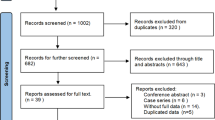
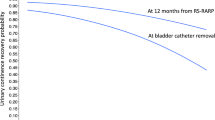
Abstract
Background
Urinary incontinence significantly impacts on health-related quality of life of patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. In the last decades, several approaches (extraperitoneal, Retzius-sparing (RS), perineal and, transvesical) for robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) have proposed with the aim to improve functional outcomes in comparison with transperitoneal, anterior ones.
Methods
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies published in English language, in the last ten years, comparing the different approaches used to perform RARP. We included only studies reporting urinary continence rates at different follow-up time points. From each eligible study, we extracted the number of analyzed patients; the study design; the continence definition; and, when available, immediate, 1-, 3-, 6-, and 12-mo urinary continence rates. Statistical analyses were performed using RevMan version 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom, UK). The Odds Ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) was calculated using the generic inverse variance. A p value of <0.05 was set as significance level when comparing studies.
Results
The meta-analyses of studies comparing anterior, transperitoneal RARP and RS-RARP in terms of immediate (OR = 3.73; 95% CI: 2.17–6.43; p < 0.0001), 1-mo (OR = 4.16; 95% CI: 2.68–6.48; p < 0.00001), 3-mo (OR 4.71; 95% CI: 3.70–6.00; p < 0.0001), 6-mo (OR 4.12; 95% CI: 2.95–5.75; p < 0.00001) and 12-mo (OR = 3.25; 95% CI: 1.76–5.99; p < 0.00001) urinary continence rates showed a statistically significant advantage in favor of RS approach. However, a sub-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials showed overlapping urinary continence rates between the two approaches at 6-mo (OR = 1.99; 95% CI: 0.90–4.42; p = 0.09) and 12-mo (OR = 1.36; 95% CI: 0.43–4.31; p = 0.60) after surgery. The meta-analysis of studies comparing extraperitoneal and transperitoneal approaches showed that 6-mo urinary continence rates were overlapping between the two approaches (OR = 1.18; 95% CI: 0.85–1.65; p = 0.32). The meta-analysis of studies comparing single-port (SP) and multi-port (MP) RARP showed comparable 6-mo urinary continence rates (OR = 0.93; 95% CI 0.65–1.33; p = 0.69).
Conclusions
Within the limitations of mainly low to moderate quality of evidence, the RS approach offers significant advantages compared to an anterior, transperitoneal, approach in terms of urinary continence recovery at different follow-up time points in patients who underwent MP-RARP. MP perineal and transvesical approaches need to be further tested and might be of interest in the setting of SP-RARP. Our meta-analysis showed comparable results between SP- and MP-RARP in terms of urinary continence rates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moretti TBC, Magna LA, Reis LO. Continence criteria of 193 618 patients after open, laparoscopic, and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.16180.
Joseph JV, Rosenbaum R, Madeb RerturkE, Patel H. Robotic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy: an alternative approach. J Urol. 2006;175:945–50.
Galfano A, Ascione A, Grimaldi S, Petralia G, Strada E, Bocciardi AM. A new anatomic approach for robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: a feasibility study for completely intrafascial surgery. Eur Urol. 2010;58:457–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.06.008.
Kaouk JH, Akca O, Zargar H, Caputo P, Ramirez D, Andrade H, et al. Descriptive technique and initial results for robotic radical perineal prostatectomy. Urology. 2016;94:129–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2016.02.063.
Desai MM, Aron M, Berger A, Canes D, Stein R, Haber GP, et al. Transvesical robotic radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2008;102:1666–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08004.x.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71.
Jeremy Howick, Iain Chalmers, Paul Glasziou, Trish Greenhalgh, Carl Heneghan, Alessandro Liberati et al. “Explanation of the 2011 Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (OCEBM) Levels of Evidence (Background Document)”. Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/explanation-of-the-2011-ocebm-levels-of-evidence/
Clark HD, Wells GA, Huët C, McAlister FA, Salmi LR, Fergusson D, et al. Assessing the quality of randomized trials: reliability of the Jadad scale. Control Clin Trials. 1999;20:448–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-2456(99)00026-4. PMID: 10503804.
