Abstract
Background
This systematic review was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) combined with volume guarantee (VG) in infants compared with HFOV alone.
Methods
We searched for electronic databases to find studies using HFOV-VG or HFOV for respiratory support in infants from the database creation to October 20, 2024. Two evaluators independently screened the literature, extracted data, and evaluated quality. Meta-analysis was performed using Rev man 5.3 software on survival-free BPD at grades 2 and 3 (SF-BPD), the incidence of BPD, mortality, duration of invasive ventilation, length of hospital stays, and complications in both groups.
Results
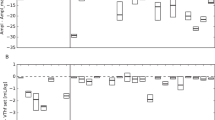
The review included 11 studies (three randomized controlled trials, one non-randomized controlled trial, and seven observational studies) with 785 participants. Data analysis showed that HFOV-VG could increase SF-BPD in preterm infants (OR 3.15, 95%CI 1.66–5.98) without reducing the overall incidence of BPD compared with HFOV alone. HFOV-VG may offer advantages in shortening the duration of MV and total hospital stay, potentially reducing mortality and the incidence of air leak syndrome.
Conclusions existing
Studies showed that HFOV-VG had certain advantages in improving oxygenation and stable ventilation to protect neonatal lungs. HFOV-VG could increase SF-BPD in preterm infants with GA < 32 weeks without reducing the overall incidence of BPD compared with HFOV alone.
Impact
-
Existing evidence suggested that HFOV-VG ventilation strategies could increase SF-BPD in preterm infants with GA < 32 weeks without reducing the overall incidence of BPD compared with HFOV alone.
-
HFOV-VG ventilation strategy has certain advantages in improving oxygenation and stable ventilation to protect neonatal lungs.
-
The effects of HFOV-VG vs. HFOV in neonates remain to be further validated by additional large sample, multicenter RCTs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data for all figure(s) and number(s) are provided with the paper and supplementary files. Aggregate data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sánchez-Luna, M., González-Pacheco, N., Belik, J., Santos, M. & Tendillo, F. New ventilator strategies: high-frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with volume guarantee. Am. J. Perinatol. 35, 545–548 (2018).
González-Pacheco, N. et al. Use of very low tidal volumes during high-frequency ventilation reduces ventilator lung injury. J. Perinatol. 39, 730–736 (2019).
Sweet, D. G. et al. European Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Respiratory Distress Syndrome: 2022 Update. Neonatology 120, 3–23 (2023).
Sánchez Luna, M., Santos González, M. & Tendillo Cortijo, F. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with volume guarantee in a neonatal animal model of respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Res. Pr. 2013, 593915 (2013).
González-Pacheco, N. et al. Dco(2)/Paco(2) correlation on high-frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with volume guarantee using increasing frequencies in an animal model. Eur. J. Pediatr. 179, 499–506 (2020).
Meyers, M., Rodrigues, N. & Ari, A. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation: a narrative review. Can. J. Respir. Ther. 55, 40–46 (2019).
Cools, F., Offringa, M. & Askie, L. M. Elective high frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for acute pulmonary dysfunction in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 3, Cd000104 (2015).
Junqueira, F. M. D., Nadal, J. A. H., Brandão, M. B., Nogueira, R. J. N. & de Souza, T. H. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 56, 1872–1888 (2021).
Moher, D. et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (Prisma-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 4, 1 (2015).
Belteki, G. & Morley, C. J. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation with volume guarantee: a single-centre experience. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 104, F384–f389 (2019).
Solís-García, G., González-Pacheco, N., Ramos-Navarro, C., Rodríguez Sánchez de la Blanca, A. & Sánchez-Luna, M. Target volume-guarantee in high-frequency oscillatory ventilation for preterm respiratory distress syndrome: low volumes and high frequencies lead to adequate ventilation. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 56, 2597–2603 (2021).
Tuzun, F. et al. Volume guarantee high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in preterm infants with RDS: Tidal Volume and Dco(2) levels for optimal ventilation using open-lung strategies. Front Pediatr. 8, 105 (2020).
Solis-Garcia, G. et al. Lung recruitment in neonatal high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with volume-guarantee. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 57, 3000–3008 (2022).
González-Pacheco, N., Sánchez-Luna, M., Ramos-Navarro, C., Navarro-Patiño, N. & de la Blanca, A. R. Using very high frequencies with very low lung volumes during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation to protect the immature lung. A pilot study. J. Perinatol. 36, 306–310 (2016).
