Abstract
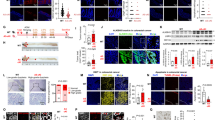
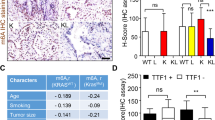
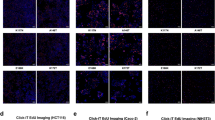
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a severe health risk, and while Cetuximab is a key treatment, resistance due to KRAS mutations poses a challenge. The role of ALKBH5, often overexpressed in cancers, in KRAS-mutated CRC and its resistance to Cetuximab is not yet fully understood. This research initiates an inquiry from both cellular and animal experimental perspectives, investigating the potential of ALKBH5 to confer resistance to Cetuximab in colorectal cancer cells harboring KRAS mutations. We investigated ALKBH5 expression in clinical samples of CRC with varying responses to Cetuximab and KRAS statuses. Drug-resistant cell lines were developed using incremental drug concentrations, and the effects of ALKBH5 modulation on cell viability and proliferation were assessed using CCK-8 and clonogenic assays. The in vivo impact of ALKBH5 on drug resistance in KRAS-mutant cells was explored. Transcriptome sequencing of ALKBH5 knockdown cells pinpointed genes linked to Cetuximab resistance. We also examined ALKBH5’s regulation of FOXM1 m6A methylation with dual-luciferase and MeRIP assays and conducted FOXM1 functional reversal studies, alongside Western blot analysis of Wnt/β-catenin pathway proteins. Elevated ALKBH5 expression is positively correlated with Cetuximab resistance in KRAS-mutant CRC. ALKBH5 confers Cetuximab resistance to CRC cells in a KRAS-mutation-dependent manner in vitro and in vivo. ALKBH5 regulates FOXM1 expression through m6A demethylation, and FOXM1 can reverse Cetuximab resistance in ALKBH5-modulated KRAS-mutated CRC cells. Additionally, FOXM1 influences the sensitivity of KRAS-mutant tumors to Cetuximab by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. ALKBH5 plays a crucial role in the resistance of KRAS-mutant CRC to Cetuximab by inhibiting the m6A RNA methylation of FOXM1 and suppressing the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Klimeck L, Heisser T, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Colorectal cancer: A health and economic problem. Best. Pr. Res Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023;66:101839.
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N, Chen WQ. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin. Med J. 2021;134:783–91.
Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023;73:233–54.
Shin AE, Giancotti FG, Rustgi AK. Metastatic colorectal cancer: mechanisms and emerging therapeutics. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2023;44:222–36.
Bando H, Ohtsu A, Yoshino T. Therapeutic landscape and future direction of metastatic colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023;20:306–22.
Cremolini C, Rossini D, Dell’Aquila E, Lonardi S, Conca E, Del Re M, et al. Rechallenge for patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to first-line Cetuximab and Irinotecan: A Phase 2 single-arm clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:343–50.
Yaeger R, Weiss J, Pelster MS, Spira AI, Barve M, Ou SI, et al. Adagrasib with or without Cetuximab in colorectal cancer with mutated KRAS G12C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023;388:44–54.
Kuboki Y, Fakih M, Strickler J, Yaeger R, Masuishi T, Kim EJ, et al. Sotorasib with panitumumab in chemotherapy-refractory KRAS(G12C)-mutated colorectal cancer: a phase 1b trial. Nat. Med. 2024;30:265–70.
Qu J, Yan H, Hou Y, Cao W, Liu Y, Zhang E, et al. RNA demethylase ALKBH5 in cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022;15:8.
Wei C, Wang B, Peng D, Zhang X, Li Z, Luo L, et al. Pan-cancer analysis shows that ALKBH5 is a potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic biomarker for multiple cancer types including Gliomas. Front. Immunol. 2022;13:849592.
Zhai J, Chen H, Wong CC, Peng Y, Gou H, Zhang J, et al. ALKBH5 drives immune suppression via targeting AXIN2 to promote colorectal cancer and is a target for boosting immunotherapy. Gastroenterology. 2023;165:445–62.
Yang Z, Zhang BL. ALKBH5 in colorectal cancer: an insufficiently explored and controversial research area. Gastroenterology. 2023;165:1581.
Zhang D, Ning J, Okon I, Zheng X, Satyanarayana G, Song P, et al. Suppression of m6A mRNA modification by DNA hypermethylated ALKBH5 aggravates the oncological behavior of KRAS mutation/LKB1 loss lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:518.
