Abstract
Background
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder with an unclear etiology and pathophysiology. Previous studies have indicated that the dysregulation of cytokines may be involved in the pathogenesis of ASD and that the levels of cytokines may serve as potential biomarkers of this disorder.
Methods
The current study employed a family triad-based case–control design to study the levels of plasma cytokines in families with ASD (n = 45 triads) and controls (n = 38 triads) with a Human Cytokine Twenty-Five-Plex Kit. The Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS) was used to measure social impairment of ASD children.
Results
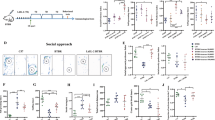
After controlling for the levels of parental cytokines, we identified that interferon-α (IFN-α), interleukin-7 (IL-7), IL-8, IFN-γ-inducible protein-10, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1β were associated with ASD, and IL-8 was the only cytokine also associated with the levels of both parental cytokines in the offspring–parents regression analysis and three subdomains of SRS (social awareness, cognition, and motivations) in the children with ASD. The receiver operating characteristic curve showed that the log-transformed IL-8 level discriminated children with autism from controls with an area under the curve of 0.858 (95% confidence interval: 0.777–0.939).
Conclusions
Our study suggests that IL-8 is a potential biomarker for ASD and may be involved in the pathogenesis of ASD.
IMPACT
-
The study suggests that IL-8 is a promising biomarker for ASD and may be involved in the pathogenesis of ASD.
-
Only a very few studies have reported the parental cytokine levels. The significant strength of this article is that we applied the family triad-based approach to explore cytokine levels in families with autism and controls.
-
There are no objective biomarkers, making the accurate diagnosis, prognostic prediction and effective treatment difficult, and our study provides promising results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lord, C., Elsabbagh, M., Baird, G. & Veenstra-Vanderweele, J. Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet 392, 508–520 (2018).
Wang, Y. et al. Social impairment of children with autism spectrum disorder affects parental quality of life in different ways. Psychiatry Res. 266, 168–74. (2018).
Ou, J. J. et al. Employment and financial burden of families with preschool children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders in urban China: results from a descriptive study. BMC Psychiatry. 15, 3 (2015).
Baio, J. et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 67, 1–23 (2018).
Xia, K. et al. Common genetic variants on 1p13.2 associate with risk of autism. Mol. Psychiatry 19, 1212–1219 (2014).
Sealey, L. A. et al. Environmental factors in the development of autism spectrum disorders. Environ. Int. 88, 288–98. (2016).
Andrews, S. V. et al. Cross-tissue integration of genetic and epigenetic data offers insight into autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Commun. 8, 1011 (2017).
Meltzer, A. & Van de Water, J. The role of the immune system in autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 42, 284–298 (2017).
Bielekova, B., Komori, M., Xu, Q., Reich, D. S. & Wu, T. Cerebrospinal fluid IL-12p40, CXCL13 and IL-8 as a combinatorial biomarker of active intrathecal inflammation. PLoS ONE 7, e48370 (2012).
Gumusoglu, S. B., Fine, R. S., Murray, S. J., Bittle, J. L. & Stevens, H. E. The role of IL-6 in neurodevelopment after prenatal stress. Brain Behav. Immun. 65, 274–83. (2017).
Schwartzer, J. J. et al. Maternal immune activation and strain specific interactions in the development of autism-like behaviors in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 3, e240 (2013).
Choi, G. B. et al. The maternal interleukin-17a pathway in mice promotes autism-like phenotypes in offspring. Science 351, 933–939 (2016).
Masi, A. et al. Cytokine aberrations in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 20, 440–446 (2015).
Leviton, A. et al. The risk of neurodevelopmental disorders at age 10 years associated with blood concentrations of interleukins 4 and 10 during the first postnatal month of children born extremely preterm. Cytokine 110, 181–188 (2018).
Hu, C. C. et al. Alterations in plasma cytokine levels in chinese children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 11, 989–999 (2018).
Shen, Y. et al. Altered plasma levels of chemokines in autism and their association with social behaviors. Psychiatry Res. 244, 300–305 (2016).
Cen, C. Q. et al. Investigating the validation of the Chinese Mandarin version of the Social Responsiveness Scale in a Mainland China child population. BMC Psychiatry. 17, 51 (2017).
Luo, B. F. et al. Heritability of metabolic syndrome traits among healthy younger adults: a population based study in China. J. Med. Genet. 47, 415–420 (2010).