Chen, L. G. R., Cheung, P. Y. & Law, B. H. Y. Lung recruitment using high-frequency oscillation volume guarantee in preterm infants with evolving bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Neonatology, 119, 119–123 (2021).
Iscan, B., Duman, N., Tuzun, F., Kumral, A. & Ozkan, H. Impact of volume guarantee on high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in preterm infants: a randomized crossover clinical trial. Neonatology 108, 277–282 (2015).
Yuan W. H. et al. Clinical efficacy of high frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with volume guarantee ventilation in the treatment of neonates with persistent pulmonary hypertension. Chin. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Pediatr. (Electron Ed) 16, 6 (December 2020).
Ramos-Navarro, C., González-Pacheco, N., Rodríguez-Sánchez de la Blanca, A. & Sánchez-Luna, M. Effect of a new respiratory care bundle on bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm neonates. Eur. J. Pediatr. 179, 1833–1842 (2020).
Tana, M. et al. Effects of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with volume guarantee during surfactant treatment in extremely low gestational age newborns with respiratory distress syndrome: an observational study. Front. Pediatr. 9, 804807 (2021).
Zheng, Y. R. et al. Impact of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with volume guarantee on lung inflammatory response in infants with acute respiratory distress syndrome after congenital heart surgery: a randomized controlled trial. J Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 36, 2368–2375 (2021).
Enomoto, M. et al. Effect of volume guarantee in preterm infants on high-frequency oscillatory ventilation: a pilot study. Am. J. Perinatol. 34, 26–30 (2017).
Zheng, Y. R. et al. Application of high-frequency oscillation ventilation combined with volume guarantee in infants with acute hypoxic respiratory failure after congenital heart surgery. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 56, 2621–2626 (2021).
Chen, L. J. & Chen, J. Y. Effect of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with volume guarantee on preterm infants with hypoxic respiratory failure. J. Chin. Med Assoc. 82, 861–864 (2019).
Lin, H. Z., Lin, W. H., Lin, S. H., Xiu, W. L. & Zheng, Y. R. Application of high-frequency oscillation ventilation combined with volume guarantee in preterm infants with acute hypoxic respiratory failure after patent ductus arteriosus ligation. Heart Surg. Forum 25, E676–E679 (2022).
Balog, V., Liszkay, G., Lantos, L., Jermendy, A. & Belteki, G. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation with or without volume guarantee during neonatal transport. J. Perinatol. 45, 43–49 (2024).
Solís-García, G., Ramos-Navarro, C., González-Pacheco, N. & Sánchez-Luna, M. Lung protection strategy with high-frequency oscillatory ventilation improves respiratory outcomes at two years in preterm respiratory distress syndrome: a before and after, quality improvement study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 35, 10698–10705 (2022).
Morley, C. J. et al. Nasal CPAP or intubation at birth for very preterm infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 700–708 (2008).
Dunn, M. S. et al. Randomized trial comparing 3 approaches to the initial respiratory management of preterm neonates. Pediatrics 128, e1069–e1076 (2011).
Norman, M., Jonsson, B., Wallstrom, L. & Sindelar, R. Respiratory support of infants born at 22–24 weeks of gestational age. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 27, 101328 (2022).
Beitler, J. R., Malhotra, A. & Thompson, B. T. Ventilator-induced lung injury. Clin. Chest Med. 37, 633–646 (2016).
Chang, H. K. Mechanisms of gas transport during ventilation by high-frequency oscillation. J. Appl. Physiol. 56, 553–563 (1984).
Slutsky, A. S. et al. Effective pulmonary ventilation with small-volume oscillations at high frequency. Science 209, 609–611 (1980).
Wheeler, H. J., Nokes, L. D. & Powell, T. A review of high frequency oscillation ventilation in the neonate. J. Med Eng. Technol. 31, 367–374 (2007).
Hurley, E. H. & Keszler, M. Effect of inspiratory flow rate on the efficiency of carbon dioxide removal at tidal volumes below instrumental dead space. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 102, F126–F130 (2017).
Ackermann, B. W., Klotz, D., Hentschel, R., Thome, U. H. & van Kaam, A. H. High-Frequency Ventilation in Preterm Infants and Neonates. Pediatr. Res. 93, 1810–1818 (2022).
