Abstract
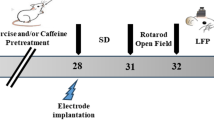
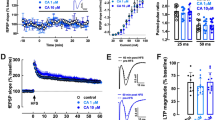
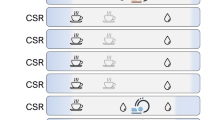
Sleep deprivation (SD) is a critical risk factor for cognitive decline and is closely linked to psychiatric disorders. The hippocampal CA2 region is critically involved in encoding social memory and regulating emotional behavior, and it has been implicated in various neuropsychiatric conditions. However, how SD affects CA2-dependent synaptic plasticity and related behaviors remains poorly understood. Here, we subjected mice to 5 h of SD via gentle handling and examined synaptic plasticity, molecular signaling, and social recognition memory. Electrophysiological recordings revealed that SD markedly impaired long-term potentiation (LTP) in CA2 and disrupted social recognition memory, as evidenced by failure to distinguish novel from familiar conspecifics. These deficits were accompanied by upregulation of adenosine A1 receptors and PDE4A5, along with reduced expression of plasticity-related proteins including PKMζ, ERK, and BDNF. Moreover, caffeine-induced synaptic potentiation was diminished in SD mice, whereas caffeine supplementation reversed both synaptic and behavioral impairments. Together, these findings demonstrate that SD compromises CA2-dependent plasticity and social cognition through adenosine receptor signaling and identify CA2 as a vulnerable, therapeutically relevant region. Targeting adenosine pathways may represent a novel strategy to mitigate sleep loss–related cognitive dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 13 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $19.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated from this study are available upon request to the corresponding authors.
References
Wong L-W, Tann JY, Ibanez CF, Sajikumar S. The p75 Neurotrophin Receptor Is an Essential Mediator of Impairments in Hippocampal-Dependent Associative Plasticity and Memory Induced by Sleep Deprivation. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 2019;39:5452–65.
Wong L-W, Chong YS, Wong W, Sajikumar S. Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase Reinstates Hippocampus-Dependent Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity and Associative Memory in Sleep-Deprived Mice. Cereb Cortex. 2020;30:4169–82.
Bolsius YG, Heckman P, Paraciani C, Wilhelm S, Raven F, Meijer EL, et al. Recovering object-location memories after sleep deprivation-induced amnesia. Curr Biol. 2023;33:298–308.e5.
Hagewoud R, Whitcomb SN, Heeringa AN, Havekes R, Koolhaas JM, Meerlo P. A time for learning and a time for sleep: the effect of sleep deprivation on contextual fear conditioning at different times of the day. Sleep. 2010;33:1315–22.
Vecsey CG, Baillie GS, Jaganath D, Havekes R, Daniels A, Wimmer M, et al. Sleep deprivation impairs cAMP signalling in the hippocampus. Nature. 2009;461:1122–5.
Havekes R, Park AJ, Tudor JC, Luczak VG, Hansen RT, Ferri SL, et al., Sleep deprivation causes memory deficits by negatively impacting neuronal connectivity in hippocampal area CA1. eLife. 2016;5:e13424.
Hitti FL, Siegelbaum SA. The hippocampal CA2 region is essential for social memory. Nature. 2014;508:88–92.
Alexander GM, Farris S, Pirone JR, Zheng C, Colgin LL, Dudek SM. Social and novel contexts modify hippocampal CA2 representations of space. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10300.
Donegan ML, Stefanini F, Meira T, Gordon JA, Fusi S, Siegelbaum SA. Coding of social novelty in the hippocampal CA2 region and its disruption and rescue in a 22q11. 2 microdeletion mouse model. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:1365–75.
Pedersen NP, Ferrari L, Venner A, Wang JL, Abbott S, Vujovic N, et al. Supramammillary glutamate neurons are a key node of the arousal system. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1–16.
Soussi R, Zhang N, Tahtakran S, Houser CR, Esclapez M. Heterogeneity of the supramammillary–hippocampal pathways: Evidence for a unique GABAergic neurotransmitter phenotype and regional differences. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;32:771–85.
Chen S, He L, Huang A, Boehringer R, Robert V, Wintzer ME, et al. A hypothalamic novelty signal modulates hippocampal memory. Nature. 2020;586:270–4.
Diekelmann S, Born J. The memory function of sleep. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:114–26.
Rasch B, Born J. About sleep’s role in memory. Physiol Rev. 2013;93:681–766.
Joo HR, Frank LM. The hippocampal sharp wave–ripple in memory retrieval for immediate use and consolidation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19:744–57.
