.
Sajo M, Ellis-Davies G, Morishita H. Lynx1 Limits dendritic spine turnover in the adult visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2016;36:9472–8.
Rowlands D, Lensjø KK, Dinh T, Yang S, Andrews MR, Hafting T, et al. Aggrecan directs extracellular matrix-mediated neuronal plasticity. J Neurosci. 2018;38:10102–13.
Pöpplau JA, Schwarze T, Dorofeikova M, Pochinok I, Günther A, Marquardt A, et al. Reorganization of adolescent prefrontal cortex circuitry is required for mouse cognitive maturation. Neuron. 2024;112:421–40.e7.
Koss WA, Belden CE, Hristov AD, Juraska JM. Dendritic remodeling in the adolescent medial prefrontal cortex and the basolateral amygdala of male and female rats. Synapse. 2014;68:61–72.
Rios O, Villalobos J. Postnatal development of the afferent projections from the dorsomedial thalamic nucleus to the frontal cortex in mice. Dev Brain Res. 2004;150:47–50.
Benoit LJ, Holt ES, Posani L, Fusi S, Harris AZ, Canetta S, et al. Adolescent thalamic inhibition leads to long-lasting impairments in prefrontal cortex function. Nat Neurosci. 2022;25:714–25.
Petersen D, Raudales R, Silva AK, Kellendonk C, Canetta S. Adolescent thalamoprefrontal inhibition leads to changes in intrinsic prefrontal network connectivity. eNeuro. 2024;11:ENEURO.0284-24.2024.
Caballero A, Flores-Barrera E, Cass DK, Tseng KY. Differential regulation of parvalbumin and calretinin interneurons in the prefrontal cortex during adolescence. Brain Struct Funct. 2014;219:395–406.
Miyamae T, Chen K, Lewis DA, Gonzalez-Burgos G. Distinct physiological maturation of parvalbumin-positive neuron subtypes in mouse prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci. 2017;37:4883–902.
Paylor JW, Lins BR, Greba Q, Moen N, de Moraes RS, Howland JG, et al. Developmental disruption of perineuronal nets in the medial prefrontal cortex after maternal immune activation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37580.
Bicks LK, Yamamuro K, Flanigan ME, Kim JM, Kato D, Lucas EK, et al. Prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons require juvenile social experience to establish adult social behavior. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1003.
Piekarski DJ, Boivin JR, Wilbrecht L. Ovarian hormones organize the maturation of inhibitory neurotransmission in the frontal cortex at puberty onset in female mice. Curr Biol. 2017;27:1735–45.e3.
Mastro K, Lee W-C, Wang W, Stevens B, Sabatini BL. Delayed developmental maturation of frontal cortical circuits impacts decision-making. [Preprint] 2025 Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.24.595609.
Drzewiecki CM, Willing J, Juraska JM. Synaptic number changes in the medial prefrontal cortex across adolescence in male and female rats: a role for pubertal onset. Synapse. 2016;70:361–8.
Evrard MR, Li M, Shen H, Smith SS. Preventing adolescent synaptic pruning in mouse prelimbic cortex via local knockdown of α4βδ GABAA receptors increases anxiety response in adulthood. Sci Rep. 2021;11:21059.
Caballero A, Orozco A, Tseng KY. Developmental regulation of excitatory-inhibitory synaptic balance in the prefrontal cortex during adolescence. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021;118:60–63.
Drzewiecki CM, Willing J, Juraska JM. Influences of age and pubertal status on number and intensity of perineuronal nets in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Struct Funct. 2020;225:2495–507.
Baker KD, Gray AR, Richardson R. The development of perineuronal nets around parvalbumin GABAergic neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala of rats. Behav Neurosci. 2017;131:289–303.
Gildawie KR, Honeycutt JA, Brenhouse HC. Region-specific effects of maternal separation on perineuronal net and parvalbumin-expressing interneuron formation in male and female rats. Neuroscience. 2020;428:23–37.
Falk EN, Norman KJ, Garkun Y, Demars MP, Im S, Taccheri G, et al. Nicotinic regulation of local and long-range input balance drives top-down attentional circuit maturation. Sci Adv. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abe1527.
Hijazi S, Pascual-García M, Nabawi Y, Kushner SA. A critical period for prefrontal cortex PV interneuron myelination and maturation [Preprint] 2025 Available from:https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.15.553393.
Canetta SE, Holt ES, Benoit LJ, Teboul E, Sahyoun GM, Ogden RT, et al. Mature parvalbumin interneuron function in prefrontal cortex requires activity during a postnatal sensitive period. eLife. 2022;11:e80324.
Nabel EM, Garkun Y, Koike H, Sadahiro M, Liang A, Norman KJ, et al. Adolescent frontal top-down neurons receive heightened local drive to establish adult attentional behavior in mice. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3983.
Makinodan M, Rosen KM, Ito S, Corfas G. A critical period for social experience–dependent oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination. Science. 2012;337:1357–60.
Bicks LK, Peng M, Taub A, Akbarian S, Morishita H. An adolescent sensitive period for social dominance hierarchy plasticity is regulated by cortical plasticity modulators in mice. Front Neural Circuits. 2021;15:676308.