Ashwood, P. et al. Associations of impaired behaviors with elevated plasma chemokines in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 232, 196–199 (2011).
Ashwood, P., Nguyen, D. V., Hessl, D., Hagerman, R. J. & Tassone, F. Plasma cytokine profiles in Fragile X subjects: is there a role for cytokines in the pathogenesis? Brain Behav. Immun. 24, 898–902 (2010).
Suzuki, K. et al. Plasma cytokine profiles in subjects with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. PLoS ONE 6, e20470 (2011).
Abdallah, M. W. et al. Amniotic fluid chemokines and autism spectrum disorders: an exploratory study utilizing a Danish Historic Birth Cohort. Brain Behav. Immun. 26, 170–176 (2012).
Tostes, M. H., Teixeira, H. C., Gattaz, W. F., Brandao, M. A. & Raposo, N. R. Altered neurotrophin, neuropeptide, cytokines and nitric oxide levels in autism. PHarmacopsychiatry 45, 241–243 (2012).
Zerbo, O. et al. Neonatal cytokines and chemokines and risk of autism spectrum disorder: the early markers for autism (EMA) study: a case-control study. J. Neuroinflamm. 11, 113 (2014).
Eftekharian, M. M. et al. Cytokine profile in autistic patients. Cytokine 108, 120–126 (2018).
Saghazadeh, A., Ataeinia, B., Keynejad, K., Abdolalizadeh, A., Hirbod-Mobarakeh, A. & Rezaei, N. A meta-analysis of pro-inflammatory cytokines in autism spectrum disorders: Effects of age, gender, and latitude. J Psychiatr Res. 115, 90–102 (2019).
Arango, D. G. & Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 5, 491 (2014).
Ballendine, S. A. et al. Behavioral alterations in rat offspring following maternal immune activation and ELR-CXC chemokine receptor antagonism during pregnancy: implications for neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 57, 155–165 (2015).
Ellman, L. M. et al. Structural brain alterations in schizophrenia following fetal exposure to the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-8. Schizophr. Res. 121, 46–54 (2010).
Stuart, M. J. & Baune, B. T. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in mood disorders, schizophrenia, and cognitive impairment: a systematic review of biomarker studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 42, 93–115 (2014).
Giovannelli, A. et al. CXC chemokines interleukin-8 (IL-8) and growth-related gene product alpha (GROalpha) modulate Purkinje neuron activity in mouse cerebellum. J. Neuroimmunol. 92, 122–132 (1998).
Li, X. et al. Elevated immune response in the brain of autistic patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 207, 111–116 (2009).
Ashwood, P. et al. Elevated plasma cytokines in autism spectrum disorders provide evidence of immune dysfunction and are associated with impaired behavioral outcome. Brain Behav. Immun. 25, 40–45 (2011).
Korzeniewski, S. J., Allred, E. N., O’Shea, T. M., Leviton, A. & Kuban, K. Elevated protein concentrations in newborn blood and the risks of autism spectrum disorder, and of social impairment, at age 10 years among infants born before the 28th week of gestation. Transl. Psychiatry. 8, 1 (2018).
Koks, N. et al. Maternal C-reactive protein concentration in early pregnancy and child autistic traits in the general population. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 30, 181–189 (2016).
Jones, K. L. et al. Autism with intellectual disability is associated with increased levels of maternal cytokines and chemokines during gestation. Mol. Psychiatry 22, 273–279 (2017).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all subjects who participated in this study. This study was supported by funding from The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.: 81901388, 81974217, 81601197, and 81873806), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB517901), and the Humanity and Social Sciences Youth Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No: 17YJC190022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.O., Y.S., Y.L., F.Z., and J.Z. designed the study. J.O., Y.S., M.L., and F.Z. performed the analyses and wrote the draft of this manuscript. Y.S., J.O., Y.L., L.S., M.L., R.W., K.X., and J.Z. managed the data collection and contributed to the data input. All authors contributed to the editing of the manuscript and agreed with the final text.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The ethics committee of the Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University approved this study, and the parents provided written informed consent for all children.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Li, Y., Shi, L. et al. Autism spectrum disorder and severe social impairment associated with elevated plasma interleukin-8. Pediatr Res 89, 591–597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-020-0910-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-020-0910-x
This article is cited by
-
Correlation of biochemical markers and inflammatory cytokines in autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
BMC Pediatrics (2024)
-
Investigation of the Relation between Epithelial Barrier Function and Autism Symptom Severity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2022)