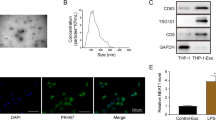
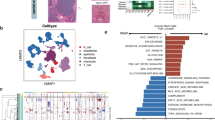
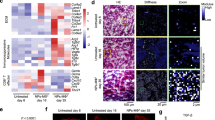
Abstract
The limited efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can arise from the involvement of immunosuppressive cells, such as macrophages. In the present study, we found that the long noncoding RNA NEAT1, particularly its short isoform (NEAT1v1) induced the expression of CD24, which is known as an immune checkpoint molecule for macrophages. Mechanistically, NEAT1v1 sponged miR-320a-3p to upregulate the transcription factor SP1, which in turn, activated CD24 transcription. A spheroid co-culture of primary or THP-1-derived macrophages with HCC cells revealed that NEAT1v1 suppressed M1 marker expression and phagocytic activity in macrophages. In a syngeneic subcutaneous model of HCC, Neat1v1 increased the tumor infiltration of M2-like macrophages and induced resistance to anti-Pd-1 antibody, while combination of the anti-Pd-1 and anti-Cd24 antibodies significantly suppressed the tumor growth. Finally, NEAT1, SP1, and CD24 expression increased in tumor tissues from patients with HCC, compared to adjacent normal tissues, whereas miR-320a-3p was significantly downregulated. Moreover, plasma NEAT1 cell-free RNA was significantly decreased after therapeutic intervention. Taken together, NEAT1v1 protects HCC cells from macrophages by sending a “Don’t Eat Me” signal via CD24, and is therefore, a potential target molecule for the treatment and diagnosis of HCC.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All raw data are available in the manuscript and its supplementary files or from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–63.
Saleh Y, Abu Hejleh T, Abdelrahim M, Shamseddine A, Chehade L, Alawabdeh T, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: the evolving role of systemic therapies as a bridging treatment to liver transplantation. Cancers. 2024;16:2081.
Zarlashat Y, Abbas S, Ghaffar A. Hepatocellular carcinoma: beyond the border of advanced stage therapy. Cancers. 2024;16:2034.
Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim TY, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1894–905.
Abou-Alfa GK, Lau G, Kudo M, Chan SL, Kelley RK, Furuse J, et al. Tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. NEJM Evid. 2022;1:EVIDoa2100070.
Gordan JD, Kennedy EB, Abou-Alfa GK, Beal E, Finn RS, Gade TP, et al. Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42:1830–50.
Arvanitakis K, Koletsa T, Mitroulis I, Germanidis G. Tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis, prognosis and therapy. Cancers. 2022;14:226.
Lopez-Yrigoyen M, Cassetta L, Pollard JW. Macrophage targeting in cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021;1499:18–41.
Wang PC, Hu ZQ, Zhou SL, Yu SY, Mao L, Su S, et al. The spatial distribution of immune cell subpopulations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2022;113:423–31.
Sheng J, Zhang J, Wang L, Tano V, Tang J, Wang X, et al. Topological analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma tumour microenvironment based on imaging mass cytometry reveals cellular neighbourhood regulated reversely by macrophages with different ontogeny. Gut. 2022;71:1176–91.
Zhou C, Weng J, Liu C, Liu S, Hu Z, Xie X, et al. Disruption of SLFN11 deficiency-induced CCL2 signaling and macrophage M2 polarization potentiates anti-PD-1 therapy efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2023;164:1261–78.
Li X, Yao W, Yuan Y, Chen P, Li B, Li J, et al. Targeting of tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2017;66:157–67.
Han S, Bao X, Zou Y, Wang L, Li Y, Yang L, et al. d-lactate modulates M2 tumor-associated macrophages and remodels immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eadg2697.
Lee TK, Castilho A, Cheung VC, Tang KH, Ma S, Ng IO. CD24(+) liver tumor-initiating cells drive self-renewal and tumor initiation through STAT3-mediated NANOG regulation. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9:50–63.