Somel M, Franz H, Yan Z, Lorenc A, Guo S, Giger T, et al. Transcriptional neoteny in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:5743–8.
Bufill E, Agustí J, Blesa R. Human neoteny revisited: the case of synaptic plasticity. Am J Hum Biol. 2011;23:729–39.
Miller DJ, Duka T, Stimpson CD, Schapiro SJ, Baze WB, McArthur MJ, et al. Prolonged myelination in human neocortical evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:16480–5.
Charvet CJ, Finlay BL. Evo-devo and the primate isocortex: the central organizing role of intrinsic gradients of neurogenesis. Brain Behav Evol. 2014;84:81–92.
Sydnor VJ, Satterthwaite TD. Neuroimaging of plasticity mechanisms in the human brain: from critical periods to psychiatric conditions. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;48:1–2.
Sydnor VJ, Bagautdinova J, Larsen B, Arcaro MJ, Barch DM, Bassett DS, et al. Human thalamocortical structural connectivity develops in line with a hierarchical axis of cortical plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2025;28:1772–86.
Lewis L, Corcoran M, Cho KIK, Kwak Y, Hayes RA, Larsen B, et al. Age-associated alterations in thalamocortical structural connectivity in youths with a psychosis-spectrum disorder. Schizophr. 2023;9:1–11.
Avery SN, Huang AS, Sheffield JM, Rogers BP, Vandekar S, Anticevic A, et al. Development of thalamocortical structural connectivity in typically developing and psychosis spectrum youths. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2022;7:782–92.
Parr AC, Perica MI, Calabro FJ, Foran W, Moon CH, Hetherington H, et al. Adolescent maturation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex glutamate:GABA and cognitive function is supported by dopamine-related neurobiology. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;30:2558–72.
Takado Y, Takuwa H, Sampei K, Urushihata T, Takahashi M, Shimojo M, et al. MRS-measured glutamate versus GABA reflects excitatory versus inhibitory neural activities in awake mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022;42:197–212.
Sydnor VJ, Larsen B, Seidlitz J, Adebimpe A, Alexander-Bloch AF, Bassett DS, et al. Intrinsic activity development unfolds along a sensorimotor–association cortical axis in youth. Nat Neurosci. 2023;26:638–49.
Nishio M, Ellwood-Lowe ME, Woodburn M, McDermott CL, Park AT, Tooley UA, et al. The development of neural inhibition across species: insights from the Hurst exponent. J Neurosci. 2025;e0025252025. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0025-25.2025.
Larsen B, Cui Z, Adebimpe A, Pines A, Alexander-Bloch A, Bertolero M, et al. A developmental reduction of the excitation:inhibition ratio in association cortex during adolescence. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabj8750.
Perica MI, Calabro FJ, Larsen B, Foran W, Yushmanov VE, Hetherington H, et al. Development of frontal GABA and glutamate supports excitation/inhibition balance from adolescence into adulthood. Prog Neurobiol. 2022;219:102370.
Thomson AR, Hwa H, Pasanta D, Hopwood B, Powell HJ, Lawrence R, et al. The developmental trajectory of 1H-MRS brain metabolites from childhood to adulthood. Cereb Cortex. 2024;34:bhae046.
Widegren E, Frick MA, Hoppe JM, Weis J, Möller S, Fällmar D, et al. The influence of anterior cingulate GABA+ and glutamate on emotion regulation and reactivity in adolescents and adults. Dev Psychobiol. 2024;66:e22492.
Volk C, Jaramillo V, Studler M, Furrer M, O’Gorman Tuura RL, Huber R. Diurnal changes in human brain glutamate + glutamine levels in the course of development and their relationship to sleep. NeuroImage. 2019;196:269–75.
Zhang S, Larsen B, Sydnor VJ, Zeng T, An L, Yan X, et al. In vivo whole-cortex marker of excitation-inhibition ratio indexes cortical maturation and cognitive ability in youth. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2024;121:e2318641121.
Saberi A, Wischnewski KJ, Jung K, Lotter LD, Schaare HL, Banaschewski T, et al. Adolescent maturation of cortical excitation-inhibition ratio based on individualized biophysical network modeling. Sci Adv. 2025;11:eadr8164.
McKeon SD, Perica MI, Parr AC, Calabro FJ, Foran W, Hetherington H, et al. Aperiodic EEG and 7T MRSI evidence for maturation of E/I balance supporting the development of working memory through adolescence. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024;66:101373.
Bero J, Humphries C, Li Y, Kumar A, Lee H, Shinn M, et al. Temporal and spatial scales of resting-state human cortical activity throughout lifespan. [Preprint] 2025 Available from:https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.03.28.645952.
Calabro FJ, LeCroy D, Foran W, Sydnor VJ, Parr AC, Constantinidis C, et al. Developmental decorrelation of local cortical activity through adolescence supports high-dimensional encoding and working memory. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025;73:101541.
Lopez-Larson MP, Anderson JS, Ferguson MA, Yurgelun-Todd D. Local brain connectivity and associations with gender and age. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2010;1:187–97.