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J., Welch V, Losos M et al. The Newcastle Ottawa 1 Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta- Analyses. Available at: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
Dalela D, Jeong W, Prasad MA, Sood A, Abdollah F, Diaz M, et al. A pragmatic randomized controlled trial examining the impact of the retzius-sparing approach on early urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2017;72:677–85.
Menon M, Dalela D, Jamil M, Diaz M, Tallman C, Abdollah F, et al. Functional recovery, oncologic outcomes and postoperative complications after robot- assisted radical prostatectomy: an evidence-based analysis comparing the Retzius sparing and standard approaches. J Urol. 2018;199:1210–7.
Asimakopoulos AD, Topazio L, De Angelis M, Agrò EF, Pastore AL, Fuschi A, et al. Retzius-sparing versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a prospective randomized comparison on immediate continence rates. Surg Endosc. 2019;33:2187–96.
Qiu X, Li Y, Chen M, Xu L, Guo S, Marra G, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy improves early recovery of urinary continence: a randomized, controlled, single-blind trial with a 1-year follow-up. BJU Int. 2020;126:633–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15195.
Turkolmez K, Akpinar C, Kubilay E, Suer E. Retzius-Sparing vs Modified Anatomical Structure Preserving and Retzius-Repairing Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Prospective Randomized Comparison on Functional Outcomes with a 1-Year Follow-Up. J Endourol 2022 https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2022.0073.
Lim SK, Kim KH, Shin TY, Han WK, Chung BH, Hong SJ, et al. Retzius-sparing robot- assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches. BJU Int. 2014;114:236–44.
Sayyid R, Simpson WG, Lu C, Terris MK, Klaassen Z, Madi R. Retzius-sparing robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a safe surgical technique with superior continence outcomes. J Endourol. 2017;31:1244–50.
Chang LW, Hung SC, Hu JC, Chiu KY. Retzius-sparing robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy associated with less bladder neck descent and better early continence outcome. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:345–51.
Lee J, Kim HY, Goh HJ, Heo JE, Almujalhem A, Alqahtani AA, et al. Retzius sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy conveys early regain of continence over conventional robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a propensity score matched analysis of 1,863 patients. J Urol. 2020;203:137–44.
Yee CH, Liu AQ, Chiu PKF, Teoh JYC, Hou SSM, Ng CF. A propensity score-matching study on retzius-sparing robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: evidence of continence advantage on the early learning curve. Asian J Surg. 2022;45:1403–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2021.09.013.
Kadono Y, Nohara T, Kawaguchi S, Kadomoto S, Iwamoto H, Yaegashi H, et al. Postoperative functional and cancer control evaluation of conventional and Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: Comparison of selected cases by propensity score matching. Prostate. 2023;83:773–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.24516.
Kadono Y, Nohara T, Kawaguchi S, Makino T, Naito R, Kadomoto S, et al. Comparison of postoperative urinary continence and incontinence types between conventional and Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Neurourol Urodyn. 2023;42:1411–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.25193.
Umari P, Eden C, Cahill D, Rizzo M, Eden D, Sooriakumaran P. Retzius-sparing versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a comparative prospective study of nearly 500 patients. J Urol. 2021;205:780–90.
Eden CG, Moschonas D, Soares R. Urinary continence four weeks following Retzius-sparing robotic radical prostatectomy: The UK experience. J Clin Urol. 2017;11:15–20.
Liao PC, Hung SC, Hu JC, Chiu KY. Retzius-sparing robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy facilitates early continence regardless of neurovascular bundle sparing. Anticancer Res. 2020;40:4075–80.
Anıl H, Karamık K, Yıldız A, Savaş M. Does transition from standard to Retzius-sparing technique in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy affect the functional and oncological outcomes? Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2021;93:399–403. https://doi.org/10.4081/aiua.2021.4.399.