Liu AY, Cai Y, Mao Y, Lin Y, Zheng H, Wu T, et al. Twist2 promotes self-renewal of liver cancer stem-like cells by regulating CD24. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:537–45.
Tsuchiya H, Shiota G. Clinical and biological implications of cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Yonago Acta Med. 2021;64:1–11.
Tsuchiya H, Shiota G. Immune evasion by cancer stem cells. Regen Ther. 2021;17:20–33.
Barkal AA, Brewer RE, Markovic M, Kowarsky M, Barkal SA, Zaro BW, et al. CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;572:392–6.
Chen GY, Tang J, Zheng P, Liu Y. CD24 and Siglec-10 selectively repress tissue damage-induced immune responses. Science. 2009;323:1722–5.
Li X, Tian W, Jiang Z, Song Y, Leng X, Yu J. Targeting CD24/Siglec-10 signal pathway for cancer immunotherapy: recent advances and future directions. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024;73:31.
Koyama S, Tsuchiya H, Amisaki M, Sakaguchi H, Honjo S, Fujiwara Y, et al. NEAT1 is required for the expression of the liver cancer stem cell marker CD44. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1927.
Sakaguchi H, Tsuchiya H, Kitagawa Y, Tanino T, Yoshida K, Uchida N, et al. NEAT1 confers radioresistance to hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inducing autophagy through GABARAP. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:711.
Tsuchiya H, Shinonaga R, Sakaguchi H, Kitagawa Y, Yoshida K, Shiota G. NEAT1 confers radioresistance to hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inducing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:14397.
Tsuchiya H, Shinonaga R, Sakaguchi H, Kitagawa Y, Yoshida K. NEAT1-SOD2 axis confers sorafenib and lenvatinib resistance by activating AKT in liver cancer cell lines. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023;45:1073–85.
Yin L, Wang Y. Extracellular vesicles derived from M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages promote immune escape in ovarian cancer through NEAT1/miR-101-3p/ZEB1/PD-L1 axis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023;72:743–58.
Heideveld E, Horcas-Lopez M, Lopez-Yrigoyen M, Forrester LM, Cassetta L, Pollard JW. Methods for macrophage differentiation and in vitro generation of human tumor associated-like macrophages. Methods Enzymol. 2020;632:131.
Yuan W, Zhang Q, Gu D, Lu C, Dixit D, Gimple RC, et al. Dual role of CXCL8 in maintaining the mesenchymal state of glioblastoma stem cells and M2-like tumor-associated macrophages. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29:3779–92.
Tsai SC, Lin CC, Shih TC, Tseng RJ, Yu MC, Lin YJ, et al. The miR-200b-ZEB1 circuit regulates diverse stemness of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2017;56:2035–47.
Thomas S, Harding MA, Smith SC, Overdevest JB, Nitz MD, Frierson HF, et al. CD24 is an effector of HIF-1-driven primary tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012;72:5600–12.
Yu W, Ma Y, Shankar S, Srivastava RK. Role of SATB2 in human pancreatic cancer: implications in transformation and a promising biomarker. Oncotarget. 2016;7:57783–97.
Chen J, Li H, Zhang B, Xiong Z, Jin Z, Chen J, et al. ABI2-mediated MEOX2/KLF4-NANOG axis promotes liver cancer stem cell and drives tumour recurrence. Liver Int. 2022;42:2562–76.
Lin CY, Tsai CL, Chao A, Lee LY, Chen WC, Tang YH, et al. Nucleophosmin/B23 promotes endometrial cancer cell escape from macrophage phagocytosis by increasing CD24 expression. J Mol Med. 2021;99:1125–37.
Agarwal N, Dancik GM, Goodspeed A, Costello JC, Owens C, Duex JE, et al. GON4L drives cancer growth through a YY1-androgen receptor-CD24 axis. Cancer Res. 2016;76:5175–85.
Rauluseviciute I, Riudavets-Puig R, Blanc-Mathieu R, Castro-Mondragon JA, Ferenc K, Kumar V, et al. JASPAR 2024: 20th anniversary of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52:D174–D182.
