Abstract
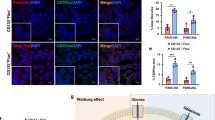
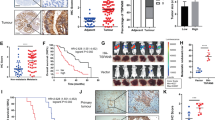
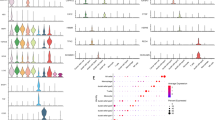
Cancer stem cells (CSC) play a crucial role in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression and therapeutic resistance. However, the underlying mechanisms and potential targeted treatment strategies remain poorly understood. In this study, we employed single-cell RNA sequencing and exosomal profiling, identifying TSPAN8-enriched exosomes secreted by CSC, which are associated with poor survival rates in PDAC patients. They enhanced stemness in the surrounding non-stem cancer cells (NSCC) by activating the Sonic Hedgehog (Hh) signalling pathway. This exosomal TSPAN8-Hh signalling axis significantly increases the clonogenic ability, invasiveness, and chemoresistance of PDAC cells. Furthermore, TSPAN8-enriched exosomes promoted a higher stem cell frequency, tumourigenicity, and tumour growth rate in vivo, confirming their critical roles in PDAC malignant progression. Our findings underscore the importance of TSPAN8-enriched exosomes for CSC-NSCC communication during PDAC progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The PDAC and adjacent non-cancerous tissue scRNA-seq data were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database with accession number GSE212966 (PRJNA879876). Corresponding analysis scripts and codes are available upon request from the lead author, Xiaoyi Yang (nicole_yang@sjtu.edu.cn).
References
Park W, Chawla A, O’Reilly EM. Pancreatic cancer: a review. JAMA. 2021;326:851–62.
Klein AP. Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:493–502.
Klose J, Ronellenfitsch U, Kleeff J. Management problems in patients with pancreatic cancer from a surgeon’s perspective. Semin Oncol. 2021;48:76–83.
Alausa A, Lawal KA, Babatunde OA, Obiwulu ENO, Oladokun OC, Fadahunsi OS, et al. Overcoming immunotherapeutic resistance in PDAC: SIRPα-CD47 blockade. Pharmacol Res. 2022;181:106264.
Zeng S, Pöttler M, Lan B, Grützmann R, Pilarsky C, Yang H. Chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:4504.
Clevers H. The cancer stem cell: premises, promises and challenges. Nat Med. 2011;17:313–9.
Shibue T, Weinberg RA. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:611–29.
Pérez-González A, Bévant K, Blanpain C. Cancer cell plasticity during tumor progression, metastasis and response to therapy. Nat Cancer. 2023;4:1063–82.
Loh J-J, Ma S. Hallmarks of cancer stemness. Cell Stem Cell. 2024;31:617–39.
Guan T, Li M, Song Y, Chen J, Tang J, Zhang C, et al. Phosphorylation of USP29 by CDK1 Governs TWIST1 stability and oncogenic functions. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2205873.
Su C, Zhang J, Yarden Y, Fu L. The key roles of cancer stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:109.
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Sci. 2020;367:eaau6977.
Huang W, Yan Y, Liu Y, Lin M, Ma J, Zhang W, et al. Exosomes with low miR-34c-3p expression promote invasion and migration of non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating integrin α2β1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:39.
Treps L, Perret R, Edmond S, Ricard D, Gavard J. Glioblastoma stem-like cells secrete the pro-angiogenic VEGF-A factor in extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017;6:1359479.
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:1470–6.
Wang Z, Sun H, Provaznik J, Hackert T, Zöller M. Pancreatic cancer-initiating cell exosome message transfer into noncancer-initiating cells: the importance of CD44v6 in reprogramming. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:132.
Sun H, Rana S, Wang Z, Zhao K, Schnölzer M, Provaznik J, et al. The pancreatic cancer-initiating cell marker CD44v6 affects transcription, translation, and signaling: consequences for exosome composition and delivery. J Oncol. 2019;2019:3516973.
Kyuno D, Zhao K, Schnölzer M, Provaznik J, Hackert T, Zöller M. Claudin7-dependent exosome-promoted reprogramming of nonmetastasizing tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:2182–2200.