McKeon SD, Perica MI, Calabro FJ, Foran W, Hetherington H, Moon C-H, et al. Prefrontal excitation/inhibition balance supports adolescent enhancements in circuit signal-to-noise ratio. Prog Neurobiol. 2024;243:102695.
Baum GL, Flournoy JC, Glasser MF, Harms MP, Mair P, Sanders AFP, et al. Graded variation in T1w/T2w ratio during adolescence: measurement, caveats, and implications for development of cortical myelin. J Neurosci. 2022;42:5681–94.
Sydnor VJ, Petrie D, McKeon SD, Famalette A, Foran W, Calabro FJ, et al. Heterochronous laminar maturation in the human prefrontal cortex. bioRxiv. [Preprint] 2025 Available from:https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.01.30.635751.
Nishio M, Liu X, Mackey AP, Arcaro MJ. Myelination across cortical hierarchies and depths in humans and macaques. bioRxiv. [Preprint] 2025 Available from:https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.02.06.636851.
Norbom LB, Doan NT, Alnæs D, Kaufmann T, Moberget T, Rokicki J, et al. Probing brain developmental patterns of myelination and associations with psychopathology in youths using gray/white matter contrast. Biol Psychiatry. 2019;85:389–98.
Grydeland H, Vértes PE, Váša F, Romero-Garcia R, Whitaker K, Alexander-Bloch AF, et al. Waves of maturation and senescence in micro-structural MRI markers of human cortical myelination over the lifespan. Cereb Cortex. 2019;29:1369–81.
Hill J, Inder T, Neil J, Dierker D, Harwell J, Essen DV. Similar patterns of cortical expansion during human development and evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:13135–40.
Mesulam MM. From sensation to cognition. Brain. 1998;121:1013–52.
Margulies DS, Ghosh SS, Goulas A, Falkiewicz M, Huntenburg JM, Langs G, et al. Situating the default-mode network along a principal gradient of macroscale cortical organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:12574–9.
Burt JB, Demirtaş M, Eckner WJ, Navejar NM, Ji JL, Martin WJ, et al. Hierarchy of transcriptomic specialization across human cortex captured by structural neuroimaging topography. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1251–9.
Huntenburg JM, Bazin P-L, Margulies DS. Large-scale gradients in human cortical organization. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22:21–31.
Hilgetag CC, Beul SF, van Albada SJ, Goulas A. An architectonic type principle integrates macroscopic cortico-cortical connections with intrinsic cortical circuits of the primate brain. Netw Neurosci. 2019;3:905–23.
Xu T, Nenning K-H, Schwartz E, Hong S-J, Vogelstein JT, Goulas A, et al. Cross-species functional alignment reveals evolutionary hierarchy within the connectome. Neuroimage. 2020;223:117346.
Flechsig of Leipsic P. Developmental (myelogenetic) localisation of the cerebral cortex in the human subject. Lancet. 1901;158:1027–30.
Huttenlocher PR, Dabholkar AS. Regional differences in synaptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1997;387:167–78.
Gogtay N, Giedd JN, Lusk L, Hayashi KM, Greenstein D, Vaituzis AC, et al. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004;101:8174–9.
Rakesh D, Lee PA, Gaikwad A, McLaughlin KA. Annual research review: associations of socioeconomic status with cognitive function, language ability, and academic achievement in youth: a systematic review of mechanisms and protective factors. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2025;66:417–39.
Amso D, Salhi C, Badre D. The relationship between cognitive enrichment and cognitive control: a systematic investigation of environmental influences on development through socioeconomic status. Dev Psychobiol. 2019;61:159–78.
Lurie LA, Hagen MP, McLaughlin KA, Sheridan MA, Meltzoff AN, Rosen ML. Mechanisms linking socioeconomic status and academic achievement in early childhood: Cognitive stimulation and language. Cogn Dev. 2021;58:101045.
Evans GW, Gonnella C, Marcynyszyn LA, Gentile L, Salpekar N. The role of chaos in poverty and children’s socioemotional adjustment. Psychol Sci. 2005;16:560–5.
Leventhal T, Brooks-Gunn J. The neighborhoods they live in: the effects of neighborhood residence on child and adolescent outcomes. Psychol Bull. 2000;126:309–37.
Noble KG, Houston SM, Brito NH, Bartsch H, Kan E, Kuperman JM, et al. Family income, parental education and brain structure in children and adolescents. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:773–8.
Mackey AP, Finn AS, Leonard JA, Jacoby-Senghor DS, West MR, Gabrieli CFO, et al. Neuroanatomical correlates of the income-achievement gap. Psychol Sci. 2015;26:925–33.
Keller AS, Moore TM, Luo A, Visoki E, Gataviņš MM, Shetty A, et al. A general exposome factor explains individual differences in functional brain network topography and cognition in youth. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024;66:101370.
Leonard JA, Mackey AP, Finn AS, Gabrieli JDE. Differential effects of socioeconomic status on working and procedural memory systems. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015;9:554.
Farah MJ. The Neuroscience of socioeconomic status: correlates, causes, and consequences. Neuron. 2017;96:56–71.