Batey, N. & Bustani, P. Neonatal high-frequency oscillatory ventilation. Paediatr. Child Health 30, 149–153 (2020).
Hibberd, J. et al. Neonatal high-frequency oscillatory ventilation: where are we now? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed (2023).
Wang, R. L., Xu, K., Yu, K. L., Tang, X. & Xie, H. Effects of dynamic ventilatory factors on ventilator-induced lung injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome dogs. World J. Emerg. Med. 3, 287–293 (2012).
Herrmann, J., Lilitwat, W., Tawhai, M. H. & Kaczka, D. W. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation and ventilator-induced lung injury: size does matter. Crit. Care Med. 48, e66–e73 (2020).
Wang, C. et al. Mechanical ventilation modes for respiratory distress syndrome in infants: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Crit. Care 19, 108 (2015).
Cools, F. et al. Elective high-frequency oscillatory versus conventional ventilation in preterm infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patients’ data. Lancet 375, 2082–2091 (2010).
Farrell, O. et al. Volume guaranteed? Accuracy of a volume-targeted ventilation mode in infants. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 103, F120–f125 (2018).
Ganguly, A., Makkar, A. & Sekar, K. Volume targeted ventilation and high frequency ventilation as the primary modes of respiratory support for elbw babies: what does the evidence say? Front Pediatr. 8, 27 (2020).
Chen, L. J. & Chen, J. Y. Volume-targeted versus pressure-limited ventilation for preterm infants. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 82, 791–794 (2019).
Shukla, V. V. & Ambalavanan, N. Recent advances in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Indian J. Pediatr. 88, 690–695 (2021).
Keszler, M. Novel ventilation strategies to reduce adverse pulmonary outcomes. Clin. Perinatol. 49, 219–242 (2022).
Hsu, J. F. et al. Therapeutic effects and outcomes of rescue high-frequency oscillatory ventilation for premature infants with severe refractory respiratory failure. Sci. Rep. 11, 8471 (2021).
Sud, S. et al. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 4, CD004085 (2016).
Cools, F., Henderson-Smart, D. J., Offringa, M. & Askie, L. M. Elective high frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for acute pulmonary dysfunction in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 3, Cd000104 (2009). Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (3) CD000104 (2015).
Sánchez-Luna, M. et al. Effect of the I/E Ratio on Co2 removal during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with volume guarantee in a neonatal animal model of RDS. Eur. J. Pediatr. 175, 1343–1351 (2016).
Pillow, J. High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation: Theory and Practical Applications. Drägerwerk AG & Co KGaA, Germany (2016).
Bhuta, T. & Henderson-Smart, D. J. Rescue high frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for pulmonary dysfunction in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 1998, Cd000438 (2000).
Henderson-Smart, D. J., Bhuta, T., Cools, F. & Offringa, M. Elective high frequency oscillatory ventilation versus conventional ventilation for acute pulmonary dysfunction in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2, Cd000104 (2000). Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (3) CD000104 (2001).
Ayoub, D., Elmashad, A., Rowisha, M., Eltomey, M. & El Amrousy, D. Hemodynamic effects of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 56, 424–432 (2021).
Bhogal, J. et al. Hemodynamic effects of high frequency oscillatory ventilation with volume guarantee in a piglet model of respiratory distress syndrome. PLoS One 16, e0246996 (2021).
Pérez-Pérez, A. et al. Impact on cerebral hemodynamics of the use of volume guarantee combined with high frequency oscillatory ventilation in a neonatal animal respiratory distress model. Eur. J. Pediatr. 183, 157–167 (2024).
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr Li for helpful comments on a draft version of this manuscript. The author(s) disclosed that no financial support was provided for the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Funding
This study is supported by Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (SZSM202211001), and Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Maternal and Child Health and Diseases (ZDSYS20230626091559006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wanjiao Liu conceptualized and designed the study, accomplished the article-extracting and data analysis, and drafted the initial manuscript. Jin Jiang accomplished the article-extracting and risk assessment work. Hai Feng Zong completed the data extraction and designed the study. Fang Li and Chuanzong Yang revised the initial manuscript, and critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Zong, H., Jiang, J. et al. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation with volume guarantee in infants: a systematic review. Pediatr Res 98, 470–478 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-03934-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-03934-0
This article is cited by
-
Are we ready for volume targeting during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in neonates?
Pediatric Research (2025)