Abstract
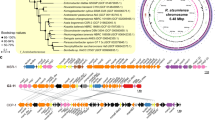
Under the same selection pressures, two genetically divergent populations may evolve in parallel toward the same adaptive solutions. Here, we hypothesized that magnetotaxis (i.e., magnetically guided chemotaxis) represents a key adaptation to micro-oxic habitats in aquatic sediments and that its parallel evolution homogenized the phenotypes of two evolutionary divergent clusters of freshwater spirilla. All magnetotactic bacteria affiliated to the Magnetospirillum genus (Alphaproteobacteria class) biomineralize the same magnetic particle chains and share highly similar physiological and ultrastructural features. We looked for the processes that could have contributed at shaping such an evolutionary pattern by reconciling species and gene trees using newly sequenced genomes of Magnetospirillum related bacteria. We showed that repeated horizontal gene transfers and homologous recombination of entire operons contributed to the parallel evolution of magnetotaxis. We propose that such processes could represent a more parsimonious and rapid solution for adaptation compared with independent and repeated de novo mutations, especially in the case of traits as complex as magnetotaxis involving tens of interacting proteins. Besides strengthening the idea about the importance of such a function in micro-oxic habitats, these results reinforce previous observations in experimental evolution suggesting that gene flow could alleviate clonal interference and speed up adaptation under some circumstances.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bazylinski DA, Frankel RB. Magnetosome formation in prokaryotes. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:217–30.
Klumpp S, Lefèvre CT, Bennet M, Faivre D. Swimming with magnets: from biological organisms to synthetic devices. Phys Rep. 2019;789:1–54.
Schleifer KH, Schüler D, Spring S, Weizenegger M, Amann R, Ludwig W, et al. The genus Magnetospirillum gen. nov. description of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense sp. nov. and transfer of Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum to Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum comb. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1991;14:379–85.
Matsunaga T, Sakaguchi T, Tadakoro F. Magnetite formation by a magnetic bacterium capable of growing aerobically. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1991;35:651–5.
Uebe R, Schüler D. Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14:621–37.
Grant CR, Wan J, Komeili A. Organelle formation in bacteria and archaea. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2018;34:217–38.
Schüler D, Spring S, Bazylinski DA. Improved technique for the isolation of magnetotactic spirilla from a freshwater sediment and their phylogenetic characterization. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1999;22:466–71.
Lefèvre CT, Schmidt ML, Viloria N, Trubitsyn D, Schüler D, Bazylinski DA. Insight into the evolution of magnetotaxis in magnetospirillum spp., based on mam gene phylogeny. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78:7238–48.
Wang Y, Lin W, Li J, Zhang T, Li Y, Tian J, et al. Characterizing and optimizing magnetosome production of Magnetospirillum sp. XM-1 isolated from Xi’an City Moat, China. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015;362:fnv167.
Dziuba M, Koziaeva V, Grouzdev D, Burganskaya E, Baslerov R, Kolganova T, et al. Magnetospirillum caucaseum sp. nov., Magnetospirillum marisnigri sp. nov. and Magnetospirillum moscoviense sp. nov., freshwater magnetotactic bacteria isolated from three distinct geographical locations in European Russia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016;66:2069–77.
Ke L, Chen Y, Liu P, Liu S, Wu D, Yuan Y, et al. Characteristics and optimised fermentation of a novel magnetotactic bacterium, Magnetospirillum sp. ME-1. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018;365:14.
Wang Y, Casaburi G, Lin W, Li Y, Wang F, Pan Y. Genomic evidence of the illumination response mechanism and evolutionary history of magnetotactic bacteria within the Rhodospirillaceae family. BMC Genomics. 2019;20:407.
Lefèvre CT, Bazylinski DA. Ecology, diversity, and evolution of magnetotactic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013;77:497–526.
Gonçalves RP, Bernadac A, Sturgis JN, Scheuring S. Architecture of the native photosynthetic apparatus of Phaeospirillum molischianum. J Struct Biol. 2005;152:221–8.
Thrash JC, Ahmadi S, Torok T, Coates JD. Magnetospirillum bellicus sp. nov., a novel dissimilatory perchlorate-reducing alphaproteobacterium isolated from a bioelectrical reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:4730–7.