Egan J, Marhamati S, Carvalho FLF, Davis M, O’Neill J, Lee H, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy leads to durable improvement in urinary function and quality of life versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy without compromise on oncologic ef!cacy: single-surgeon series and step-by- step guide. Eur Urol. 2021;79:839–57.
Deng W, Chen R, Jiang X, Zheng P, Zhu K, Zhou X, et al. Independent factors affecting postoperative short-term urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Oncol. 2021;2021:9523442 https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9523442.
Ota Y, Hamamoto S, Matsuyama N, Hamakawa T, Iwatsuki S, Etani T, et al. Pelvic anatomical features after Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prosta- tectomy intended for early recovery of urinary symptoms. J Endourol. 2021;35:296–304.
A. Tahra, U.T. Sen, R. Sobay, A., İnkaya, E.V. Kucuk, U. Boylu. Comparison of Retzius-sparing versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. Actas Urol Esp. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acuro.2021.01.011
Ficarra V, Rossanese M, Gilante M, Foti M, Macchione L, Mucciardi G, et al. Retzius-sparing vs. standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy for clinically localised prostate cancer: a comparative study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023;26:568–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00625-3.
Yılmaz K, Ölçücü MT, Özsoy Ç, Aksaray EE, Kılıç Ş, Ateş M. Comparison of early urinary continence, oncological outcomes, and postoperative complications in retzius-sparing and standard approach robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2023;33:150–4. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2022.0409.
Oshima M, Washino S, Nakamura Y, Konishi T, Saito K, Miyagawa T. Retzius-sparing robotic prostatectomy is associated with higher positive surgical margin rate in anterior tumors, but not in posterior tumors, compared to conventional anterior robotic prostatectomy. Prostate Int. 2023;11:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prnil.2022.07.005.
Lambert E, Allaeys C, Berquin C, De Visschere P, Verbeke S, Vanneste B, et al. Is it safe to switch from a standard anterior to retzius-sparing approach in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy? Curr Oncol. 2023;30:3447–60. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030261.
Anceschi U, Morelli M, Flammia RS, Brassetti A, Dell’Oglio P, Galfano A, et al. Predictors of trainees’ proficiency during the learning curve of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy at high-volume institutions: results from a multicentric series. Cent Eur J Urol. 2023;76:38–43. https://doi.org/10.5173/ceju.2023.260.
Tay LJ, Makin R, Ioannis S, Dokubo Ibi, Patel Keval, Sivathasan Sailantra, et al. Comparative analysis of early post-operative outcomes between retzius-sparing and anterior approach robotic radical prostatectomy for a single surgeon. J Clin Urol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/20514158231156314
Santok GD, Abdel Raheem A, Kim LH, Chang K, Lum TG, Chung BH, et al. Perioperative and short-term outcomes of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy stratified by gland size. BJU Int. 2017;119:135–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13632.
Galfano A, Panarello D, Secco S, Di Trapani D, Barbieri M, Napoli G, et al. Does prostate volume have an impact on the functional and oncological results of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy? Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2018;70:408–13. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0393-2249.18.03069-2.
Qian J, Fu Y, Wu X, Xu L, Zhang M, Zhang Q, et al. Impact of protruded median lobe on perioperative, urinary continence and oncological outcomes of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Transl Androl Urol. 2021;10:538–47. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-1229.
Xu D, Yang Z, Qi J, Mundhenk J, Zanker P, Schwentner C, et al. Early urinary continence recovery following retzius-sparing robotic-assistant radical prostatectomy with suprapubic catheter: a short-term follow-up outcome. World J Urol. 2021;39:3251–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-021-03643-3.
Galfano A, Secco S, Dell’Oglio P, Rha K, Eden C, Fransis K, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: early learning curve experience in three continents. BJU Int. 2021;127:412–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15196.
