Abstract
Background
Point of care functional echocardiography is an emerging tool in neonatology to assess hemodynamic dysfunction and its timely management.
Methods
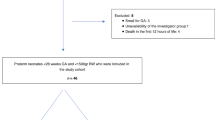
Following PRISMA guidelines, we searched PubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL, Medline, and Web of Sciences databases till December 2024. We selected 2680 text articles of which 21 studies qualified for full-text review and finally, eight studies were included in the systematic review.
Results
Meta-analysis using REM (Random effects model) showed no significant difference in the primary outcome of Inferior Vena Cava Collapsibility Index (IVC-CI) between shock versus controls [SMD = −0.99 (95% CI: −2.89, 0.91), P = 0.31, I2 = 96%. Meta-analysis showed significantly lower values of Shortening Fraction(SF) [SMD = −0.84 (95% CI: −1.61, −0.07), P = 0.031, I2 = 92%, REM], Left Ventricle Velocity Time Integral(LVVTI) [SMD = 0.22 (95% CI: 0.01, 0.42), P = 0.04, I2 = 27%, FEM], Right Ventricle Velocity Time Integral(RVVTI) [SMD = −0.55 (95% CI: −0.77, −0.33), P < 0.00001, I2 = 0%, FEM], and Ejection fraction(EF) [SMD = −1.82 (95% CI: −3.09, –0.55), P = 0.005, I2 = 89%]. The difference between the remaining outcomes was not statistically significant between the two groups.
Conclusions
This review reinforces the clinical utility of echocardiographic parameters in diagnosing and monitoring neonatal shock and underscores the need for conducting multicentre, prospective studies to validate dynamic changes in echocardiographic parameters before and after treatment of shock.
Impact
-
Our study highlights role of functional echocardiography as an adjunct to clinical and biochemical markers of shock in neonates providing more comprehensive understanding of cardiac function.
-
No significant difference in the Inferior Vena Cava Collapsibility Index values was seen in neonates with shock. However, Shortening Fraction, Left Ventricle Velocity Time Integral, Right Ventricle Velocity Time Integral, and Ejection Fraction were significantly decreased in this group.
-
Impact of this study lies in its potential to increase researchers’ awareness of need to conduct multicentre, prospective studies to validate dynamic changes in echocardiographic parameters before and after treatment of shock.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kleinman, C. S. & Seri, I. Hemodynamics and cardiology: neonatology questions and controversies E-book (Elsevier Health Sciences, 2012).
Gupta, S. & Donn, S. M. Assessment of neonatal perfusion. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 25, 101144 (2020).
Osborn, D., Evans, N. & Kluckow, M. Clinical detection of low upper body blood flow in very premature infants using blood pressure, capillary refill time, and central-peripheral temperature difference. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 89, F168–F173 (2004).
de Boode, W. P. Individualized hemodynamic management in newborns. Front. Pediatr. 8, 580470 (2020).
Gupta, S. & Donn, S. M. In Seminars in fetal and neonatal medicine, 101144 (Elsevier, 2020).
de Boode, W. P. et al. The role of neonatologist performed echocardiography in the assessment and management of neonatal shock. Pediatr. Res 84, 57–67 (2018).
Singh, Y. et al. Expert consensus statement ‘Neonatologist-Performed Echocardiography (Nope)’-training and accreditation in Uk. Eur. J. Pediatr. 175, 281–287 (2016).
McNamara, P. J. & Sehgal, A. Towards rational management of the patent ductus arteriosus: the need for disease staging. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 92, F424–F427 (2007).
Sehgal, A. & McNamara, P. J. In Seminars in fetal and neonatal medicine, 278–284 (Elsevier, 2018).
Vrancken, S. L., Van Heijst, A. F. & De Boode, W. P. Neonatal hemodynamics: from developmental physiology to comprehensive monitoring. Front. Pediatr. 6, 87 (2018).
de Boode, W. P. Advanced hemodynamic monitoring in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clin. Perinatol. 47, 423–434 (2020).
McNamara, P. J. et al. Guidelines and recommendations for targeted neonatal echocardiography and cardiac point-of-care ultrasound in the neonatal intensive care unit: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 37, 171–215 (2024).
de Boode, W. P. et al. Recommendations for neonatologist performed echocardiography in Europe: consensus statement endorsed by European Society for Paediatric Research (Espr) and European Society for Neonatology (Esn). Pediatr. Res 80, 465–471 (2016).
Mertens, L. et al. Targeted neonatal echocardiography in the neonatal intensive care unit: practice guidelines and recommendations for training: writing group of the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) in collaboration with the European Association of Echocardiography (EAE) and the Association for European Pediatric Cardiologists (AEPC). Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 12, 715–736 (2011).
Tissot, C. & Singh, Y. Neonatal functional echocardiography. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 32, 235–244 (2020).
Page, M. J. et al. The Prisma 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n71 (2021).
Brooke, B., Schwartz, T. & Pawlik, T. Moose reporting guidelines for meta-analyses of observational studies. JAMA Surg. 156, 787–788 (2021).
Singh, Y. Echocardiographic evaluation of hemodynamics in neonates and children. Front. Pediatr. 5, 201 (2017).
Nagueh, S. F. et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 29, 277–314 (2016).
Lester, S. J. et al. Unlocking the mysteries of diastolic function: deciphering the Rosetta stone 10 years later. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 51, 679–689 (2008).
