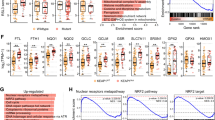
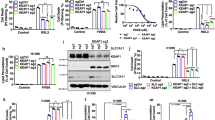
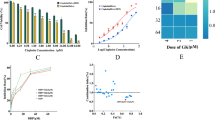
Abstract
Ferroptosis, a distinct form of programmed cell death characterized by the iron-dependent aberrant buildup of lipid peroxides, has emerged as a promising approach in cancer therapy. The KEAP1-NRF2 axis serves as a critical regulator of ferroptosis, exerting its suppressive effects by preserving cellular redox homeostasis and orchestrating the transcriptional activation of downstream antioxidant genes. NRF2 hyperactivation is frequently observed across multiple cancer types and is associated with tumor progression and therapeutic resistance. Here, we identified the transcription factor TFAP2C as a novel regulator of the KEAP1-NRF2 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer (OC). TFAP2C knockdown inactivated KEAP1-NRF2 signaling, consequently reducing cell viability while inducing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ferrous iron (Fe²⁺). Additionally, a decrease in the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was observed upon TFAP2C knockdown. These alterations collectively triggered ferroptosis, thereby inhibiting the progression of OC to some extent. Moreover, NRF2 knockdown partially attenuated the pro-proliferative and ferroptosis-resistant phenotypes driven by TFAP2C overexpression in OC. ChIP and dual-luciferase reporter gene assays confirmed that TFAP2C transcriptionally repressed KEAP1 expression, thereby weakening the ubiquitination degradation of NRF2 by KEAP1. The upregulation of TFAP2C expression stabilized the NRF2 protein, activated the NRF2-dependent transcriptional program, and strengthened cellular antioxidant defenses, ultimately conferring resistance to ferroptosis. Mechanistically, TFAP2C bound to the promoter region of KEAP1 and recruited histone deacetylases 1/2 (HDAC1/2), resulting in the deacetylation of H3K27 and subsequent transcriptional repression of KEAP1. In summary, our mechanistic investigations revealed TFAP2C as a novel oncogenic driver in OC and a key regulator of ferroptosis via its epigenetic modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 axis. These findings highlight TFAP2C as a potential therapeutic target for ferroptosis-inducing therapies in OC patients with high TFAP2C expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The supporting data for this study are provided in the supplementary materials. The raw ChIP-seq data are available upon request via email.
References
Ramos S, Hartenian E, Santos JC, Walch P, Broz P. NINJ1 induces plasma membrane rupture and release of damage-associated molecular pattern molecules during ferroptosis. EMBO J. 2024;43:1164–86.
Gong J, Liu Y, Wang W, He R, Xia Q, Chen L, et al. TRIM21-promoted FSP1 plasma membrane translocation confers ferroptosis resistance in human cancers. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2302318.
Hassannia B, Vandenabeele P, Vanden Berghe T. Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:830–49.
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:381–96.
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B. The roles of ferroptosis in cancer: Tumor suppression, tumor microenvironment, and therapeutic interventions. Cancer Cell. 2024;42:513–34.
Han B, Zhen F, Sun Y, Sun B, Wang HY, Liu W, et al. Tumor suppressor KEAP1 promotes HSPA9 degradation, controlling mitochondrial biogenesis in breast cancer. Cell Rep. 2024;43:114507.
Leinonen HM, Kansanen E, Pölönen P, Heinäniemi M, Levonen AL. Role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2014;122:281–320.
Xu K, Ma J, Hall SRR, Peng RW, Yang H, Yao F. Battles against aberrant KEAP1-NRF2 signaling in lung cancer: intertwined metabolic and immune networks. Theranostics. 2023;13:704–23.
Culletta G, Buttari B, Arese M, Brogi S, Almerico AM, Saso L, et al. Natural products as non-covalent and covalent modulators of the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway exerting antioxidant effects. Eur J Med Chem. 2024;270:116355.
Zhang DD. Thirty years of NRF2: advances and therapeutic challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025;24:421–444.
Liu Y, Tao S, Liao L, Li Y, Li H, Li Z, et al. TRIM25 promotes the cell survival and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Nat Commun. 2020;11:348.
Zhou Y, Chen Y, Shi Y, Wu L, Tan Y, Li T, et al. FAM117B promotes gastric cancer growth and drug resistance by targeting the KEAP1/NRF2 signaling pathway. J Clin Invest. 2023;133:e158705.