Sayyid RK, Sherwood D, Simpson WG, Terris MK, Klaassen Z, Madi R. Retzius-sparing robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: racial considerations for 250 consecutive cases. J Robot Surg. 2021;15:221–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-020-01096-1.
Olivero A, Galfano A, Piccinelli M, Secco S, Di Trapani D, Petralia G, et al. Retzius-sparing robotic radical prostatectomy for surgeons in the learning curve: a propensity score-matching analysis. Eur Urol Focus. 2021;7:772–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2020.03.002.
Bahouth Z, Laniado M, Fowler R, Charlesworth PJS. Positive surgical margins rate of Retzius-Sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy in a contemporary, unselected cohort. J Urol. 2022;207:609–16. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000002295.
Tappero S, Dell’Oglio P, Longoni M, Buratto C, Palagonia E, Scilipoti P, et al. Challenging cases in high-risk prostate cancer patients treated with Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. World J Urol. 2022;40:1993–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04073-5.
Galfano A, Tappero S, Eden C, Dell’oglio P, Fransis K, Guo H, et al. Multicentric experience in Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy performed by expert surgeons for high-risk prostate cancer. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2022;74:607–14. https://doi.org/10.23736/S2724-6051.22.04857-1.
Dell’Oglio P, Tappero S, Longoni M, Buratto C, Scilipoti P, Secco S, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy in high-risk prostate cancer patients: results from a large single-institution series. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2022;38:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euros.2022.02.007.
Fonseca J, Froes G, Moraes-Fontes MF, Rebola J, Lúcio R, Almeida M, et al. Urinary continence recovery after Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy in relation to surgeon experience. J Robot Surg. 2023;17:2503–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01687-8.
Akand M, Erdogru T, Avci E, Ates M. Transperitoneal versus extraperitoneal robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a prospective single surgeon randomized comparative study. Int J Urol. 2015;22:916–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.12854.
Guimarães GC, Oliveira RAR, Santana TBM, Favaretto RL, Mourão TC, Rocha MM, et al. Comparative analysis of functional outcomes between two different techniques after 1088 robotic-assisted radical prostatectomies in a high-volume cancer center: a clipless approach. J Endourol. 2019;33:1017–24. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2019.0361.
Yang Y, Liu Z, Guo Y, Li X, Liu L, Wang X, et al. The efficiency and safety of transperitoneal versus extraperitoneal robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy for patients with prostate cancer: a single center experience with 1-year follow-up. Urol J. 2020;17:480–5. https://doi.org/10.22037/uj.v16i7.5475.
Fan S, Hao H, Chen S, Wang J, Dai X, Zhang M, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy using the KangDuo surgical robot system vs the da Vinci Si robotic system. J Endourol. 2023;37:568–74. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2022.0739. Epub 2023 May 5. PMID: 36924278.
Xylinas E, Durand X, Ploussard G, Campeggi A, Allory Y, Vordos D, et al. Evaluation of combined oncologic and functional outcomes after robotic-assisted laparoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy: trifecta rate of achieving continence, potency and cancer control. Urol Oncol. 2013;31:99–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.10.012.
Cochetti G, Boni A, Barillaro F, Pohja S, Cirocchi R, Mearini E. Full neurovascular sparing extraperitoneal robotic radical prostatectomy: our experience with PERUSIA technique. J Endourol. 2017;31:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2016.0477.
Scarcia M, Zazzara M, Divenuto L, Cardo G, Portoghese F, Romano M, et al. Extraperitoneal robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a high-volume surgical center experience. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2018;70:479–85. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0393-2249.18.03114-4.
Paladini A, Cochetti G, Felici G, Russo M, Saqer E, Cari L, et al. Complications of extraperitoneal robot-assisted radical prostatectomy in high-risk prostate cancer: a single high-volume center experience. Front Surg. 2023;10:1157528 https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2023.1157528.
Tuğcu V, Akça O, Şimşek A, Yiğitbaşı İ, Şahin S, Yenice MG, et al. Robotic-assisted perineal versus transperitoneal radical prostatectomy: a matched-pair analysis. Turk J Urol. 2019;45:265–72. https://doi.org/10.5152/tud.2019.98254.
