Abstract
Introduction
Spontaneous spinal epidural abscess (SEA) is a rare diagnosis; only eight cases have been reported during pregnancy. Diagnosis of SEA can be difficult, especially when the classic triad of fever, back pain, and neurologic deficits are not present. Early diagnosis and treatment are necessary to reduce potential morbidity and mortality.
Case presentations
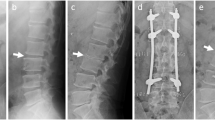
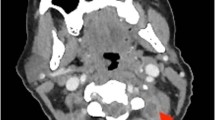
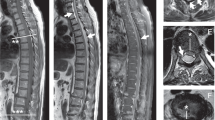
We report two separate cases of SEA in pregnancy and summarize the existing literature. Case 1: A 20-year-old G1P0 presented at 35-week gestation with low back pain and lower extremity (LE) weakness. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed thoracic SEA. The patient underwent cesarian delivery followed by posterior thoracic laminectomy and fusion (T9–11), abscess decompression, and antibiotic therapy. Unfortunately, there was a recurrence of her infection requiring a second irrigation and debridement 1 month after index procedure. At final follow-up, the patient had complete neurologic recovery. Case 2: A 38-year-old G10P0 presented at 36-week gestation in labor with LE weakness and difficulty ambulating. After delivery, she had significant LE neurologic deficits. MRI demonstrated thoracic osteodiscitis with associated epidural abscess. She underwent thoracic laminectomy and fusion (T7–12), abscess decompression, and antibiotic therapy. Unfortunately, despite aggressive treatment, she has persistent LE neurologic deficits.
Discussion
Pregnancy complicates the diagnosis and treatment strategies of SEA: back pain is very commonly underestimated, especially in the absence of fever and gross neurologic deficits. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are paramount to prevent neurologic decline and facilitate recovery. It is important to perform a focused physical exam noting motor strength, sensation, and reflexes. Coordinated management between the Emergency Department, OB-GYN, and spinal surgery team is required for best possible patient outcomes. Typically, management consists of aggressive surgical decompression and antibiotic therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Pennick VE, Young G Interventions for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD001139. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001139.pub2.
Anderson BL, Nau GJ, Simhan HN. Idiopathic vertebral abscess in pregnancy: case report and literature review. Am J Perinatol. 2007;24:377–9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-981850.
Nakano H, Yanase D, Mae K, Toribatake Y, Yamada M. Successful antibacterial therapy of a spinal epidural abscess in pregnancy: a case report and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 2017;372:101–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.11.042.
Spiegel Strauss TN, Pachtman SL, Rochelson B. Bacterial spinal epidural and psoas abscess in pregnancy associated with intravenous drug use. Case Rep. Obstet Gynecol 2018;2018:1797421. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1797421.
D’Angelo R, Smiley RM, Riley ET, Segal S. Serious complications related to obstetric anesthesia: the serious complication repository project of the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology. Anesthesiology. 2014;120:1505–12. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000000253.
Rigamonti D, Liem L, Sampath P, Knoller N, Namaguchi Y, Schreibman DL, et al. Spinal epidural abscess: contemporary trends in etiology, evaluation, and management. Surg Neurol. 1999;52:189–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(99)00055-5.
Darouiche RO. Spinal epidural abscess. N Engl J Med 2006;355:2012–20. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra055111.
Krishnamohan P, Berger JR. Spinal epidural abscess. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2014;16:436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11908-014-0436-7.
Tanamai VW, Seagle BL, Luo G. Methicillin-resistant Staphyloccocus aureus intracranial epidural abscess with osteomyelitis during pregnancy: a case report. J Reprod Med. 2016;61:295–8.
Connealy BD, Lovgren TR, Tomich PG, Smith CV, Berg TG. Spontaneous methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidural abscess in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2010;116:498–501. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181e74fe9.
Hunter JC, Ryan MD, Taylor TK, Pennington JC. Spinal epidural abscess in pregnancy. Aust N Z J Surg. 1977;47:672–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-2197.1977.tb06602.x.
Van Winter JT, Nielsen SN, Ogburn PL Jr. Epidural abscess associated with intravenous drug abuse in a pregnant patient. Mayo Clin Proc. 1991;66:1036–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-6196(12)61727-3.
Lampen R, Bearman G. Epidural abscess caused by Streptococcus milleri in a pregnant woman. BMC Infect Dis. 2005;5:100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-5-100.
Burton KR, Wang X, Dhanoa D. Holocord spinal epidural abscess in a pregnant patient presenting as premature labour: a rare presentation of an unusual diagnosis. CJEM. 2014;16:334–8. https://doi.org/10.2310/8000.2013.131134.
Singh UB, Chandola HC, Gopal NN. Spinal epidural abscess with pregnancy leading to paraplegia. J Obstet Gynecol India. 2016;66:123–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-015-0701-1.
Abbassi-Ghanavati M, Greer LG, Cunningham FG. Pregnancy and laboratory studies: a reference table for clinicians. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114:1326–31. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181c2bde8.
Davis DP, Wold RM, Ptael RJ, Tran AJ, Tokhi RN, Chan TC, et al. The clinical presentation and impact of diagnostic delay on emergency department patients with spinal epidural abscess. J Emerg Med. 2004;26:285–91.
Del Curling OJ, Gower D, McWhorter J. Changing concepts in spinal epidural abscess: a report of 29 cases. Neurosurgery. 1990;27:185–92. https://doi.org/10.1227/000006123-199008000-00002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
We would like to thank Dr. Conor Regan for allowing us to share two of his surgical cases.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, D.L., Lewis, S. & Regan, C. Spontaneous spinal epidural abscess in pregnancy: a case series. Spinal Cord Ser Cases 7, 79 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-021-00437-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41394-021-00437-y
This article is cited by
-
Vancomycin
Reactions Weekly (2022)