Jin C, Luo Y, Liang Z, Li X, Kołat D, Zhao L, et al. Crucial role of the transcription factors family activator protein 2 in cancer: current clue and views. J Transl Med. 2023;21:371.
Liu K, Xiao Y, Gan L, Li W, Zhang J, Min J. Structural basis for specific DNA sequence motif recognition by the TFAP2 transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51:8270–82.
Li L, Lai F, Liu L, Lu X, Hu X, Liu B, et al. Lineage regulators TFAP2C and NR5A2 function as bipotency activators in totipotent embryos. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024;31:950–63.
Zeng M, Wei X, He YL, Chen JX, Lin WT. TFAP2C inhibits cell autophagy to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating miR-23a-5p/SFRP5/Wnt5a axis. FASEB J. 2023;37:e22959.
Zhao Y, Liu J, Liu S, Yang P, Liang Y, Ma J, et al. Fibroblast exosomal TFAP2C induced by chitosan oligosaccharides promotes peripheral axon regeneration via the miR-132-5p/CAMKK1 axis. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:249–63.
Alim I, Caulfield JT, Chen Y, Swarup V, Geschwind DH, Ivanova E, et al. Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell. 2019;177:1262–79.e25.
Park JM, Wu T, Cyr AR, Woodfield GW, De Andrade JP, Spanheimer PM, et al. The role of Tcfap2c in tumorigenesis and cancer growth in an activated Neu model of mammary carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2015;34:6105–14.
De Andrade JP, Park JM, Gu VW, Woodfield GW, Kulak MV, Lorenzen AW, et al. EGFR is regulated by TFAP2C in luminal breast cancer and is a target for vandetanib. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15:503–11.
Li L, Zheng YL, Jiang C, Fang S, Zeng TT, Zhu YH, et al. HN1L-mediated transcriptional axis AP-2γ/METTL13/TCF3-ZEB1 drives tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:2268–83.
Wang X, Sun D, Tai J, Chen S, Yu M, Ren D, et al. TFAP2C promotes stemness and chemotherapeutic resistance in colorectal cancer via inactivating hippo signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:27.
Jiang X, Guo S, Xu M, Ma B, Liu R, Xu Y, et al. TFAP2C-mediated lncRNA PCAT1 inhibits ferroptosis in docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer through c-Myc/miR-25-3p/SLC7A11 signaling. Front Oncol. 2022;12:862015.
Yuan L, Zhou D, Li W, Guan J, Li J, Xu B. TFAP2C activates CST1 transcription to facilitate breast cancer progression and suppress ferroptosis. Biochem Genet. 2024;62:3858–75.
Shao Y, Jia H, Huang L, Li S, Wang C, Aikemu B, et al. An original ferroptosis-related gene signature effectively predicts the prognosis and clinical status for colorectal cancer patients. Front Oncol. 2021;11:711776.
Yuan H, Hua Z, Zhang H, Xu D. Ferroptosis and ovarian cancer: a bibliometric study and visualization analysis. Discov Oncol. 2025;16:1572.
Wang Y, Zhao G, Condello S, Huang H, Cardenas H, Tanner EJ, et al. Frizzled-7 identifies platinum-tolerant ovarian cancer cells susceptible to ferroptosis. Cancer Res. 2021;81:384–99.
Hong T, Lei G, Chen X, Li H, Zhang X, Wu N, et al. PARP inhibition promotes ferroptosis via repressing SLC7A11 and synergizes with ferroptosis inducers in BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer. Redox Biol. 2021;42:101928.
Kapper C, Oppelt P, Arbeithuber B, Gyunesh AA, Vilusic I, Stelzl P, et al. Targeting ferroptosis in ovarian cancer: novel strategies to overcome chemotherapy resistance. Life Sci. 2024;349:122720.
Wang Y, Xie H, Chang X, Hu W, Li M, Li Y, et al. Single-cell dissection of the multiomic landscape of high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2022;82:3903–16.
Shen J, He Y, Zhou B, Qin H, Zhang S, Huang Z, et al. TFAP2C/FLT3 axis reduces ferroptosis in breast cancer cells by inhibiting mitochondrial autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2024;177:106691.
Li Y, Yang C, Xie L, Shi F, Tang M, Luo X, et al. CYLD induces high oxidative stress and DNA damage through class I HDACs to promote radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15:95.
Koppula P, Lei G, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Mao C, Kondiparthi L, et al. A targetable CoQ-FSP1 axis drives ferroptosis- and radiation-resistance in KEAP1 inactive lung cancers. Nat Commun. 2022;13:2206.