Hanson JL, Hair N, Shen DG, Shi F, Gilmore JH, Wolfe BL, et al. Family poverty affects the rate of human infant brain growth. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e80954.
Luby J, Belden A, Botteron K, Marrus N, Harms MP, Babb C, et al. The effects of poverty on childhood brain development: the mediating effect of caregiving and stressful life events. JAMA Pediatr. 2013;167:1135–42.
Miller JG, López V, Buthmann JL, Garcia JM, Gotlib IH. A social gradient of cortical thickness in adolescence: relationships with neighborhood socioeconomic disadvantage, family socioeconomic status, and depressive symptoms. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2022;2:253–62.
Norbom LB, Hanson J, van der Meer D, Ferschmann L, Røysamb E, von Soest T, et al. Parental socioeconomic status is linked to cortical microstructure and language abilities in children and adolescents. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022;56:101132.
Hyde LW, Gard AM, Tomlinson RC, Suarez GL, Westerman HB. Parents, neighborhoods, and the developing brain. Child Dev Perspect. 2022;16:148–56.
Rakesh D, Zalesky A, Whittle S. Assessment of parent income and education, neighborhood disadvantage, and child brain structure. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2226208.
Hackman DA, Cserbik D, Chen J-C, Berhane K, Minaravesh B, McConnell R, et al. Association of local variation in neighborhood disadvantage in metropolitan areas with youth neurocognition and brain structure. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175:e210426.
Tooley UA, Bassett DS, Mackey AP. Environmental influences on the pace of brain development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021;22:372–84.
Zhao S, Su H, Cong J, Wen X, Yang H, Chen P, et al. Hierarchical individual variation and socioeconomic impact on personalized functional network topography in children. BMC Med. 2024;22:556.
Michael C, Taxali A, Angstadt M, Kardan O, Weigard A, Molloy MF, et al. Socioeconomic resources in youth are linked to divergent patterns of network integration/segregation across the brain’s transmodal axis. PNAS Nexus. 2024;3:pgae412.
Tooley UA, Latham A, Kenley JK, Alexopoulos D, Smyser TA, Nielsen AN, et al. Prenatal environment is associated with the pace of cortical network development over the first three years of life. Nat Commun. 2024;15:7932.
Sharma A, Dorman MF, Spahr AJ. A sensitive period for the development of the central auditory system in children with cochlear implants: implications for age of implantation. Ear Hearing. 2002;23:532.
Harrison RV, Gordon KA, Mount RJ. Is there a critical period for cochlear implantation in congenitally deaf children? Analyses of hearing and speech perception performance after implantation. Dev Psychobiol. 2005;46:252–61.
Sharma A, Campbell J. A sensitive period for cochlear implantation in deaf children. J Matern-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;24:151.
McConkey Robbins A, Koch DB, Osberger MJ, Zimmerman-Phillips S, Kishon-Rabin L. Effect of age at cochlear implantation on auditory skill development in infants and toddlers. Arch Otolaryngol–Head Neck Surg. 2004;130:570–4.
Holmes JM, Lazar EL, Melia BM, Astle WF, Dagi LR, Donahue SP, et al. Effect of age on response to amblyopia treatment in children. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011;129:1451–7.
Fronius M, Cirina L, Ackermann H, Kohnen T, Diehl CM. Efficiency of electronically monitored amblyopia treatment between 5 and 16years of age: new insight into declining susceptibility of the visual system. Vision Res. 2014;103:11–19.
Papageorgiou E, Asproudis I, Maconachie G, Tsironi EE, Gottlob I. The treatment of amblyopia: current practice and emerging trends. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019;257:1061–78.
Holmes JM, Levi DM. Treatment of amblyopia as a function of age. Visual Neurosci. 2018;35:E015.
Lewis TL, Maurer D. Multiple sensitive periods in human visual development: evidence from visually deprived children. Dev Psychobiol. 2005;46:163–83.
Mayberry RI. First-language acquisition after childhood differs from second-language acquisition: the case of American Sign Language. J Speech Hearing Res. 1993;36:1258–70.
Mayberry RI, Lock E. Age constraints on first versus second language acquisition: evidence for linguistic plasticity and epigenesis. Brain Lang. 2003;87:369–84.
Friedmann N, Rusou D. Critical period for first language: the crucial role of language input during the first year of life. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015;35:27–34.
Cepeda NJ, Kramer AF, Gonzalez de Sather JC. Changes in executive control across the life span: examination of task-switching performance. Dev Psychol. 2001;37:715–30.
Karbach J, Könen T, Spengler M. Who benefits the most? individual differences in the transfer of executive control training across the lifespan. J Cogn Enhanc. 2017;1:394–405.
Karbach J, Kray J. How useful is executive control training? Age differences in near and far transfer of task-switching training. Dev Sci. 2009;12:978–90.
Delalande L, Moyon M, Tissier C, Dorriere V, Guillois B, Mevell K, et al. Complex and subtle structural changes in prefrontal cortex induced by inhibitory control training from childhood to adolescence. Dev Sci. 2020;23:e12898.
