Abstract
Introduction
Spinal cord injury (SCI) with atlantoaxial dislocation (AAD) is often fatal. We present the case of a resuscitated patient with AAD and traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) at the craniovertebral junction (CVJ).
Case presentation
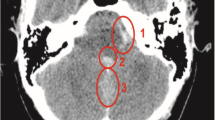
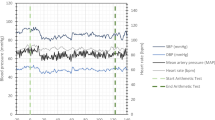
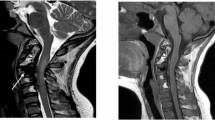
We present the case of an 84-year-old man who suffered an observed cardiopulmonary arrest. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was initiated and spontaneous circulation returned. In the emergency room, the patient’s Glasgow Coma Scale was 3 (E1V1M1). No spontaneous respiration was noted. Neuroimaging revealed SAH at the CVJ. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) revealed a vessel running through the left C2/3 intervertebral foramen into the spinal canal. The ventral space of spinal cord revealed contrast enhancement. Angiography revealed extravasation from the spinal branch of the left vertebral artery, without venous filling. It did not appear to be a vascular malformation with an arteriovenous shunt, but rather a traumatic laceration of the artery. Plain CT and CT angiography suggested AAD. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed injury to the medulla oblongata and upper cervical spinal cord, with AAD and retrodental subligamentous hemorrhage. We embolized the branch of the left vertebral artery and performed a C1 laminectomy. The patient moved his extremities postoperatively.
Discussion
This was a case of injury to the medulla oblongata and upper cervical spinal cord due to AAD with SAH. This is the first report of resuscitated case of traumatic AAD with SAH in the CVJ. Traumatic AAD should be included in the differential diagnosis in case of SAH in CVJ, which may be misdiagnosed as intrinsic SAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Meyer C, Eysel P, Stein G. Traumatic atlantoaxial and fracture-related dislocation. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5297950.
Steinmetz MP, Mroz TE, Benzel EC. Craniovertebral junction: biomechanical considerations. Neurosurgery. 2010;66:7–12.
Martin MD, Bruner HJ, Maiman DJ. Anatomic and biomechanical considerations of the craniovertebral junction. Neurosurgery. 2010;66:2–6.
Oostveen JC, van de Laar MA, Tuynman FH. Anterior atlantoaxial subluxation in a patient with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:1441–4.
Kleweno CP, Zampini JM, White AP, Kasper EM, McGuire KJ. Survival after concurrent traumatic dislocation of the atlanto-occipital and atlanto-axial joints: a case report and review of the literature. Spine. 2008;33:659–62.
Coast GC, Gee DJ. Traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage: an alternative source. J Clin Pathol. 1984;37:1245–8.
Harland WA, Pitts JF, Watson AA. Subarachnoid haemorrhage due to upper cervical trauma. J Clin Pathol. 1983;36:1335–41.
Xu Y, Li F, Guan H, Xiong W. Traumatic posterior atlantoaxial dislocation without associated fracture but with neurological deficit: a case report and literature review. Medicine. 2015;94:1–6.
Przybylski GJ, Welch WC. Longitudinal atlantoaxial dislocation with type III odontoid fracture. J Neurosurg. 1996;84:666–70.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kageyama, H., Kakumoto, K., Yasuoka, H. et al. Cardiopulmonary arrest induced by atlantoaxial dislocation with subarachnoid hemorrhage: a case report and review of the literature. Spinal Cord Ser Cases 5, 100 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-019-0247-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-019-0247-z
This article is cited by
-
Successful recovery from cardiac arrest due to atlantoaxial subluxation in Down syndrome: a case report
Spinal Cord Series and Cases (2024)