Huang C, Zeng Q, Chen J, Wen Q, Jin W, Dai X, et al. TMEM160 inhibits KEAP1 to suppress ferroptosis and induce chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2025;16:287.
Wei J, Wang L, Zhang Y, Sun T, Zhang C, Hu Z, et al. TRIM25 promotes temozolomide resistance in glioma by regulating oxidative stress and ferroptotic cell death via the ubiquitination of Keap1. Oncogene. 2023;42:2103–12.
Kant R, Manne RK, Anas M, Penugurti V, Chen T, Pan BS, et al. Deregulated transcription factors in cancer cell metabolisms and reprogramming. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86:1158–74.
Gunton JE. Hypoxia-inducible factors and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:5063–73.
Yu B, Wang X, Song Y, Xie G, Jiao S, Shi L, et al. The role of hypoxia-inducible factors in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;238:108186.
Wu Y, Chen S, Shao Y, Su Y, Li Q, Wu J, et al. KLF5 promotes tumor progression and PARP inhibitor resistance in ovarian cancer. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2304638.
Gao R, Yang G, Wang M, Xiao J, Yi S, Huang Y, et al. Defining a TFAP2C-centered transcription factor network during murine peri-implantation. Dev Cell. 2024;59:1146–58.e6.
Xing J, Chen W, Chen K, Zhu S, Lin F, Qi Y, et al. TFAP2C knockdown sensitizes bladder cancer cells to cisplatin treatment via regulation of EGFR and NF-κB. Cancers. 2022;14:4809.
Do H, Kim D, Kang J, Son B, Seo D, Youn H, et al. TFAP2C increases cell proliferation by downregulating GADD45B and PMAIP1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biol Res. 2019;52:35.
Kim W, Kim E, Lee S, Kim D, Chun J, Park KH, et al. TFAP2C-mediated upregulation of TGFBR1 promotes lung tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Exp Mol Med. 2016;48:e273.
Adinolfi S, Patinen T, Jawahar Deen A, Pitkänen S, Härkönen J, Kansanen E, et al. The KEAP1-NRF2 pathway: targets for therapy and role in cancer. Redox Biol. 2023;63:102726.
Chang K, Chen Y, Zhang X, Zhang W, Xu N, Zeng B, et al. DPP9 stabilizes NRF2 to suppress ferroptosis and induce sorafenib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2023;83:3940–55.
Sun C, Han B, Zhai Y, Zhao H, Li X, Qian J, et al. Dihydrotanshinone I inhibits ovarian tumor growth by activating oxidative stress through Keap1-mediated Nrf2 ubiquitination degradation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;180:220–35.
Zhou RW, Xu J, Martin TC, Zachem AL, He J, Ozturk S, et al. A local tumor microenvironment acquired super-enhancer induces an oncogenic driver in colorectal carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2022;13:6041.
Wang Z, Chen K, Zhang K, He K, Zhang D, Guo X, et al. Agrocybe cylindracea fucoglucogalactan induced lysosome-mediated apoptosis of colorectal cancer cell through H3K27ac-regulated cathepsin D. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;319:121208.
Kim MY, Yan B, Huang S, Qiu Y. Regulating the regulators: the role of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) in erythropoiesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:8460.
Yang Y, Song S, Li S, Kang J, Li Y, Zhao N, et al. GATA4 regulates the transcription of MMP9 to suppress the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via HDAC1-mediated p65 deacetylation. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15:289.
Bahia RK, Hao X, Hassam R, Cseh O, Bozek DA, Luchman HA, et al. Epigenetic and molecular coordination between HDAC2 and SMAD3-SKI regulates essential brain tumour stem cell characteristics. Nat Commun. 2023;14:5051.
Acknowledgements
The graphical abstract was created with the assistance of MedPeer (https://product.medpeer.cn/). We sincerely thank everyone who participated in and contributed to this study.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82403097), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2024M761831), and Shandong Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. SDCx-ZG-202400049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GC conducted the experiments, analyzed the data, prepared the figures, and wrote the manuscript. WJ and ZL conducted animal experiments and contributed to manuscript writing. YM and XL designed the study, supervised the project, revised the manuscript, and provided funding.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, G., Jiang, W., Li, Z. et al. TFAP2C protects against ferroptosis in ovarian cancer through the KEAP1-NRF2 axis by recruiting HDAC1/2. Oncogene (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-026-03692-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-026-03692-1