Parr AC, Sydnor VJ, Calabro FJ, Luna B. Adolescent-to-adult gains in cognitive flexibility are adaptively supported by reward sensitivity, exploration, and neural variability. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2024;58:101399.
Lloyd A, McKay R, Sebastian CL, Balsters JH. Are adolescents more optimal decision-makers in novel environments? Examining the benefits of heightened exploration in a patch foraging paradigm. Dev Sci. 2021;24:e13075.
Chierchia G, Soukupová M, Kilford EJ, Griffin C, Leung J, Palminteri S, et al. Confirmatory reinforcement learning changes with age during adolescence. Dev Sci. 2023;26:e13330.
Eckstein MK, Master SL, Dahl RE, Wilbrecht L, Collins AGE. Reinforcement learning and Bayesian inference provide complementary models for the unique advantage of adolescents in stochastic reversal. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022;55:101106.
van der Schaaf ME, Warmerdam E, Crone EA, Cools R. Distinct linear and non-linear trajectories of reward and punishment reversal learning during development: Relevance for dopamine’s role in adolescent decision making. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2011;1:578–90.
Davidow JY, Foerde K, Galván A, Shohamy D. An upside to reward sensitivity: the hippocampus supports enhanced reinforcement learning in adolescence. Neuron. 2016;92:93–99.
Teding van Berkhout E, Malouff JM. The efficacy of empathy training: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Counsel Psychol. 2016;63:32–41.
Wang X-J. Macroscopic gradients of synaptic excitation and inhibition in the neocortex. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020;21:169–78.
Michael C, Gard AM, Tillem S, Hardi FA, Dunn EC, Smith ADAC, et al. Developmental timing of associations among parenting, brain architecture, and mental health. JAMA Pediatr. 2024;178:1326–36.
Tan X, Shiyko MP, Li R, Li Y, Dierker L. A time-varying effect model for intensive longitudinal data. Psychol Methods. 2012;17:61–77.
Stallworthy I, DeJoseph M, Padrutt E, Greifer N, Berry D. Investigating causal questions in human development using marginal structural models: a tutorial introduction to the devMSMs Package in R. 2024.
Hawes SW, Littlefield AK, Lopez DA, Sher KJ, Thompson EL, Gonzalez R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of the ABCD® study. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025;72:101518.
Smith BJ, Smith ADAC, Dunn EC. Statistical modeling of sensitive period effects using the structured life course modeling approach (SLCMA). Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022;53:215–34.
Ramphal B, Pagliaccio D, Dworkin JD, Herbstman J, Noble KG, Margolis AE. Timing-specific associations between income-to-needs ratio and hippocampal and amygdala volumes in middle childhood: a preliminary study. Dev Psychobiol. 2021;63:e22153.
Conley MI, Hindley I, Baskin-Sommers A, Gee DG, Casey BJ, Rosenberg MD. The importance of social factors in the association between physical activity and depression in children. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2020;14:28.
Newbold DJ, Laumann TO, Hoyt CR, Hampton JM, Montez DF, Raut RV, et al. Plasticity and spontaneous activity pulses in disused human brain circuits. Neuron. 2020;107:580–89.e6.
Siu T-SC, Ho S-HC. Investigating effects of bilingualism on syntactic processing: testing structural sensitivity theory. Language Learn. 2022;72:534–75.
Saragosa-Harris NM, Cohen AO, Reneau TR, Villano WJ, Heller AS, Hartley CA. Real-world exploration increases across adolescence and relates to affect, risk taking, and social connectivity. Psychol Sci. 2022;33:1664–79.
Scott RM, Nguyentran G, Sullivan JZ. The COVID-19 pandemic and social cognitive outcomes in early childhood. Sci Rep. 2024;14:28939.
Shanmugan S, Wolf DH, Calkins ME, Moore TM, Ruparel K, Hopson RD, et al. Common and dissociable mechanisms of executive system dysfunction across psychiatric disorders in youth. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173:517–26.
Halse M, Steinsbekk S, Hammar Å, Wichstrøm L. Longitudinal relations between impaired executive function and symptoms of psychiatric disorders in childhood. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2022;63:1574–82.
Romer AL, Pizzagalli DA. Is executive dysfunction a risk marker or consequence of psychopathology? A test of executive function as a prospective predictor and outcome of general psychopathology in the adolescent brain cognitive development study®. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2021;51:100994.
Grant JE, Chamberlain SR. Impaired cognitive flexibility across psychiatric disorders. CNS Spectr. 2023;28:688–92.
Heinz A, Schlagenhauf F, Beck A, Wackerhagen C. Dimensional psychiatry: mental disorders as dysfunctions of basic learning mechanisms. J Neural Transm. 2016;123:809–21.
Forbes EE, Dahl RE. Altered reward function in adolescent depression: what, when, and how?. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2012;53:3–15.
Letkiewicz AM, Cochran AL, Mittal VA, Walther S, Shankman SA. Reward-based reinforcement learning is altered among individuals with a history of major depressive disorder and psychomotor retardation symptoms. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;152:175–81.
Luther L, Raugh IM, Strauss GP. Probabalistic reinforcement learning impairments predict negative symptom severity and risk for conversion in youth at clinical high-risk for psychosis. Psychol Med. 2025;55:e28.
