Abstract
Introduction
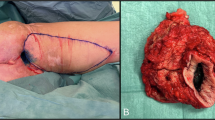
Trochanteric pressure ulcers (PrUs) are difficult to treat and are often complicated by infection spreading to the hip joint. We review three cases from India where proximal femoral resection and pedicled Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL) flapping was used in the management of infected deep trochanteric ulcers communicating to the hip joint.
Case presentation
Three patients had a total of four trochanteric PrUs communicating to the hip joint. Proximal femoral resection along with radical debridement of the pressure ulcer (PrU) was the first step in our surgical protocol. Serial debridements were performed to make the resulting cavity healthier and ready for the subsequent flap surgery. TFL flapping was done to cover the raw area of the PrU and the donor site was closed either primarily or with a split skin graft. All patients were males with AIS A spinal cord injury (SCI) and stage 4 PrUs in the trochanteric region. One patient had bilateral trochanteric ulcers. There was complete healing of all PrUs with improvement in wheelchair mobility, and general health.
Discussion
PrUs are a common complication of patients with SCI and are often considered one of the most neglected issues of health care delivery in India. Proximal femoral resection with pedicled TFL muscle flap is a versatile and reliable procedure for the coverage of recalcitrant trochanteric PrU with hip joint involvement. Minimal donor site morbidity occurs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Chauhan VS, Goel S, Kumar P, Srivastava S, Shukla VK. The prevalence of pressure ulcers in hospitalized patients in a university hospital in India. J Wound Care. 2005;14:36–7.
Mehta C, George JV, Mehta Y, Wangmo N. Pressure ulcer and patient characteristics - a point prevalence study in a tertiary hospital of India based on the European pressure ulcer advisory panel minimum data set. J Tissue Viability. 2015;24:123–30.
Kottner J, Dassen T, Lahmann NA. Pressure ulcers in German nursing homes: frequencies, grades and origins. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2011;44:318–22.
Zhou Q, Yu T, Liu Y, Shi R, Tian S, Yang C, et al. The prevalence and specific characteristics of hospitalised pressure ulcer patients: a multicentre cross-sectional study. J Clin Nurs. 2018;27:694–704.
Amir Y, Tan FE, Halfens R, Lohrmann C, Schols J. Pressure ulcer prevalence and care in Indonesian hospitals: a multicenter, Cross-sectional evaluation using an extended Donabedian Model. Ostomy Wound Manag. 2017;63:8–23.
Acartürk TO. Treatment of large ischial ulcers communicating with the hip joint with proximal femoral resection and reconstruction with a combined vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius and rectus femoris musculocutaneous flap. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62:1497–502.
Singh R, Singh R, Rohilla RK, Siwach R, Verma V, Kaur K. Surgery for pressure ulcers improves general health and quality of life in patients with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2010;33:396–400.
Middleton JW, Lim K, Taylor L, Soden R, Rutkowski S. Patterns of morbidity and rehospitalisation following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2004;42:359–67.
Rish BL, Dilustro JF, Salazar AM, Schwab KA, Brown HR. Spinal cord injury: a 25- year morbidity and mortality study. Mil Med. 1997;162:141–8.
Pandey V, Nigam V, Goyal TD, Chhabra H. Care of post‑traumatic spinal cord injury patients in India: An analysis. Indian J Orthop. 2007;41:295–9.
Dinsdale SM. Decubitus ulcers: role of pressure and friction in causation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1974;55:147.
Chhabra HS, Arora M. Neglected traumatic spinal cord injuries: causes, consequences and outcomes in an Indian setting. Spinal Cord. 2013;51:238–44.
Singh R, Rohilla RK, Siwach R, Dhankar SS, Magu NK, Sangwan SS. Health related problems and effect of specific interventions in spinal cord injury: an outcome study in Northern India. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2010;46:47–53.
Singh R, Singh RB, Rohilla RK, Magu NK, Goel R, Kaur K. Improvisations in classic and modified techniques of flap surgery to improve the success rate for pressure ulcer healing in patients with spinal cord injury. Int Wound J. 2013;10:455–60.
Girdlestone GR. Acute pyogenic arthritis of the hip: an operation giving free access and effective drainage (Classic reprint). Clin Orthop. 1982;170:3–7.
Klein NE, Luster S, Green S, Moore T, Capen D. Closure of defects from pressure sores requiring proximal femoral resection. Ann Plast Surg. 1988;21:246–50.
Hill HL, Nahai F, Vasconez LO. The tensor fascia lata myocutaneous free flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1978;61:517–22.
Schmidt AB, Fromberg G, Ruidisch MH. Applications of the pedicled vastus lateralis flap for patients with complicated pressure sores. Spinal Cord. 1997;35:437–42.
Bovet JL, Nassif TM, Guimberteau JC, Baudet J. The vastus lateralis musculocutaneous flap in the repair of trochanteric pressure sores: technique and indication. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982;69:830–4.
Mathes SJ, Alpert BS. Advances in muscle and musculocutaneous flaps. Clin Plast Surg. 1980;7:15–26.
Rubayi S, Pompan D, Garland D. Proximal femoral resection and myocutaneous flap for treatment of pressure ulcers in spinal injury patients. Ann Plast Surg. 1991;27:132–8.
Jones NF, Eadie P, Johnson PC, Mears DC. Treatment of chronic infected hip arthroplasty wounds by radical debridement and obliteration with pedicled and free muscle flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;88:95–101.
Hubmer MG, Schwaiger N, Windisch G, Feigl G, Koch H, Haas FM, et al. The vascular anatomy of the tensor fasciae latae perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:181–9.
Evans GR, Lewis VL, Mason PN, Loomis M, Vander Kolk CA. Hip joint communication with pressure sore: the refractory wound and the role of girdlestone arthroplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993;91:288–94.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the design, analysis, and writing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of ethics
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of institution, the governmental regulations and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Wadhwani, J., Rohilla, R.K. et al. Proximal femoral resection and Tensor Fascia Lata flap for recalcitrant trochanteric pressure ulcers. Spinal Cord Ser Cases 5, 15 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-019-0157-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-019-0157-0