Saleh RO, Alkhafaji AT, Mohammed JS, Bansal P, Kaur H, Ahmad I, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 in the pathogenesis of liver-related diseases. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024;42:e4006.
Zhang Y, Huang C, Zhu Z, Hou Y, Huang S, Sun C, et al. lncRNA NEAT1 regulates the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by acting as a miR‑320a molecular sponge and targeting L antigen family member 3. Int J Oncol. 2020;57:1001–12.
Zhang W, Yang H, Wang Z, Wu Y, Wang J, Duan G, et al. miR-320a/SP1 negative reciprocal interaction contributes to cell growth and invasion in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:175.
Benes V, Collier P, Kordes C, Stolte J, Rausch T, Muckentaler MU, et al. Identification of cytokine-induced modulation of microRNA expression and secretion as measured by a novel microRNA specific qPCR assay. Sci Rep. 2015;25:11590.
Portugal J. Mithramycin and its analogs: molecular features and antitumor action. Pharmacol Ther. 2024;260:108672.
Hill J, Shalaby KE, Bihaqi SW, Alansi BH, Barlock B, Parang K, et al. Tolfenamic acid derivatives: a new class of transcriptional modulators with potential therapeutic applications for Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:15216.
Fujii M, Shibazaki Y, Wakamatsu K, Honda Y, Kawauchi Y, Suzuki K, et al. A murine model for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis showing evidence of association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Mol Morphol. 2013;46:141–52.
Toker J, Iorgulescu JB, Ling AL, Villa GR, Gadet JAMA, Parida L, et al. Clinical importance of the lncRNA NEAT1 in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29:2226–38.
Zhang P, Cao L, Zhou R, Yang X, Wu M. The lncRNA Neat1 promotes activation of inflammasomes in macrophages. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1495.
Chen Y, Wu Y, Guo L, Yuan S, Sun J, Zhao K, et al. Exosomal Lnc NEAT1 from endothelial cells promote bone regeneration by regulating macrophage polarization via DDX3X/NLRP3 axis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21:98.
Yang Y, Ma S, Ye Z, Zheng Y, Zheng Z, Liu X, et al. NEAT1 in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promotes melanoma by inducing M2 macrophage polarization. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022;29:1228–39.
Zhen S, Jia Y, Zhao Y, Wang J, Zheng B, Liu T, et al. NEAT1_1 confers gefitinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma through promoting AKR1C1-mediated ferroptosis defence. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10:131.
Liu Y, Li Y, Wu Y, Zhao Y, Hu X, Sun C. The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes the progression of human ovarian cancer through targeting miR-214-3p and regulating angiogenesis. J Ovarian Res. 2023;16:219.
Tripathi SK, Pal A, Ghosh S, Goel A, Aggarwal R, Banerjee S, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 regulates HCV-induced Hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating the miR-9-BGH3 axis. J Gen Virol. 2022;103.
Zhang H, Yu S, Fei K, Huang Z, Deng S, Xu H. NEAT1 promotes the malignant development of bladder cancer by regulating the miR-101/VEGF-C pathway in vitro and in vivo. BMC Urol. 2022;22:193.
Yang L, Xie F, Xu W, Xu T, Ni Y, Tao X, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST accelerates hepatic carcinoma progression by targeting the microRNA-320a/PIK3CA axis. Oncol Lett. 2021;22:801.
Galbiati S, Bettiga A, Colciago G, Senti C, Trevisani F, Villa G, et al. The long noncoding RNA SUMO1P3 as urinary biomarker for monitoring bladder cancer progression. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1325157.
Bozgeyik E, Arslan A, Temiz E, Batar B, Koyuncu I, Tozkir H. miR-320a promotes p53-dependent apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by negatively regulating TP73-AS1 invitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;619:130–6. 2022;619:130–136.
Hao X, Xin R, Dong W. Decreased serum exosomal miR-320a expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Int Med Res. 2020;48:300060519896144.