Tsomokos DI, Flouri E. The role of social cognition in mental health trajectories from childhood to adolescence. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2024;33:771–86.
Derntl B, Habel U. Deficits in social cognition: a marker for psychiatric disorders?. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;261:145.
Sloover M, van Est LAC, Janssen PGJ, Hilbink M, van Ee E. A meta-analysis of mentalizing in anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive and related disorders, and trauma and stressor related disorders. J Anxiety Disord. 2022;92:102641.
Oberle E, Ji XR, Guhn M, Schonert-Reichl KA, Gadermann AM. Benefits of extracurricular participation in early adolescence: associations with peer belonging and mental health. J Youth Adolesc. 2019;48:2255–70.
Yu J, Patel RA, Gilman SE. Childhood disadvantage, neurocognitive development and neuropsychiatric disorders: Evidence of mechanisms. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2021;34:306.
Erickson J, El-Gabalawy R, Palitsky D, Patten S, Mackenzie CS, Stein MB, et al. Educational attainment as a protective factor for psychiatric disorders: findings from a nationally representative longitudinal study. Depress Anxiety. 2016;33:1013–22.
Heller AS, Shi TC, Ezie CEC, Reneau TR, Baez LM, Gibbons CJ, et al. Association between real-world experiential diversity and positive affect relates to hippocampal-striatal functional connectivity. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:800–4.
Davis EP, Glynn LM. Annual research review: The power of predictability – patterns of signals in early life shape neurodevelopment and mental health trajectories. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2024;65:508–34.
Glynn LM, Stern HS, Howland MA, Risbrough VB, Baker DG, Nievergelt CM, et al. Measuring novel antecedents of mental illness: the Questionnaire of Unpredictability in Childhood. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019;44:876–82.
van Harmelen A-L, Kievit RA, Ioannidis K, Neufeld S, Jones PB, Bullmore E, et al. Adolescent friendships predict later resilient functioning across psychosocial domains in a healthy community cohort. Psychol Med. 2017;47:2312–22.
Allen K-A, Greenwood CJ, Berger E, Patlamazoglou L, Reupert A, Wurf G, et al. Adolescent school belonging and mental health outcomes in young adulthood: findings from a multi-wave prospective cohort study. School Ment Health. 2024;16:149–60.
Shochet IM, Dadds MR, Ham D, Montague R. School connectedness is an underemphasized parameter in adolescent mental health: results of a community prediction study. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2006;35:170–9.
Modabbernia A, Janiri D, Doucet GE, Reichenberg A, Frangou S. Multivariate patterns of brain-behavior-environment associations in the adolescent brain and cognitive development study. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;89:510–20.
Reiss F. Socioeconomic inequalities and mental health problems in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2013;90:24–31.
Caspi A, Houts RM, Ambler A, Danese A, Elliott ML, Hariri A, et al. Longitudinal assessment of mental health disorders and comorbidities across 4 decades among participants in the Dunedin Birth Cohort Study. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e203221.
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602.
Solmi M, Radua J, Olivola M, Croce E, Soardo L, Salazar de Pablo G, et al. Age at onset of mental disorders worldwide: large-scale meta-analysis of 192 epidemiological studies. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:281–95.
Li F, Zheng X, Wang H, Meng L, Chen M, Hui Y, et al. Mediodorsal thalamus projection to medial prefrontal cortical mediates social defeat stress-induced depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024;49:1318–29.
Miller OH, Bruns A, Ben Ammar I, Mueggler T, Hall BJ. Synaptic Regulation of a thalamocortical circuit controls depression-related behavior. Cell Rep. 2017;20:1867–80.
Benoit LJ, Canetta S, Kellendonk C. Thalamocortical development: a neurodevelopmental framework for schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2022;92:491–500.
Lewis DA, Curley AA, Glausier JR, Volk DW. Cortical parvalbumin interneurons and cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci. 2012;35:57–67.
Kaar SJ, Angelescu I, Marques TR, Howes OD. Pre-frontal parvalbumin interneurons in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of post-mortem studies. J Neural Transm. 2019;126:1637–51.
Mulvey AG, Gabhart KM, Grent-’t-Jong T, Herculano-Houzel S, Uhlhaas PJ, Bastos AM. Cell density and mRNA expression of inhibitory interneurons in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. [Preprint] 2025 Available from:https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.05.23.655812.
Mukherjee A, Carvalho F, Eliez S, Caroni P. Long-lasting rescue of network and cognitive dysfunction in a genetic schizophrenia model. Cell. 2019;178:1387–402.e14.
Do KQ, Cuenod M, Hensch TK. Targeting oxidative stress and aberrant critical period plasticity in the developmental trajectory to schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2015;41:835–46.
Fogaça MV, Duman RS. Cortical GABAergic dysfunction in stress and depression: new insights for therapeutic interventions. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:87.
Lake EMR, Steffler EA, Rowley CD, Sehmbi M, Minuzzi L, Frey BN, et al. Altered intracortical myelin staining in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in severe mental illness. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017;267:369–76.