Gorlenko VM, Dziuba MV, Maleeva AN, Panteleeva AN, Kolganova TV, Kuznetsov BB. Magnetospirillum aberrantis sp. nov., a new freshwater bacterium with magnetic inclusions. Mikrobiologiia. 2011;80:679–90.
Lin W, Zhang W, Zhao X, Roberts AP, Paterson GA, Bazylinski DA, et al. Genomic expansion of magnetotactic bacteria reveals an early common origin of magnetotaxis with lineage-specific evolution. ISME J. 2018;1:1508–19.
Burgess JG, Kawaguchi R, Sakaguchi T, Thornhill RH, Matsunaga T. Evolutionary relationships among Magnetospirillum strains inferred from phylogenetic analysis of 16S rDNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:6689–94.
Bazylinski DA, Dean AJ, Williams TJ, Long LK, Middleton SL, Dubbels BL. Chemolithoautotrophy in the marine, magnetotactic bacterial strains MV-1 and MV-2. Arch Microbiol. 2004;182:373–87.
Bazylinski DA, Blakemore RP. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene-reduction) in Aquaspirillum-magnetotacticum. Curr Microbiol. 1983;9:305–8.
Bazylinski DA, Dean AJ, Schüler D, Phillips EJ, Lovley DR. N2-dependent growth and nitrogenase activity in the metal-metabolizing bacteria, Geobacter and Magnetospirillum species. Environ Microbiol. 2000;2:266–73.
Bazylinski DA, Blakemore RP. Denitrification and assimilatory nitrate reduction in Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983;46:1118–24.
Blakemore RP, Short KA, Bazylinski DA, Rosenblatt C, Frankel RB. Microaerobic conditions are required for magnetite formation within Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum. Geomicrobiol J. 1985;4:53–71.
Schüler D, Baeuerlein E. Dynamics of iron uptake and Fe3O4 biomineralization during aerobic and microaerobic growth of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. J Bacteriol. 1998;180:159–62.
Heyen U, Schüler D. Growth and magnetosome formation by microaerophilic Magnetospirillum strains in an oxygen-controlled fermentor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003;61:536–44.
Geelhoed JS, Kleerebezem R, Sorokin DY, Stams AJM, van Loosdrecht MCM. Reduced inorganic sulfur oxidation supports autotrophic and mixotrophic growth of Magnetospirillum strain J10 and Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12:1031–40.
Grünberg K, Wawer C, Tebo BM, Schüler D. A large gene cluster encoding several magnetosome proteins is conserved in different species of magnetotactic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67:4573–82.
Grünberg K, Müller E-C, Otto A, Reszka R, Linder D, Kube M, et al. Biochemical and proteomic analysis of the magnetosome membrane in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:1040–50.
Ullrich S, Kube M, Schübbe S, Reinhardt R, Schüler D. A hypervariable 130-kilobase genomic region of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense comprises a magnetosome island which undergoes frequent rearrangements during stationary growth. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:7176–84.
Lefèvre CT, Trubitsyn D, Abreu F, Kolinko S, Almeida LGP, Vasconcelos ATR, et al. Monophyletic origin of magnetotaxis and the first magnetosomes. Environ Microbiol. 2013;15:2267–74.
Lin W, Paterson GA, Zhu Q, Wang Y, Kopylova E, Li Y, et al. Origin of microbial biomineralization and magnetotaxis during the Archean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:2171–6.
Jogler C, Kube M, Schübbe S, Ullrich S, Teeling H, Bazylinski DA, et al. Comparative analysis of magnetosome gene clusters in magnetotactic bacteria provides further evidence for horizontal gene transfer. Environ Microbiol. 2009;11:1267–77.
Wang S, Chen Y. Origin of magnetotaxis: vertical inheritance or horizontal transfer? Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017;114:E5016–8.
Monteil CL, Perrière G, Menguy N, Ginet N, Alonso B, Waisbord N, et al. Genomic study of a novel magnetotactic Alphaproteobacteria uncovers the multiple ancestry of magnetotaxis. Environ Microbiol. 2018;20:4415–30.