Conigliaro A, Costa V, Lo Dico A, Saieva L, Buccheri S, Dieli F, et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:155.
Mirzaei R, Sarkar S, Dzikowski L, Rawji KS, Khan L, Faissner A, et al. Brain tumor-initiating cells export tenascin-C associated with exosomes to suppress T cell activity. Oncoimmunology. 2018;7:e1478647.
Hwang WL, Lan HY, Cheng WC, Huang SC, Yang MH. Tumor stem-like cell-derived exosomal RNAs prime neutrophils for facilitating tumorigenesis of colon cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:10.
Mashouri L, Yousefi H, Aref AR, Ahadi AM, Molaei F, Alahari SK. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:75.
Huang Y, Zucker B, Zhang S, Elias S, Zhu Y, Chen H, et al. Migrasome formation is mediated by assembly of micron-scale tetraspanin macrodomains. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21:991–1002.
Wang T, Wang X, Wang H, Li L, Zhang C, Xiang R, et al. High TSPAN8 expression in epithelial cancer cell-derived small extracellular vesicles promote confined diffusion and pronounced uptake. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10:e12167.
Malla RR, Pandrangi S, Kumari S, Gavara MM, Badana AK. Exosomal tetraspanins as regulators of cancer progression and metastasis and novel diagnostic markers. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2018;14:383–91.
Susa KJ, Kruse AC, Blacklow SC. Tetraspanins: structure, dynamics, and principles of partner-protein recognition. Trends Cell Biol. 2024;34:509–22.
Zhu R, Gires O, Zhu L, Liu J, Li J, Yang H, et al. TSPAN8 promotes cancer cell stemness via activation of sonic Hedgehog signaling. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2863.
Andreu Z, Yáñez-Mó M. Tetraspanins in extracellular vesicle formation and function. Front Immunol. 2014;5:442.
Pan SJ, Wu YB, Cai S, Pan YX, Liu W, Bian LG, et al. Over-expression of tetraspanin 8 in malignant glioma regulates tumor cell progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;458:476–82.
Nazarenko I, Rana S, Baumann A, McAlear J, Hellwig A, Trendelenburg M, et al. Cell surface tetraspanin Tspan8 contributes to molecular pathways of exosome-induced endothelial cell activation. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1668–78.
Liu Y, Fan J, Xu T, Ahmadinejad N, Hess K, Lin SH, et al. Extracellular vesicle tetraspanin-8 level predicts distant metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer after concurrent chemoradiation. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eaaz6162.
Voglstaetter M, Thomsen AR, Nouvel J, Koch A, Jank P, Navarro EG, et al. Tspan8 is expressed in breast cancer and regulates E-cadherin/catenin signalling and metastasis accompanied by increased circulating extracellular vesicles. J Pathol. 2019;248:421–37.
Fan G, Yu B, Tang L, Zhu R, Chen J, Zhu Y, et al. TSPAN8(+) myofibroblastic cancer-associated fibroblasts promote chemoresistance in patients with breast cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16:eadj5705.
Guo X, Zhang Y, Zheng L, Zheng C, Song J, Zhang Q, et al. Global characterization of T cells in non-small-cell lung cancer by single-cell sequencing. Nat Med. 2018;24:978–85.
Zhang L, Yu X, Zheng L, Zhang Y, Li Y, Fang Q, et al. Lineage tracking reveals dynamic relationships of T cells in colorectal cancer. Nature. 2018;564:268–72.
Cao J, Spielmann M, Qiu X, Huang X, Ibrahim DM, Hill AJ, et al. The single-cell transcriptional landscape of mammalian organogenesis. Nature. 2019;566:496–502.
Van Deun J, Mestdagh P, Sormunen R, Cocquyt V, Vermaelen K, Vandesompele J, et al. The impact of disparate isolation methods for extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.24858.
Gallmeier E, Hermann PC, Mueller M-T, Machado JG, Ziesch A, De Toni EN, et al. Inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia- and Rad3-related function abrogates the in vitro and in vivo tumorigenicity of human colon cancer cells through depletion of the CD133+ tumor-initiating cell fraction. Stem Cells. 2011;29:418–29.
