Abstract
Study design
Prospective cohort study.
Objectives
This prospective cohort study aims to evaluate the recovery of penetration/aspiration and functional feeding outcome in patients with acute TCSCI.
Setting
Tampere University Hospital, Tampere, Finland
Methods
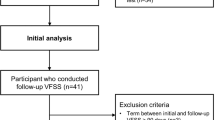
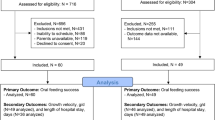
Forty-six patients with TCSCI were enrolled. All the patients received speech therapeutic interventions based on their clinical needs and were examined with a videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) at enrollment. The incidence of VFSS-verified laryngeal penetration/aspiration according to Rosenbek’s Penetration-Aspiration Scale (PAS) served as the primary outcome. The secondary outcome was the level of functional oral intake (as per the Functional Oral Intake Scale; FOIS). Based on the PAS results, the patients were divided into two groups: (i) penetrator/aspirators (PAS score ≥3) and (ii) non-penetrator/aspirators (PAS score ≤2). Follow-up VFS studies were primarily conducted on the patients with penetration/aspiration in prior VFS studies. The follow-up VFS studies were scheduled on the basis of clinical demand.
Results
Of the 46 patients, 48% had penetration/aspiration in the first VFSS. The second VFSS was conducted on 20 patients, of whom 6 patients (30%) had penetration/aspiration. The third VFSS was conducted on 9 patients. Of these, only two (22%) patients were still penetrator/aspirators. The majority (n = 37, 88%) of the patients presented a total oral intake without restrictions at the time of the final follow-up. Only one patient (2%) was still tube-dependent with consistent oral intake.
Conclusion
Swallowing physiology in patients with TCSCI improved during the first months after injury, and the number of penetrator/aspirators decreased progressively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kirshblum S, Johnston MV, Brown J, O’Connor KC, Jarosz P. Predictors of dysphagia after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80:1101–5.
Wolf C, Meiners TH. Dysphagia in patients with acute cervical spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2003;41:347–53.
Brady S, Miserendino R, Statkus R, Springer T, Hakel M, Stambolis V. Predictors to dysphagia and recovery after cervical spinal cord injury during acute rehabilitation. J Appl Res 2004;4:1–11.
Abel R, Ruf S, Spahn B. Cervical spinal cord injury and deglutition disorders. Dysphagia . 2004;19:87–94.
Shem K, Castillo K, Naran B. Factors associated with dysphagia in individuals with high tetraplegia. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2005;10:8–18.
Seidl RO, Nusser-Muller-Busch R, Kurzweil M, Niedeggen A. Dysphagia in acute tetraplegics: a retrospective study. Spinal Cord. 2010;48:197–201.
Shin JC, Yoo JH, Lee YS, Goo HR, Kim DH. Dysphagia in cervical spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2011;49:1008–13.
Shem K, Castillo K, Wong S, Chang J. Dysphagia in individuals with tetraplegia: incidence and risk factors. J Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34:85–92.
Shem K, Castillo K, Wong SL, Chang J, Kolakowsky-Hayner S. Dysphagia and respiratory care in individuals with tetraplegia: incidence, associated factors, and preventable complications. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2012;18:15–22.
Chaw E, Shem K, Castillo K, Wong SL, Chang J. Dysphagia and associated respiratory considerations in cervical spinal cord injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2012;18:291–9.
Shem KL, Castillo K, Wong SL, Chang J, Kao MC, Kolakowsky-Hayner SA. Diagnostic accuracy of bedside swallow evaluation versus videofluoroscopy to assess dysphagia in individuals with tetraplegia. Pm R. 2012 ;4:283–9.
Ihalainen T, Rinta-Kiikka I, Luoto TM, Koskinen EA, Korpijaakko-Huuhka A, Ronkainen A. Traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: a prospective clinical study of laryngeal penetration and aspiration. Spinal Cord. 2017;55:979–84.
Ihalainen T, Rinta-Kiikka I, Luoto TM, Thesleff T, Helminen M, Korpijaakko-Huuhka A, et al. Risk factors for laryngeal penetration-aspiration in patients with acute traumatic cervical spinal cord injury. Spine J. 2018;18:81–87.
DeVivo M, Biering-Sorensen F, Charlifue S, Noonan V, Post M, Stripling T. et al. International spinal cord injury core data set. Spinal Cord. 2006;44:535–40.
Kirshblum SC, Burns SP, Biering-Sorensen F, Donovan W, Graves DE, Jha A, et al. International standards for neurological classification of spinal cord injury (revised 2011). J Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34:535–46.
Kirshblum SC, Waring W, Biering-Sorensen F, Burns SP, Johansen M, Schmidt-Read M, et al. Reference for the 2011 revision of the International Standards For Neurological Classification Of Spinal Cord Injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34:547–54.
Robbins J, Coyle J, Rosenbek J, Roecker E, Wood J. Differentiation of normal and abnormal airway protection during swallowing using the penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1999;14:228–32.
Daggett A, Logemann J, Rademaker A, Pauloski B. Laryngeal penetration during deglutition in normal subjects of various ages. Dysphagia. 2006;21:270–4.
Allen JE, White CJ, Leonard RJ, Belafsky PC. Prevalence of penetration and aspiration on videofluoroscopy in normal individuals without dysphagia. Otolaryngol-Head & Neck Surg. 2010;142:208–13.
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia . 1996;11:93–98.
Crary MA, Mann GDC, Groher ME. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86:1516–20.
Hansen TS, Engberg AW, Larsen K. Functional oral intake and time to reach unrestricted dieting for patients with traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89:1556–62.
Molen Lvd, Rossum MAv, Burkhead LM, Smeele LE Rasch CRN, Hilgers FJM. A randomized preventive rehabilitation trial in advanced head and neck cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy: feasibility, compliance, and short-term effects. Dysphagia. 2011;26:155–70.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients, biostatistician Mika Helminen, and research assistant Anne Simi for their assistance.
Funding
This study was funded by Maire Taponen säätiö, The Finnish Dysphagia Rehabilitation Association, and Finnish Association of Speech Therapists.
Author contributions
TI contributed to the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, and article preparation. TML contributed to the data interpretation and article preparation. IR-K contributed to the data collection and article preparation. A-MK-H contributed to the article preparation. AR contributed to the study design and article preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
TI has received research grants from Maire Taponen säätiö, The Finnish Dysphagia Rehabilitation Association, and Finnish Association of Speech Therapists. TML declares that he has no conflict of interest. IR-K declares that she has no conflict of interest. AR declares that he has no conflict of interest. A-MK-H declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ihalainen, T., Luoto, T.M., Rinta-Kiikka, I. et al. Traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: recovery of penetration/aspiration and functional feeding outcome. Spinal Cord 56, 1000–1007 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41393-018-0091-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41393-018-0091-1