Khan MA, Khan P, Ahmad A, Fatima M, Nasser MW. FOXM1: A small fox that makes more tracks for cancer progression and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023;92:1–15.
Chu XY, Zhu ZM, Chen LB, Wang JH, Su QS, Yang JR, et al. FOXM1 expression correlates with tumor invasion and a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Acta Histochem. 2012;114:755–62.
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, et al. m(6)A Demethylase ALKBH5 maintains Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 Expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:591–606.e596.
Biller LH, Schrag D. Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review. JAMA. 2021;325:669–85.
Awad MM, Liu S, Rybkin II, Arbour KC, Dilly J, Zhu VW, et al. Acquired resistance to KRAS(G12C) inhibition in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:2382–93.
Huang L, Guo Z, Wang F, Fu L. KRAS mutation: from undruggable to druggable in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021;6:386.
Tan AC, Tan DSW. Targeted therapies for lung cancer patients with oncogenic driver molecular alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:611–25.
Li Y, Zhang X, Cai J, Ren L, Liu B, Wu M, et al. The pathological tissue expression pattern and clinical significance of m6A-regulatory genes in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Gene Med. 2022;24:e3397.
Nie S, Zhang L, Liu J, Wan Y, Jiang Y, Yang J, et al. ALKBH5-HOXA10 loop-mediated JAK2 m6A demethylation and cisplatin resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res: CR. 2021;40:284.
Abner JJ, Franklin JL, Clement MA, Hinger SA, Allen RM, Liu X, et al. Depletion of METTL3 alters cellular and extracellular levels of miRNAs containing m(6)A consensus sequences. Heliyon. 2021;7:e08519.
Alimardan Z, Abbasi M, Hasanzadeh F, Aghaei M, Khodarahmi G, Kashfi K. Heat shock proteins and cancer: The FoxM1 connection. Biochem Pharm. 2023;211:115505.
Kuai XY, Lei ZY, Liu XS, Shao XY. The Interaction of GLUT1 and FOXM1 leads to a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20:941–50.
Rather TB, Parveiz I, Bhat GA, Rashid G, Wani RA, Khan IY, et al. Evaluation of Forkhead BOX M1 (FOXM1) gene expression in colorectal cancer. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023;23:2385–405.
Zhang H, Zhong H, Li L, Ji W, Zhang X. Overexpressed transcription factor FOXM1 contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer. Mol. Med Rep. 2016;13:2696–2700.
Valverde A, Peñarando J, Cañas A, López-Sánchez LM, Conde F, Guil-Luna S, et al. The addition of celecoxib improves the antitumor effect of cetuximab in colorectal cancer: role of EGFR-RAS-FOXM1-β- catenin signaling axis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:21754–69.
Zhao H, Ming T, Tang S, Ren S, Yang H, Liu M, et al. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: pathogenic role and therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer. 2022;21:144.
Dong S, Liang S, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Luo L, Li L, et al. ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signalings activate HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022;41:15.
Liu X, Su K, Sun X, Jiang Y, Wang L, Hu C, et al. Sec62 promotes stemness and chemoresistance of human colorectal cancer through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021;40:132.
Lu Y, Zhao X, Liu Q, Li C, Graves-Deal R, Cao Z, et al. lncRNA MIR100HG-derived miR-100 and miR-125b mediate cetuximab resistance via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Nat. Med. 2017;23:1331–41.
Shan W, Dai C, Zhang H, Han D, Yi Q, Xia B. ACY1 downregulation enhances the radiosensitivity of Cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer by inactivating the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Cancers 2022;14:5704.
Liu YF, Feng ZQ, Chu TH, Yi B, Liu J, Yu H, et al. Andrographolide sensitizes KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer cells to cetuximab by inhibiting the EGFR/AKT and PDGFRβ/AKT signaling pathways. Phytomed: Int J. Phytother. Phytopharmacol. 2024;126:155462.
Funding
This work was supported by the Hospital-Level Doctoral Fund Project (grant number BS202206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH designed the study. HH, YL, ZL, XM, WH, CL, RM, and RH performed the research and analyzed the data. HH, Y,L and ZL contributed new methods and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research protocol was also reviewed and granted approval by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University. Written informed consent was secured from every participant prior to their inclusion in the study. The study was executed with the utmost rigor, adhering to the ethical guidelines for animal care, and experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Li, Y., Lin, Z. et al. ALKBH5 suppresses m6A mRNA modification of FOXM1 to drive Cetuximab resistance in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Oncogene 44, 3225–3238 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03490-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03490-1