Oliva A, Fernández-Ruiz A, Leroy F, Siegelbaum SA. Hippocampal CA2 sharp-wave ripples reactivate and promote social memory. Nature. 2020;587:264–9.
Clemens Z, Fabo D, Halasz P. Overnight verbal memory retention correlates with the number of sleep spindles. Neuroscience. 2005;132:529–35.
Wagner U, Kashyap N, Diekelmann S, Born J. The impact of post-learning sleep vs. wakefulness on recognition memory for faces with different facial expressions. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007;87:679–87.
Sawangjit A, Kelemen E, Born J, Inostroza M. Sleep enhances recognition memory for conspecifics as bound into spatial context. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017;11:28.
Bin Ibrahim MZ, Benoy A, Sajikumar S. Long-term plasticity in the hippocampus: maintaining within and ‘tagging’between synapses. FEBS J. 2022;289:2176–201.
Tudor JC, Davis EJ, Peixoto L, Wimmer ME, van Tilborg E, Park AJ, et al. Sleep deprivation impairs memory by attenuating mTORC1-dependent protein synthesis. Sci Signal. 2016;9:ra41
Dasgupta A, Baby N, Krishna K, Hakim M, Wong YP, Behnisch T, et al. Substance P induces plasticity and synaptic tagging/capture in rat hippocampal area CA2. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017;114:E8741–9.
Benoy A, Bin Ibrahim MZ, Behnisch T, Sajikumar S. Metaplastic reinforcement of long-term potentiation in hippocampal area CA2 by cholinergic receptor activation. J Neurosci. 2021;41:9082–98.
Simons SB, Caruana DA, Zhao M, Dudek SM. Caffeine-induced synaptic potentiation in hippocampal CA2 neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:23–5.
Alhaider IA, Aleisa AM, Tran TT, Alzoubi KH, Alkadhi KA. Chronic caffeine treatment prevents sleep deprivation-induced impairment of cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. Sleep. 2010;33:437–44.
Chevaleyre V, Siegelbaum SA. Strong CA2 pyramidal neuron synapses define a powerful disynaptic cortico-hippocampal loop. Neuron. 2010;66:560–72.
Zhao M, Choi YS, Obrietan K, Dudek SM. Synaptic plasticity (and the lack thereof) in hippocampal CA2 neurons. J Neurosci. 2007;27:12025–32.
Caruana DA, Dudek SM. Adenosine A1 receptor-mediated synaptic depression in the developing hippocampal area CA2. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020;12:21.
Florian C, Vecsey CG, Halassa MM, Haydon PG, Abel T. Astrocyte-derived adenosine and A1 receptor activity contribute to sleep loss-induced deficits in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory in mice. J Neurosci. 2011;31:6956–62.
Redondo RL, Okuno H, Spooner PA, Frenguelli BG, Bito H, Morris RG. Synaptic tagging and capture: differential role of distinct calcium/calmodulin kinases in protein synthesis-dependent long-term potentiation. J Neurosci. 2010;30:4981–9.
Sajikumar S, Navakkode S, Sacktor TC, Frey JU. Synaptic tagging and cross-tagging: the role of protein kinase Mζ in maintaining long-term potentiation but not long-term depression. J Neurosci. 2005;25:5750–6.
Impey S, Obrietan K, Storm DR. Making new connections: role of ERK/MAP kinase signaling in neuronal plasticity. Neuron. 1999;23:11–4.
Roth TL, Sweatt JD. Rhythms of memory. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:993–4.
Panagiotou M, Meijer M, Meijer JH, Deboer T. Effects of chronic caffeine consumption on sleep and the sleep electroencephalogram in mice. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33:122–31.
Reichert CF, Deboer T, Landolt HP. Adenosine, caffeine, and sleep–wake regulation: state of the science and perspectives. J sleep Res. 2022;31:e13597.
Moura PJ, Gimenes-Júnior JA, Valentinuzzi VS, Xavier GF. Circadian phase and intertrial interval interfere with social recognition memory. Physiol Behav. 2009;96:51–6.
Lopez-Rojas J, de Solis CA, Leroy F, Kandel ER, Siegelbaum SA. A direct lateral entorhinal cortex to hippocampal CA2 circuit conveys social information required for social memory. Neuron. 2022;110:1559–72.e4.
Qin H, Fu L, Jian T, Jin W, Liang M, Li J, et al. REM sleep-active hypothalamic neurons may contribute to hippocampal social-memory consolidation. Neuron. 2022;110:4000–14.e6.