Mauney SA, Athanas KM, Pantazopoulos H, Shaskan N, Passeri E, Berretta S, et al. Developmental pattern of perineuronal nets in the human prefrontal cortex and their deficit in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;74:427–35.
Lisboa JRF, Costa O, Pakes GH, Colodete DAE, Gomes FV. Perineuronal net density in schizophrenia: a systematic review of postmortem brain studies. Schizophrenia Res. 2024;271:100–9.
Ziegler G, Hauser TU, Moutoussis M, Edward TB, Goodyer IM, Fonagy P, et al. Compulsivity and impulsivity traits linked to attenuated developmental frontostriatal myelination trajectories. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:992–9.
Hettwer MD, Dorfschmidt L, Puhlmann LMC, Jacob LM, Paquola C, Bethlehem RAI, et al. Longitudinal variation in resilient psychosocial functioning is associated with ongoing cortical myelination and functional reorganization during adolescence. Nat Commun. 2024;15:6283.
Knudsen EI. Sensitive periods in the development of the brain and behavior. J Cogn Neurosci. 2004;16:1412–25.
Fuhrmann D, Knoll LJ, Blakemore S-J. Adolescence as a sensitive period of brain development. Trends Cogn Sci. 2015;19:558–66.
Thomas MSC, Johnson MH. New advances in understanding sensitive periods in brain development. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2008;17:1–5.
Bruer JT. A critical and sensitive period primer. Critical thinking about critical periods, Baltimore, MD, US: Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.; 2001. p. 3–26.
Bailey DB. Are critical periods critical for early childhood education?: The role of timing in early childhood pedagogy. Early Child Res Q. 2002;17:281–94.
Mower GD. The effect of dark rearing on the time course of the critical period in cat visual cortex. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991;58:151–8.
Greifzu F, Pielecka-Fortuna J, Kalogeraki E, Krempler K, Favaro PD, Schlüter OM, et al. Environmental enrichment extends ocular dominance plasticity into adulthood and protects from stroke-induced impairments of plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:1150–5.
Baroncelli L, Sale A, Viegi A, Maya Vetencourt JF, De Pasquale R, Baldini S, et al. Experience-dependent reactivation of ocular dominance plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Exp Neurol. 2010;226:100–9.
Hofer SB, Mrsic-Flogel TD, Bonhoeffer T, Hübener M. Prior experience enhances plasticity in adult visual cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:127–32.
Hooks BM, Chen C. Critical Periods in the visual system: changing views for a model of experience-dependent plasticity. Neuron. 2007;56:312–26.
Sawtell NB, Frenkel MY, Philpot BD, Nakazawa K, Tonegawa S, Bear MF. NMDA receptor-dependent ocular dominance plasticity in adult visual cortex. Neuron. 2003;38:977–85.
Nardou R, Lewis EM, Rothhaas R, Xu R, Yang A, Boyden E, et al. Oxytocin-dependent reopening of a social reward learning critical period with MDMA. Nature. 2019;569:116–20.
Bodin D, Yeates KO, Cass J Sensitive Periods. Encyclopedia of clinical neuropsychology, Springer, New York, NY; 2011. p. 2255–6.
Gee DG, Cohodes EM. Caregiving influences on development: a sensitive period for biological embedding of predictability and safety cues. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2021;30:376–83.
Blakemore S-J, Mills KL. Is adolescence a sensitive period for sociocultural processing?. Annu Rev Psychol. 2014;65:187–207.
Callaghan B. Nested sensitive periods: how plasticity across the microbiota-gut-brain axis interacts to affect the development of learning and memory. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2020;36:55–62.
Cusick SE, Barks A, Georgieff MK. Nutrition and brain development. In: Andersen SL, editor. Sensitive periods of brain development and preventive interventions, Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2022. p. 131–65.
Trakoshis S, Martínez-Cañada P, Rocchi F, Canella C, You W, Chakrabarti B, et al. Intrinsic excitation-inhibition imbalance affects medial prefrontal cortex differently in autistic men versus women. eLife. 2020;9:e55684.
Lazari A, Lipp I. Can MRI measure myelin? Systematic review, qualitative assessment, and meta-analysis of studies validating microstructural imaging with myelin histology. Neuroimage. 2021;230:117744.
Mancini M, Karakuzu A, Cohen-Adad J, Cercignani M, Nichols TE, Stikov N. An interactive meta-analysis of MRI biomarkers of myelin. eLife. 2020;9:e61523.
Lee J, Hyun J-W, Lee J, Choi E-J, Shin H-G, Min K, et al. So you want to image myelin using MRI: an overview and practical guide for myelin water imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;53:360–73.
Magri C, Schridde U, Murayama Y, Panzeri S, Logothetis NK. The amplitude and timing of the bold signal reflects the relationship between local field potential power at different frequencies. J Neurosci. 2012;32:1395–407.
Shmuel A, Leopold DA. Neuronal correlates of spontaneous fluctuations in fMRI signals in monkey visual cortex: implications for functional connectivity at rest. Hum Brain Mapp. 2008;29:751–61.
Laumann TO, Snyder AZ. Brain activity is not only for thinking. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2021;40:130–6.