Liu Y, Liu DL, Dong LL, Wen D, Shi DM, Zhou J, et al. miR-612 suppresses stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by modulating Sp1/Nanog signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2377.
Liu S, Bu X, Kan A, Luo L, Xu Y, Chen H, et al. SP1-induced lncRNA DUBR promotes stemness and oxaliplatin resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma via E2F1-CIP2A feedback. Cancer Lett. 2022;528:16–30.
Tsui YM, Ho DW, Sze KM, Lee JM, Lee E, Zhang Q, et al. Sorted-cell sequencing on HCC specimens reveals EPS8L3 as a key player in CD24/CD13/EpCAM-triple positive, stemness-related HCC cells. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;18:101358.
Mao D, Zhou Z, Chen H, Liu X, Li D, Chen X, et al. Pleckstrin-2 promotes tumour immune escape from NK cells by activating the MT1-MMP-MICA signalling axis in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2023;572:216351.
Cao T, Zhang W, Wang Q, Wang C, Ma W, Zhang C, et al. Cancer SLC6A6-mediated taurine uptake transactivates immune checkpoint genes and induces exhaustion in CD8+ T cells. Cell. 2024;187:2288–2304.e27.
Abdelrahim M, Baker CH, Abbruzzese JL, Safe S. Tolfenamic acid and pancreatic cancer growth, angiogenesis, and Sp protein degradation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:855–68.
Hou C, Mandal A, Rohr J, Tsodikov OV. Allosteric interference in oncogenic FLI1 and ERG transactions by mithramycins. Structure. 2021;29:404–412.e4.
Cheng YH, Yin P, Xue Q, Yilmaz B, Dawson MI, Bulun SE. Retinoic acid (RA) regulates 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 expression in endometrium: interaction of RA receptors with specificity protein (SP) 1/SP3 for estradiol metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1915–23.
Poursharifi P, Schmitt C, Chenier I, Leung YH, Oppong AK, Bai Y, et al. ABHD6 suppression promotes anti-inflammatory polarization of adipose tissue macrophages via 2-monoacylglycerol/PPAR signaling in obese mice. Mol Metab. 2023;78:101822.
Zhao Y, Chai X, Peng J, Zhu Y, Dong R, He J, et al. Proline exacerbates hepatic gluconeogenesis via paraspeckle-dependent mRNA retention. Nat Metab. 2025;7:367–82.
Kay EJ, Paterson K, Riera-Domingo C, Sumpton D, Däbritz JHM, Tardito S, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts require proline synthesis by PYCR1 for the deposition of pro-tumorigenic extracellular matrix. Nat Metab. 2022;4:693–710.
Tharp KM, Kersten K, Maller O, Timblin GA, Stashko C, Canale FP, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages restrict CD8+ T cell function through collagen deposition and metabolic reprogramming of the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat Cancer. 2024;5:1045–62.
Luo X, Wei Q, Jiang X, Chen N, Zuo X, Zhao H, et al. CSTF3 contributes to platinum resistance in ovarian cancer through alternative polyadenylation of lncRNA NEAT1 and generating the short isoform NEAT1_1. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15:432.
Liu T, Wang H, Fu Z, Wang Z, Wang J, Gan X, et al. Methyltransferase-like 14 suppresses growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by decreasing long noncoding RNA NEAT1. Cancer Sci. 2022;113:446–58.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Mirco Castoldi (University Hospital of Düsseldorf) for technical advice on miQPCR. This research was partly performed at Research Initiative Center, Tottori University, and the Tottori Bio Frontier managed by Tottori prefecture. The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 23K07437 (HT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HT performed most of the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. TH, NT, and TN contributed to the collection of liver and blood samples and the curation of clinical information. TS and YU conducted immunohistochemistry and its quantitative analysis. HI and YF conceptualized and supervised the project. DN supervised the project, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuchiya, H., Hanaki, T., Sakabe, T. et al. Immune evasion from macrophages by NEAT1-induced CD24 in liver cancer. Oncogene 44, 3652–3664 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03537-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03537-3