Abstract
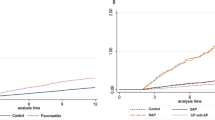
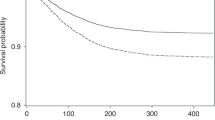
For children, there are very few published reviews focusing on severe acute pancreatitis (AP). PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Scopus, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang data, EBSCO, and Cochrane Library were searched from inception until March 2020. Meta-regression analyses were used to estimate the etiology, case fatality, recurrence, and severity of pediatric AP in different regions (North America, Asia, South America, Europe, and Oceania). Pooled data from 47 papers (48 studies) found that main causes of pediatric AP were gallstones in Asia; trauma in Oceania; and idiopathic in Europe, North America, and South America. The case-fatality rate (CFR) of pediatric AP is 4.7% (North America), 6.2% (Europe), 2.4% (Asia), 3.1% (South America), and 7.4% (Oceania). The incidence rates of recurrent acute pancreatitis (RAP) in children who have had an episode of acute pancreatitis in North American, Asia, and Europe were 15.3, 13.1, and 13.8%, respectively. The incidence of severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) in different regions was 30.3% (Oceania), 29.2% (South America), 20.8% (Europe), 15.8% (Asia), and 13.7% (North America). It suggests that physicians should notice the etiology of pediatric AP for the initial assessment, diagnosis, prediction of relapse, and appropriate treatment at a later stage.
Impact
-
It indicates the etiology of pediatric acute pancreatitis for the initial assessment, diagnosis, and prediction of relapse.
-
Main causes of pediatric AP were gallstones in Asia; trauma in Oceania; and idiopathic in Europe, North America, and South America. The case-fatality rate of pediatric AP is diverse worldwide.
-
It suggests that physicians noticed the etiology of pediatric AP for the initial assessment, diagnosis, prediction of relapse, and appropriate treatment at a later stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Yadav, D. & Lowenfels, A. B. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 144, 1252–1261 (2013).
Bai, H. X., Lowe, M. E. & Husain, S. Z. What have we learned about acute pancreatitis in children? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 52, 262–270 (2011).
Morinville, V. D., Barmada, M. M. & Lowe, M. E. Increasing incidence of acute pancreatitis at an American pediatric tertiary care center: is greater awareness among physicians responsible? Pancreas 39, 5–8 (2010).
Marta, K. et al. Aging and comorbidities in acute pancreatitis I: a meta-analysis and systematic review based on 194,702 patients. Front. Physiol. 10, 328 (2019).
Knobloch, K., Yoon, U. & Vogt, P. M. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement and publication bias. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 39, 91–92 (2011).
Balthazar, E. J., Robinson, D. L., Megibow, A. J. & Ranson, J. H. Acute pancreatitis: value of CT in establishing prognosis. Radiology 174, 331–336 (1990).
Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 25, 603–605 (2010).
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J. & Altman, D. G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327, 557–560 (2003).
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315, 629–634 (1997).
Balshem, H. et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64, 401–406 (2011).
Vitale, D. S. et al. Blood urea nitrogen elevation is a marker for pediatric severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 48, 363–366 (2019).
Vidal, E., Alberici, I. & Verrina, E. Acute pancreatitis in children on chronic maintenance dialysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 34, 1501–1512 (2019).
Nauka, P. C. et al. Validation of lipase and systemic inflammatory response syndrome as prognostic indicators in pediatric acute pancreatitis: a retrospective analysis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 68, 389–393 (2019).
Galai, T. et al. Young age predicts acute pancreatitis severity in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 68, 720–726 (2019).
Cheng, Y. J. et al. Epidemiology of pediatric acute pancreatitis in taiwan: a nationwide population-based study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 68, e7–e12 (2019).
Sweeny, K. F. et al. Rapid progression of acute pancreatitis to acute recurrent pancreatitis in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 68, 104–109 (2019).
Zheng, W. et al. Amalgamation of systemic inflammatory response syndrome score with C-reactive protein level in evaluating acute pancreatitis severity in children. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 53, 755–759 (2018).
Sag, E. et al. Acute pancreatitis in children: a single center experience over ten years. Turk. J. Pediatr. 60, 153–158 (2018).