Bin Ibrahim MZ, Goh L, Koh N, Polepalli JS, Behnisch T, Sajikumar S. Hippocampal CA2 to CA1: A metaplastic switch for memory encoding. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2025;122:e2505936122.
Prediger RD, Takahashi RN. Modulation of short-term social memory in rats by adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Neurosci Lett. 2005;376:160–5.
Ochiishi T, Saitoh Y, Yukawa A, Saji M, Ren Y, Shirao T, et al. High level of adenosine A1 receptor-like immunoreactivity in the CA2/CA3a region of the adult rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1999;93:955–67.
Wu C, Wong T, Wu X, Sheppy E, Zhang L. Adenosine as an endogenous regulating factor of hippocampal sharp waves. Hippocampus. 2009;19:205–20.
Muñoz M-D, Solís JM. Characterisation of the mechanisms underlying the special sensitivity of the CA2 hippocampal area to adenosine receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology. 2019;144:9–18.
Angelucci ME, Cesário C, Hiroi RH, Rosalen PL, Da Cunha C. Effects of caffeine on learning and memory in rats tested in the Morris water maze. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2002;35:1201–8.
Kopf SR, Melani A, Pedata F, Pepeu G. Adenosine and memory storage. Psychopharmacology. 1999;146:214–9.
Fredholm BB, Jonzon B, Lindström K. Effect of adenosine receptor agonists and other compounds on cyclic AMP accumulation in forskolin-treated hippocampal slices. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986;332:173–8.
Fredholm BB, Bättig K, Holmén J, Nehlig A, Zvartau EE. Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51:83–133.
Nehlig A, Daval J-L, Debry G. Caffeine and the central nervous system: mechanisms of action, biochemical, metabolic and psychostimulant effects. Brain Res Rev. 1992;17:139–70.
Ferré S. An update on the mechanisms of the psychostimulant effects of caffeine. J Neurochem. 2008;105:1067–79.
Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977;57:71–108.
Halassa MM, Florian C, Fellin T, Munoz JR, Lee SY, Abel T, et al. Astrocytic modulation of sleep homeostasis and cognitive consequences of sleep loss. Neuron. 2009;61:213–9.
Granado N, Ortiz O, Suárez LM, Martín ED, Ceña V, Solís JM, et al. D1 but not D5 dopamine receptors are critical for LTP, spatial learning, and LTP-Induced arc and zif268 expression in the hippocampus. Cereb Cortex. 2007;18:1–12.
Dale E, Pehrson AL, Jeyarajah T, Li Y, Leiser SC, Smagin G, et al. Effects of serotonin in the hippocampus: how SSRIs and multimodal antidepressants might regulate pyramidal cell function. CNS Spectr. 2016;21:143–61.
Cui Z, Gerfen CR, Young WS. 3rd, Hypothalamic and other connections with dorsal CA2 area of the mouse hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 2013;521:1844–66.
Ihara N, Ueda S, Kawata M, Sano Y. Immunohistochemical demonstration of serotonin-containing nerve fibers in the mammalian hippocampal formation. Cells Tissues Organs. 1988;132:335–46.
Rey CC, Robert V, Bouisset G, Loisy M, Lopez S, Cattaud V, et al. Altered inhibitory function in hippocampal CA2 contributes in social memory deficits in Alzheimer’s mouse model. Iscience. 2022;25:103895.
Parhizkar S, Gent G, Chen Y, Rensing N, Gratuze M, Strout G, et al. Sleep deprivation exacerbates microglial reactivity and Aβ deposition in a TREM2-dependent manner in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2023;15:eade6285.
Funding
This work was supported by the NUHS Seed Fund (NUHSRO/2024/089/T1/Seed-Mar24/02) and the Ministry of Health (MOH-000641-00 and MOH-001883-00) awarded to SS, the NUHS Seed Fund (NUHSRO/2024/084/RO5 + 6/Seed-Mar24/04) awarded to L-WW and the National University of Singapore (NUS) Research Scholarship awarded to MZBI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L-WW and SS conceptualized the idea for the manuscript. L-WW, MZBI and ALK performed experiments. L-WW wrote the first draft. L-WW, MZBI and SS edited, read and then approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, LW., Bin Ibrahim, M.Z., Kannan, A.L. et al. Caffeine reverses sleep deprivation-induced synaptic and social memory deficits via adenosine receptor modulation in the male mouse hippocampal CA2 region. Neuropsychopharmacol. (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-026-02362-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-026-02362-w