Tibby, S. M., Hatherill, M., Marsh, M. J. & Murdoch, I. A. Clinicians’ abilities to estimate cardiac index in ventilated children and infants. Arch. Dis. Child 77, 516–518 (1997).
Egan, J. R. et al. Clinical assessment of cardiac performance in infants and children following cardiac surgery. Intensive Care Med. 31, 568–573 (2005).
Mertens, L. et al. Targeted neonatal echocardiography in the neonatal intensive care unit: practice guidelines and recommendations for training. Writing Group of the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) in Collaboration with the European Association of Echocardiography (EAE) and the Association for European Pediatric Cardiologists (AEPC). J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 24, 1057–1078 (2011).
Lopez, L. et al. Recommendations for quantification methods during the performance of a pediatric echocardiogram: a report from the pediatric measurements writing group of the American Society of Echocardiography Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease Council. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 23, 465–495 (2010). quiz 576-467.
Klugman, D. & Berger, J. T. Echocardiography as a hemodynamic monitor in critically Ill children. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 12, S50–S54 (2011).
Tsai-Goodman, B., Martin, R. P., Marlow, N. & Skinner, J. R. The repeatability of echocardiographic determination of right ventricular output in the newborn. Cardiol. Young. 11, 188–194 (2001).
Evans, N. & Kluckow, M. Early determinants of right and left ventricular output in ventilated preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 74, F88–F94 (1996).
Tei, C. et al. New index of combined systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: a simple and reproducible measure of cardiac function–a study in normals and dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Cardiol. 26, 357–366 (1995).
Ficial, B. et al. Echocardiographic quantification of Superior Vena Cava (SVC) flow in neonates: pilot study of modified technique. Diagnostics 12, 2083 (2022).
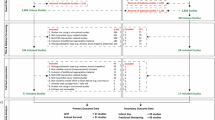
Higgins, J. P. et al. The cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343, d5928 (2011).
Gunjan, K., Modi, M., Thakur, A., Soni, A. & Saluja, S. Echocardiographic characteristics in neonates with septic shock. Eur. J. Pediatr. 183, 1849–1855 (2024).
Saini, S. S., Sundaram, V., Kumar, P. & Rohit, M. K. Functional echocardiographic preload markers in neonatal septic shock. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 35, 6815–6822 (2022).
Pawale, D. et al. Echocardiographic assessment of hemodynamic changes in preterm neonates with shock: a prospective pragmatic cohort study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 179, 1893–1899 (2020).
Saini, S. S., Kumar, P. & Kumar, R. M. Hemodynamic changes in preterm neonates with septic shock: a prospective observational study*. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 15, 443–450 (2014).
Gill, A. B. & Weindling, A. M. Echocardiographic assessment of cardiac function in shocked very low birthweight infants. Arch. Dis. Child 68, 17–21 (1993).
Shokr, A. A.-E. S., Tomerak, R. H., Agha, H. M., ElKaffas, R. M. H. & Ali, S. B. I. Echocardiography-directed management of hemodynamically unstable neonates in tertiary care hospitals. Egypt. Pediatr. Assoc. Gaz. 71, 10 (2023).
Simma, B. et al. Changes in left ventricular function in shocked newborns. Intensive Care Med. 23, 982–986 (1997).
Bandyopadhyay, T., Saili, A., Yadav, D. K. & Kumar, A. Correlation of functional echocardiography and clinical parameters in term neonates with shock. J. Neonatal. Perinat. Med. 13, 167–173 (2020).
Pugnaloni, F. et al. Assessment of hemodynamic dysfunction in septic newborns by functional echocardiography: a systematic review. Pediatr. Res. 95, 1422–1431 (2024).
Mahmoud, R. O., Moawad, K. M. H. E., Mansi, Y. A. & Hashem, R. H. IVC collapsibility indices in assessment of volume overload in neonatal cardiac patients. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 55, 142 (2024).
Osborn, D. A. Role of echocardiography in management of shock. J. Neonatol. 22, 212–222 (2008).
El-Khuffash, A., Herbozo, C., Jain, A., Lapointe, A. & McNamara, P. J. Targeted neonatal echocardiography (Tnecho) service in a Canadian neonatal intensive care unit: a 4-year experience. J. Perinatol. 33, 687–690 (2013).
Sehgal, A. & McNamara, P. J. The ductus arteriosus: a refined approach! Semin. Perinatol. 36, 105–113 (2012).
Kluckow, M., Jeffery, M., Gill, A. & Evans, N. A randomised placebo-controlled trial of early treatment of the patent ductus arteriosus. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 99, F99–f104 (2014).
Azhibekov, T., Noori, S., Soleymani, S. & Seri, I. Transitional cardiovascular physiology and comprehensive hemodynamic monitoring in the neonate: relevance to research and clinical care. Semin. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 19, 45–53 (2014).
El-Khuffash, A. & McNamara, P. J. Hemodynamic assessment and monitoring of premature infants. Clin. Perinatol. 44, 377–393 (2017).
Acknowledgements
None No financial assistance was taken for supporting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.G and A.H contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by N.G, A.H., S.M. and S.S. The first draft of the manuscript was written by N.G. and revised by A.H., S.M. and S.S. A.H. critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent statement
Patient consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, N., Ananthan, A., Subhadarsini, S. et al. Role of functional echocardiography in neonatal shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Res (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-04298-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-025-04298-1