Tuğcu V, Ekşi M, Sahin S, Çolakoğlu Y, Simsek A, Evren İ, et al. Robot-assisted radical perineal prostatectomy: a review of 95 cases. BJU Int. 2020;125:573–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15018.
Carbonara U, Lippolis G, Rella L, Minafra P, Guglielmi G, Vitarelli A, et al. Intermediate-term oncological and functional outcomes in prostate cancer patients treated with perineal robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a single center analysis. Asian J Urol. 2023;10:423–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajur.2023.05.005.
Deng W, Zhang C, Jiang H, Li Y, Zhu K, Liu X, et al. Transvesical versus posterior approach to retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a retrospective comparison with a 12-month follow-up. Front Oncol. 2021;11:641887 https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.641887.
Zhou X, Fu B, Zhang C, Liu W, Guo J, Chen L, et al. Transvesical robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: initial experience and surgical outcomes. BJU Int. 2020;126:300–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15111.
Bravi CA, Balestrazzi E, De Loof M, Rebuffo S, Piramide F, Mottaran A, et al. Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy performed with different robotic platforms: first comparative evidence between Da Vinci and HUGO robot-assisted surgery robots. Eur Urol Focus. 2024;10:107–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2023.08.001.
Bravi CA, Paciotti M, Balestrazzi E, Piro A, Piramide F, Peraire M, et al. Outcomes of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy with the Hugo RAS surgical system: initial experience at a high-volume robotic center. Eur Urol Focus. 2023;9:642–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2023.01.008.
Moschovas MC, Bhat S, Sandri M, Rogers T, Onol F, Mazzone E, et al. Comparing the approach to radical prostatectomy using the multiport da Vinci Xi and da Vinci SP robots: a propensity score analysis of perioperative outcomes. Eur Urol. 2021;79:393–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.11.042.
Noh TI, Kang YJ, Shim JS, Kang SH, Cheon J, Lee JG, et al. Single-port vs multiport robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a propensity score matching comparative study. J Endourol. 2022;36:661–7. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2021.0660. PMID: 34861794.
Ju GQ, Wang ZJ, Shi JZ, Zhang ZQ, Wu ZJ, Yin L, et al. A comparison of perioperative outcomes between extraperitoneal robotic single-port and multiport radical prostatectomy with the da Vinci Si Surgical System. Asian J Androl. 2021;23:640–7. https://doi.org/10.4103/aja.aja_50_21.
Lenfant L, Sawczyn G, Aminsharifi A, Kim S, Wilson CA, Beksac AT, et al. Pure single-site robot-assisted radical prostatectomy using single-port versus multiport robotic radical prostatectomy: a single-institution comparative study. Eur Urol Focus. 2021;7:964–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2020.10.006.
Saidian A, Fang AM, Hakim O, Magi‐Galluzzi C, Nix JW, Rais‐Bahrami S. Perioperative outcomes of single vs multi‐port robotic assisted radical prostatectomy: a single institutional experience. J Urol. 2020;204:490–495.
Vigneswaran HT, Schwarzman LS, Francavilla S, Abern MR, Crivellaro S. A comparison of perioperative outcomes between single‐port and mul- tiport robot‐assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2020;77:671–674.
Kaouk J, Aminsharifi A, Wilson CA, Sawczyn G, Garisto J, Francavilla S, et al. Extraperitoneal versus transperitoneal single port robotic radical prostatectomy: a comparative analysis of perioperative outcomes. J Urol. 2020;203:1135–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000000700.
Abou Zeinab M, Beksac AT, Ferguson E, Kaviani A, Kaouk J. Transvesical versus extraperitoneal single-port robotic radical prostatectomy: a matched-pair analysis. World J Urol. 2022;40:2001–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04056-6.