Chen J, Zhao D, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang Y, Feng T. et al. Lactylated Apolipoprotein C-II induces immunotherapy resistance by promoting extracellular lipolysis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11:e2406333.
Chen K, Wang Q, Li M, Guo H, Liu W, Wang F, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals dynamic change in tumor microenvironment during pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma malignant progression. EBioMedicine. 2021;66:103315.
Peng J, Sun BF, Chen CY, Zhou JY, Chen YS, Chen H, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intra-tumoral heterogeneity and malignant progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Res. 2019;29:725–38.
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget I, Raposo G, Savina A, et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:19–30.
Lai H, Li Y, Zhang H, Hu J, Liao J, Su Y, et al. exoRBase 2.0: an atlas of mRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in extracellular vesicles from human biofluids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D118–d128.
Huang H, Hou J, Liu K, Liu Q, Shen L, Liu B, et al. RAB27A-dependent release of exosomes by liver cancer stem cells induces Nanog expression in their differentiated progenies and confers regorafenib resistance. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36:3429–37.
Cheng WC, Liao TT, Lin CC, Yuan LE, Lan HY, Lin HH, et al. RAB27B-activated secretion of stem-like tumor exosomes delivers the biomarker microRNA-146a-5p, which promotes tumorigenesis and associates with an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:2209–24.
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A, Ellwart JW, Guba M, et al. Distinct populations of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:313–23.
Jiang W, Liu L, Wang M, Li X, Zhou T, Hou X, et al. KLF15 suppresses stemness of pancreatic cancer by decreasing USP21-mediated Nanog stability. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81:417.
Li C, Heidt DG, Dalerba P, Burant CF, Zhang L, Adsay V, et al. Identification of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1030–7.
Lin L, Jou D, Wang Y, Ma H, Liu T, Fuchs J, et al. STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in ALDH+ and CD44+/CD24+ stem cell-like pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:2265–74.
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ, Ivy SP. Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:97–106.
Zhang Y, Beachy PA. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:668–87.
Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang J, et al. Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:8.
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao M-J, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:704–15.
Natu J, Nagaraju GP. Gemcitabine effects on tumor microenvironment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Special focus on resistance mechanisms and metronomic therapies. Cancer Lett. 2023;573:216382.
Longley DB, Harkin DP, Johnston PG. 5-Fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nature Rev Cancer. 2003;3:330–8.
Du L, Li YJ, Fakih M, Wiatrek RL, Duldulao M, Chen Z, et al. Role of SUMO activating enzyme in cancer stem cell maintenance and self-renewal. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12326.
Chu X, Tian W, Ning J, Xiao G, Zhou Y, Wang Z, et al. Cancer stem cells: advances in knowledge and implications for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9:170.
Sousa D, Lima RT, Vasconcelos MH. Intercellular transfer of cancer drug resistance traits by extracellular vesicles. Trends Mol Med. 2015;21:595–608.
Becker A, Thakur BK, Weiss JM, Kim HS, Peinado H, Lyden D. Extracellular vesicles in cancer: cell-to-cell mediators of metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:836–48.
Goel HL, Mercurio AM. VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:871–82.
Février B, Raposo G. Exosomes: endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:415–21.
Lakkaraju A, Rodriguez-Boulan E. Itinerant exosomes: emerging roles in cell and tissue polarity. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18:199–209.
Charrin S, Jouannet S, Boucheix C, Rubinstein E. Tetraspanins at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:3641–8.
Gesierich S, Paret C, Hildebrand D, Weitz J, Zgraggen K, Schmitz-Winnenthal FH, et al. Colocalization of the tetraspanins, CO-029 and CD151, with integrins in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma: impact on cell motility. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2840–52.
Lu X, An L, Fan G, Zang L, Huang W, Li J, et al. EGFR signaling promotes nuclear translocation of plasma membrane protein TSPAN8 to enhance tumor progression via STAT3-mediated transcription. Cell Res. 2022;32:359–74.
Zhang H-S, Liu H-Y, Zhou Z, Sun H-L, Liu M-Y. TSPAN8 promotes colorectal cancer cell growth and migration in LSD1-dependent manner. Life Sci. 2020;241:117114.