Ghisleni C, Bollmann S, Poil S-S, Brandeis D, Martin E, Michels L, et al. Subcortical glutamate mediates the reduction of short-range functional connectivity with age in a developmental cohort. J Neurosci. 2015;35:8433–41.
Gao R, Peterson EJ, Voytek B. Inferring synaptic excitation/inhibition balance from field potentials. NeuroImage. 2017;158:70–78.
Gao R, van den Brink RL, Pfeffer T, Voytek B. Neuronal timescales are functionally dynamic and shaped by cortical microarchitecture. Elife. 2020;9:e61277.
Salvatore SV, Lambert PM, Benz A, Rensing NR, Wong M, Zorumski CF, et al. Periodic and aperiodic changes to cortical EEG in response to pharmacological manipulation. J Neurophysiol. 2024;131:529–40.
Sherman SM. Thalamus plays a central role in ongoing cortical functioning. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19:533–41.
Theyel BB, Llano DA, Sherman SM. The corticothalamocortical circuit drives higher-order cortex in the mouse. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:84–88.
Tervo-Clemmens B, Karim ZA, Khan SZ, Ravindranath O, Somerville LH, Schuster RM, et al. The developmental timing but not magnitude of adolescent risk-taking propensity is consistent across social, environmental, and psychological factors. J Adolesc Health. 2024;74:613–6.
Favuzzi E, Marques-Smith A, Deogracias R, Winterflood CM, Sánchez-Aguilera A, Mantoan L, et al. Activity-dependent gating of parvalbumin interneuron function by the perineuronal net protein brevican. Neuron. 2017;95:639–55.e10.
Baroncelli L, Braschi C, Spolidoro M, Begenisic T, Sale A, Maffei L. Nurturing brain plasticity: impact of environmental enrichment. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:1092–103.
Mainardi M, Landi S, Gianfranceschi L, Baldini S, De Pasquale R, Berardi N, et al. Environmental enrichment potentiates thalamocortical transmission and plasticity in the adult rat visual cortex. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88:3048–59.
Cancedda L, Putignano E, Sale A, Viegi A, Berardi N, Maffei L. Acceleration of visual system development by environmental enrichment. J Neurosci. 2004;24:4840–8.
Baroncelli L, Scali M, Sansevero G, Olimpico F, Manno I, Costa M, et al. Experience affects critical period plasticity in the visual cortex through an epigenetic regulation of histone post-translational modifications. J Neurosci. 2016;36:3430–40.
Larsen B, Olafsson V, Calabro F, Laymon C, Tervo-Clemmens B, Campbell E, et al. Maturation of the human striatal dopamine system revealed by PET and quantitative MRI. Nat Commun. 2020;11:846.
Peterson ET, Kwon D, Luna B, Larsen B, Prouty D, De Bellis MD, et al. Distribution of brain iron accrual in adolescence: Evidence from cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018;40:1480–95.
Aquino D, Bizzi A, Grisoli M, Garavaglia B, Bruzzone MG, Nardocci N, et al. Age-related iron deposition in the basal ganglia: quantitative analysis in healthy subjects. Radiology. 2009;252:165–72.
Teicher MH, Andersen SL, Hostetter JC. Evidence for dopamine receptor pruning between adolescence and adulthood in striatum but not nucleus accumbens. Dev Brain Res. 1995;89:167–72.
Andersen SL, Rutstein M, Benzo JM, Hostetter JC, Teicher MH. Sex differences in dopamine receptor overproduction and elimination. NeuroReport. 1997;8:1495.
Rosenberg DR, Lewis DA. Postnatal maturation of the dopaminergic innervation of monkey prefrontal and motor cortices: a tyrosine hydroxylase immunohistochemical analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1995;358:383–400.
Kuhn C, Johnson M, Thomae A, Luo B, Simon SA, Zhou G, et al. The emergence of gonadal hormone influences on dopaminergic function during puberty. Hormones Behav. 2010;58:122–37.
Sato SM, Schulz KM, Sisk CL, Wood RI. Adolescents and androgens, receptors and rewards. Hormones Behav. 2008;53:647–58.
Pfeifer JH, Allen NB. Puberty initiates cascading relationships between neurodevelopmental, social, and internalizing processes across adolescence. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;89:99–108.
Harden KP, Mann FD, Grotzinger A, Patterson MW, Steinberg L, Tackett JL, et al. Developmental differences in reward sensitivity and sensation seeking in adolescence: testing sex-specific associations with gonadal hormones and pubertal development. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2018;115:161–78.
Funding
Funding for some authors was provided by the Staunton Farm Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Valerie J. Sydnor, Amar Ojha, and Angela Martinez performed literature reviews for material presented in the article. Valerie J. Sydnor, Bart Larsen, and Beatriz Luna conceived of the topic; Finnegan J. Calabro provided expert input. Valerie J. Sydnor wrote the original article and created the figures. All authors critically revised the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sydnor, V.J., Ojha, A., Larsen, B. et al. Investigating hierarchical critical periods in human neurodevelopment. Neuropsychopharmacol. 51, 67–85 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-025-02246-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-025-02246-5