Izquierdo, Y. E. et al. Multivariate model for the prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 66, 949–952 (2018).
Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk, U. et al. Acute pancreatitis in children. Prz. Gastroenterol. 13, 69–75 (2018).
Alabdulkareem, A. et al. Etiology and clinical characteristics of pediatric acute pancreatitis in Saudi Arabia: a 20-year experience from a single tertiary center. Int. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 5, 13–17 (2018).
Suzuki, M. et al. Validation of severity assessment for acute pancreatitis in children. Pediatr. Int. 59, 1127–1128 (2017).
Grover, A. S. et al. The utility of the systemic inflammatory respsonse syndrome score on admission in children with acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 46, 106–109 (2017).
Majbar, A. A. et al. Incidence and clinical associations of childhood acute pancreatitis. Pediatrics. 138, e20161198 (2016).
Hashimoto, N. et al. Efficacy of pediatric acute pancreatitis scores at a Japanese tertiary center. Pediatr. Int. 58, 224–228 (2016).
Hao, F., Guo, H., Luo, Q. & Guo, C. Disease progression of acute pancreatitis in pediatric patients. J. Surg. Res. 202, 422–427 (2016).
Bierma, M. J. et al. Predicting severe acute pancreatitis in children based on serum lipase and calcium: a multicentre retrospective cohort study. Pancreatology 16, 529–534 (2016).
Abu-El-Haija, M. et al. Early enteral nutrition in children with acute pancreatitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 62, 453–456 (2016).
Suzuki, M. et al. Scoring system for the prediction of severe acute pancreatitis in children. Pediatr. Int. 57, 113–118 (2015).
Goday, P. S. et al. Acute pancreatitis in the pediatric intensive care unit. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 61, 108–112 (2015).
Bolia, R. et al. Prevalence, natural history, and outcome of acute fluid collection and pseudocyst in children with acute pancreatitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 61, 451–455 (2015).
Terlizzi, V. et al. Prediction of acute pancreatitis risk based on PIP score in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 13, 579–584 (2014).
Guo, Q. et al. Predictors for mortality following acute pancreatitis in children. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 30, 1111–1115 (2014).
Boskovic, A. et al. The role of D-dimer in prediction of the course and outcome in pediatric acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 14, 330–334 (2014).
Antunes, H., Nascimento, J., Mesquita, A. & Correia-Pinto, J. Acute pancreatitis in children: a tertiary hospital report. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 49, 642–647 (2014).
Kim, S. C. & Yang, H. R. Clinical efficacy of gabexate mesilate for acute pancreatitis in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 172, 1483–1490 (2013).
Lautz, T. B. et al. Utility of the computed tomography severity index (Balthazar score) in children with acute pancreatitis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 47, 1185–1191 (2012).
Fabre, A. et al. Severity scores in children with acute pancreatitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 55, 266–267 (2012).
Zhu, Y. M. et al. [Clinical characteristics of children with acute pancreatitis]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 49, 10–16 (2011).
Chang, Y. J. et al. Acute pancreatitis in children. Acta Paediatr. 100, 740–744 (2011).
Park, A. et al. Changing referral trends of acute pancreatitis in children: a 12-year single-center analysis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 49, 316–322 (2009).
Li, N. & Wang, X. Y. [Relationship between acute pancreatitis and systemic inflammation response syndrome in children]. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 10, 715–718 (2008).
Kandula, L. & Lowe, M. E. Etiology and outcome of acute pancreatitis in infants and toddlers. J. Pediatr. 152, 106.e1–110.e1 (2008).
Nydegger, A. et al. Changing incidence of acute pancreatitis: 10-year experience at the Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22, 1313–1316 (2007).
Chen, C. F., Kong, M. S., Lai, M. W. & Wang, C. J. Acute pancreatitis in children: 10-year experience in a medical center. Acta Paediatr. Taiwan 47, 192–196 (2006).
Stringer, M. D. et al. Multidisciplinary management of surgical disorders of the pancreas in childhood. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 40, 363–367 (2005).
Laugel, V. et al. [Severe acute pancreatitis in children receiving asparaginase: multicenter retrospective study]. Arch. Pediatr. 12, 34–41 (2005).