Du H, Zhang W, Zhang W, Zhang W, Pan H, Pan Y, et al. Magnetosome Gene Duplication as an Important Driver in the Evolution of Magnetotaxis in the Alphaproteobacteria. mSystems. 2019;4:e00315–9.
Rundle HD, Nosil P. Ecological speciation. Ecol Lett. 2005;8:336–52.
Conte GL, Arnegard ME, Peichel CL, Schluter D. The probability of genetic parallelism and convergence in natural populations. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci. 2012;279:5039–47.
Orr HA. The probability of parallel evolution. Evolution. 2005;59:216–20.
Gompel N, Prud’homme B. The causes of repeated genetic evolution. Dev Biol. 2009;332:36–47.
Maynard Smith J, Smith NH, O’Rourke M, Spratt BG. How clonal are bacteria? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:4384–8.
Lawrence JG, Retchless AC. The interplay of homologous recombination and horizontal gene transfer in bacterial speciation. In: Gogarten MB, Gogarten JP, Olendzenski LC (eds.). Horizontal gene transfer: Genomes in Flux. 2009. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 29–53.
Wiedenbeck J, Cohan FM. Origins of bacterial diversity through horizontal genetic transfer and adaptation to new ecological niches. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011;35:957–76.
Bailey SF, Blanquart F, Bataillon T, Kassen R. What drives parallel evolution?: How population size and mutational variation contribute to repeated evolution. BioEssays N. Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol. 2017;39:1–9.
Fraser C, Alm EJ, Polz MF, Spratt BG, Hanage WP. The bacterial species challenge: making sense of genetic and ecological diversity. Science. 2009;323:741–6.
Barrick JE, Lenski RE. Genome dynamics during experimental evolution. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:827–39.
Cohan FM. Bacterial species and speciation. Syst Biol. 2001;50:513–24.
Nakamura Y, Itoh T, Matsuda H, Gojobori T. Biased biological functions of horizontally transferred genes in prokaryotic genomes. Nat Genet. 2004;36:760–6.
Vallenet D, Calteau A, Cruveiller S, Gachet M, Lajus A, Josso A, et al. MicroScope in 2017: an expanding and evolving integrated resource for community expertise of microbial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D517–28.
Matsunaga T, Okamura Y, Fukuda Y, Wahyudi AT, Murase Y, Takeyama H. Complete genome sequence of the facultative anaerobic magnetotactic bacterium Magnetospirillum sp. strain AMB-1. DNA Res. 2005;12:157–66.
Wang X, Wang Q, Zhang W, Wang Y, Li L, Wen T, et al. Complete genome sequence of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1. Genome Announc. 2014;2:e00171–14.
Smalley MD, Marinov GK, Bertani LE, DeSalvo G. Genome sequence of Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum Strain MS-1. Genome Announc. 2015;3:e00233–15.
Grouzdev DS, Dziuba MV, Sukhacheva MS, Mardanov AV, Beletskiy AV, Kuznetsov BB, et al. Draft genome sequence of Magnetospirillum sp. Strain SO-1, a freshwater magnetotactic bacterium isolated from the Ol’khovka River, Russia. Genome Announc. 2014;2:e00235–14.
Dzyuba MV, Mardanov AV, Beletskii AV, Kolganova TV, Sukhacheva MV, Shelenkov AA, et al. Reconstruction of iron metabolism pathways of bacteria Magnetospirillum aberrantis SpK spp. based on sequenced genome analysis. Dokl Biol Sci. 2012;444:202–5.
Melnyk RA, Engelbrektson A, Clark IC, Carlson HK, Byrne-Bailey K, Coates JD. Identification of a perchlorate reduction genomic island with novel regulatory and metabolic genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:7401–4.
Wang Y, Zhang T, Lin W, Zhang B, Cai Y, Yang C, et al. Complete genome sequence of Magnetospirillum sp. Strain XM-1, isolated from the Xi’an City Moat, China. Genome Announc. 2016;4:e01171–16.
Ke L, Liu P, Liu S, Gao M. Complete genome sequence of Magnetospirillum sp. ME-1, a novel magnetotactic bacterium isolated from East Lake, Wuhan, China. Genome Announc 2017;5:e00485–17.