Balasubramanian S, Shiang A, Vetter JM, Henning GM, Figenshau RS, Kim EH. Comparison of three approaches to single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: our institution’s initial experience. J Endourol. 2022;36:1551–8. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2022.0330.
Kaouk J, Beksac AT, Abou Zeinab M, Duncan A, Schwen ZR, Eltemamy M. Single port transvesical robotic radical prostatectomy: initial clinical experience and description of technique. Urology. 2021;155:130–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2021.05.022.
Bassett JC, Salibian S, Crivellaro S. Single-Port Retzius-Sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: feasibility and early outcomes. J Endourol. 2022;36:620–5. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2021.0542.
Chang Y, Xu W, Xiao Y, Wang Y, Yan S, Ren S. Super-veil nerve-sparing extraperitoneal pure single-port robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy on da Vinci Si robotic system. World J Urol. 2022;40:1413–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-03976-7.
Noh TI, Tae JH, Shim JS, Kang SH, Cheon J, Lee JG, et al. Initial experience of single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a single surgeon’s experience with technique description. Prostate Int. 2022;10:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prnil.2021.10.003.
Yu C, Xu L, Ye L, Zheng Q, Hu H, Ni K, et al. Single-port robot-assisted perineal radical prostatectomy with the da Vinci XI system: initial experience and learning curve using the cumulative sum method. World J Surg Oncol. 2023;21:46 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-023-02927-9.
Zhang H, Ning Z, Jia G, Zhang G, Wang J, Liu H, et al. Modified hood technique for single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy contributes to early recovery of continence. Front Surg. 2023;10:1132303 https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2023.1132303.
Zhou X, Deng W, Li Z, Zhang C, Liu W, Guo J, et al. Initial experience and short-term outcomes of single-port extraperitoneal transvesical robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a two-center study. Transl Androl Urol. 2023;12:989–1001. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau-23-98.
Soputro NA, Ferguson EL, Ramos-Carpinteyro R, Chavali JS, Geskin A, Kaouk J. Vesicourethral anastomosis in transvesical single-port robotic radical prostatectomy: a technical description and perioperative outcomes. J Endourol. 2023;37:1001–11. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2023.0269.
Ramos-Carpinteyro R, Ferguson E, Soputro N, Chavali JS, Abou Zeinab M, Pedraza A, et al. Predictors of early continence after single-port transvesical robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2024;184:176–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2023.11.010.
Ficarra V, Novara G, Rosen RC, Artibani W, Carroll PR, Costello A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:405–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.05.045.
Visscher J, Hiwase M, Bonevski B, O’Callaghan M. The association of smoking with urinary and sexual function recovery following radical prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024;27:222–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-023-00701-2.
Rosenberg JE, Jung JH, Edgerton Z, Lee H, Lee S, Bakker CJ, et al. Retzius-sparing versus standard robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;8:CD013641 https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013641.pub2.
Liu J, Zhang J, Yang Z, Liu Q, Zhang W, Qing Z, et al. Comparison of Retzius-sparing and conventional robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy regarding continence and sexual function: an updated meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022;25:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-021-00459-5.
Chung DY, Jung HD, Kim DK, Lee MH, Lee SW, Paick S, et al. Outcomes of Retzius-sparing versus conventional robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a KSER update series systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0268182 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VF had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: VF. Acquisition of data: VF, MR, IR. Analysis and interpretation of data: VF, MR, IR. Drafting of the manuscript: RF. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: RF, GG, AM, CT, FC, AG, FA, EDiT. Statistical analysis: VF, IR. Obtaining funding: None. Administrative, technical, or material support: None. Supervision: RF, GG, AM, CT, FC, AG, FA, EDiT. Other: None.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ficarra, V., Rossanese, M., Ilaria, R. et al. Impact of transperitoneal anterior, retzius-sparing, extraperitoneal, transvesical and perineal approaches on urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 28, 328–341 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-025-00943-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-025-00943-2
This article is cited by
-
New trends on the management of localized prostate cancer
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2025)