Werlin, S. L., Kugathasan, S. & Frautschy, B. C. Pancreatitis in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 37, 591–595 (2003).
Choi, B. H. et al. Acute pancreatitis associated with biliary disease in children. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 915–921 (2003).
Alvarez Calatayud, G. et al. Acute pancreatitis in childhood. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 95, 40–44, 45-48 (2003).
Tiao, M. M. et al. Pancreatitis in children: clinical analysis of 61 cases in southern Taiwan. Chang Gung Med. J. 25, 162–168 (2002).
Pezzilli, R. et al. Acute pancreatitis in children. An Italian multicentre study. Dig. Liver Dis. 34, 343–348 (2002).
DeBanto, J. R. et al. Acute pancreatitis in children. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 97, 1726–1731 (2002).
Javid, G. et al. Etiology and outcome of acute pancreatitis in children in Kashmir (India). An endemic area of hepatobiliary ascariasis. World J. Surg. 37, 1133–1140 (2013).
Yeung, C. Y. et al. Pancreatitis in children–experience with 43 cases. Eur. J. Pediatr. 155, 458–463 (1996).
Berney, T. et al. Influence of severe underlying pathology and hypovolemic shock on the development of acute pancreatitis in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 31, 1256–1261 (1996).
Weizman, Z. & Durie, P. R. Acute pancreatitis in childhood. J. Pediatr. 113, 24–29 (1988).
Uc, A. & Husain, S. Z. Pancreatitis in children. Gastroenterology 156, 1969–1978 (2019).
Husain, S. Z. & Srinath, A. I. What’s unique about acute pancreatitis in children: risk factors, diagnosis and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14, 366–372 (2017).
Steer, M. L., Waxman, I. & Freedman, S. Chronic pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1482–1490 (1995).
Zhu, Y. et al. A study on the etiology, severity, and mortality of 3260 patients with acute pancreatitis according to the Revised Atlanta Classification in Jiangxi, China over an 8-year period. Pancreas 46, 504–509 (2017).
Shukla-Udawatta, M., Madani, S. & Kamat, D. An update on pediatric pancreatitis. Pediatr. Ann. 46, e207–e211 (2017).
Restrepo, R. et al. Acute pancreatitis in pediatric patients: demographics, etiology, and diagnostic imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 206, 632–644 (2016).
Zheng, J., Yang, Q. J., Dang, F. T. & Yang, J. Drug-induced pancreatitis: an update. Arab J. Gastroenterol. 20, 183–188 (2019).
Pant, C. et al. Acute recurrent pancreatitis in children: a study from the pediatric health information system. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 62, 450–452 (2016).
Abu-El-Haija, M. et al. Genetic variants in acute, acute recurrent and chronic pancreatitis affect the progression of disease in children. Pancreatology 19, 535–540 (2019).
Heidari, S. et al. Sex and Gender Equity in Research: rationale for the SAGER guidelines and recommended use. Res Integr. Peer Rev. 1, 2 (2016).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0114900), the Development Project of National Major Scientific Research Instrument (82027803), the Development Project of National Major Scientific Research Instrument of China (8202780008), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81971623), the Major Research plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91630311), the National S&T Major Project of China (2018ZX10301201), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LZ20H180001), and Zhejiang Provincial Association Project for Mathematical Medicine (LSY19H180015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: T.J. Acquisition of data: all authors. Analysis and interpretation of data: G.T., L.Z. Writing—original draft: G.T. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: T.J. Formal analysis: G.T., Q.Z. Funding acquisition: Q.Z., T.J. Methodology: Q.Z. Supervision: T.J.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Patient consent
Because this is a meta-analysis, patient consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, G., Zhu, L., Chen, S. et al. Etiology, case fatality, recurrence, and severity in pediatric acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis of 48 studies. Pediatr Res 91, 56–63 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01454-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01454-1
This article is cited by
-
Acute pancreatitis adversely impacts the outcome in hospitalized pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients
Pediatric Research (2026)
-
Utility of the modified computed tomography severity index in prognostication of acute pancreatitis in children
Pediatric Radiology (2025)
-
Clinical Epidemiology and Burden of Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis in Chinese Children: A Nationwide Study
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2025)