Thakur A, Xu C, Li WK, Qiu G, He B, Ng S-P, et al. In vivo liquid biopsy for glioblastoma malignancy by the AFM and LSPR based sensing of exosomal CD44 and CD133 in a mouse model. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;191:113476.
Mu W, Xu Y, Gu P, Wang W, Li J, Ge Y, et al. Exosomal CD44 cooperates with integrin α6β4 to support organotropic metastasis via regulating tumor cell motility and target host cell activation. Engineering. 2021;7:1413–23.
Kaneko K, Liang Y, Liu Q, Zhang S, Scheiter A, Song D, et al. Identification of CD133+ intercellsomes in intercellular communication to offset intracellular signal deficit. Elife. 2023;12:RP86824.
Min J, Yang S, Cai Y, Vanderwall DR, Wu Z, Li S, et al. Tetraspanin Tspan8 restrains interferon signaling to stabilize intestinal epithelium by directing endocytosis of interferon receptor. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023;80:154.
Zhuang L, Jin G, Hu X, Yang Q, Pei X, Zhao W. TSPAN8 alleviates high glucose-induced apoptosis and autophagy via targeting mTORC2. Cell Biol Int. 2022;46:1693–703.
Sun Z, Wang L, Dong L, Wang X. Emerging role of exosome signalling in maintaining cancer stem cell dynamic equilibrium. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:3719–28.
Seo N, Akiyoshi K, Shiku H. Exosome-mediated regulation of tumor immunology. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:2998–3004.
Li W, Zhang L, Guo B, Deng J, Wu S, Li F, et al. Exosomal FMR1-AS1 facilitates maintaining cancer stem-like cell dynamic equilibrium via TLR7/NFκB/c-Myc signaling in female esophageal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:22.
Sun Z, Wang L, Zhou Y, Dong L, Ma W, Lv L, et al. Glioblastoma stem cell-derived exosomes enhance stemness and tumorigenicity of glioma cells by transferring Notch1 protein. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40:767–84.
Morris JPT, Wang SC, Hebrok M. KRAS, Hedgehog, Wnt and the twisted developmental biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:683–95.
Jiang J. Hedgehog signaling mechanism and role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;85:107–22.
Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2140–1.
Zhao Y, Qin C, Zhao B, Wang Y, Li Z, Li T, et al. Pancreatic cancer stemness: dynamic status in malignant progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42:122.
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:178–96.
Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:69–84.
Li H, Jiang W, Liu X-N, Yuan L-Y, Li T-J, Li S, et al. TET1 downregulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in PDAC by demethylating CHL1 to inhibit the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2020;39:5825–38.
Tirosh I, Venteicher AS, Hebert C, Escalante LE, Patel AP, Yizhak K, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq supports a developmental hierarchy in human oligodendroglioma. Nature. 2016;539:309–13.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant number 2023YFC2506400), National Natural Science Funds (grant number 82225038, 82430092, 82272828, 82172735, 32270749, 32370755, and M-0349), Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan (grant number 23J21900900), National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars Fund (grant number 82125026), Innovative research team of high-level local universities in Shanghai (grant number SHSMU-ZLCX20211600), Talent Introduction Fund of Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center (grant number YJRC202403), Shanghai Anticancer Association SOAR PROJECT (SACA-AX202401), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (grant number 22ZR1450000), Shanghai leading talent project (grant number QNWS2024019). Additional support came from Medical Innovation Research Special Project of Shanghai (Grant No. 22Y11908600). All authors involved in this study have declared that they have no financial conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY, RZ, JX, JW, YJ, YZ, SC, BS, ML, WR, JL, RL and JJ, performed experiments. HS, HW, BY, RL, and JJ provided human samples. XY and JW performed bioinformatics analyses. XY, RZ, WL, GF, and BY interpreted data and wrote the manuscript. HW, WL, GF, and BY supervised the study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Liu, R., Jin, J. et al. Cancer stem cells-derived exosomal TSPAN8 enhances non-stem cancer cells stemness and promotes malignant progression in PDAC. Oncogene 44, 2328–2341 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03412-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03412-1