Ivanovsky RN, Keppen OI, Lebedeva NN, Beletsky AV, Mardanov AV, Grouzdev DS. Draft genome sequence of the anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium Phaeospirillum fulvum MGU-K5. Genome Announc. 2017;5:e00895–17.
Duquesne K, Prima V, Ji B, Rouy Z, Médigue C, Talla E, et al. Draft genome sequence of the purple photosynthetic bacterium Phaeospirillum molischianum DSM120, a particularly versatile bacterium. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:3559–60.
Contreras-Moreira B, Vinuesa P. GET_HOMOLOGUES, a versatile software package for scalable and robust microbial pangenome analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:7696–701.
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT. The enveomics collection: a toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Inc. 2016;4:e1900v1.
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinforma. 2013;14:60.
Qin Q-L, Xie B-B, Zhang X-Y, Chen X-L, Zhou B-C, Zhou J, et al. A proposed genus boundary for the Prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol. 2014;196:2210–5.
Pantiukh K, Grouzdev D. POCP-matrix calculation for a numberof genomes. 2017; https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.4577953.v1.
Vallenet D, Belda E, Calteau A, Cruveiller S, Engelen S, Lajus A, et al. MicroScope-an integrated microbial resource for the curation and comparative analysis of genomic and metabolic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D636–47.
Karp PD, Latendresse M, Caspi R. The pathway tools pathway prediction algorithm. Stand Genom Sci. 2011;5:424–9.
Caspi R, Altman T, Dreher K, Fulcher CA, Subhraveti P, Keseler IM, et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D742–53.
Abby SS, Néron B, Ménager H, Touchon M, Rocha EPC. MacSyFinder: a program to mine genomes for molecular systems with an application to CRISPR-Cas systems. PloS One. 2014;9:e110726.
Abby SS, Rocha EPC. Identification of protein secretion systems in bacterial genomes using MacSyFinder. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2017;1615:1–21.
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Dray S, Dufour A-B. The ade4 package: implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. J Stat Softw. 2007;22:1–20.
de Vienne DM, Ollier S, Aguileta G. Phylo-MCOA: a fast and efficient method to detect outlier genes and species in phylogenomics using multiple co-inertia analysis. Mol Biol Evol. 2012;29:1587–98.
Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:772–80.
Criscuolo A, Gribaldo S. BMGE (block mapping and gathering with entropy): a new software for selection of phylogenetic informative regions from multiple sequence alignments. BMC Evol Biol. 2010;10:210.
Nguyen L-T, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ. IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32:268–74.
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods. 2017;14:587–9.
Stolzer M, Lai H, Xu M, Sathaye D, Vernot B, Durand D. Inferring duplications, losses, transfers and incomplete lineage sorting with nonbinary species trees. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:i409–15.
Koziaeva VV, Dziuba MV, Ivanov TM, Kuznetsov BB, Skryabin KG, Grouzdev DS. Draft Genome Sequences of Two Magnetotactic Bacteria, Magnetospirillum moscoviense BB-1 and Magnetospirillum marisnigri SP-1. Genome Announc. 2016;4:e00814–16.
Uebe R, Voigt B, Schweder T, Albrecht D, Katzmann E, Lang C, et al. Deletion of a fur-like gene affects iron homeostasis and magnetosome formation in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. J Bacteriol. 2010;192:4192–204.
Guglielmini J, Néron B, Abby SS, Garcillán-Barcia MP, de la Cruz F, Rocha EPC. Key components of the eight classes of type IV secretion systems involved in bacterial conjugation or protein secretion. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:5715–27.
Cury J, Touchon M, Rocha EPC. Integrative and conjugative elements and their hosts: composition, distribution and organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:8943–56.
Scheffel A, Gruska M, Faivre D, Linaroudis A, Plitzko JM, Schüler D. An acidic protein aligns magnetosomes along a filamentous structure in magnetotactic bacteria. Nature. 2006;440:110–4.
Murat D, Quinlan A, Vali H, Komeili A. Comprehensive genetic dissection of the magnetosome gene island reveals the step-wise assembly of a prokaryotic organelle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:5593–8.
Chen K, Durand D, Farach-Colton M. NOTUNG: a program for dating gene duplications and optimizing gene family trees. J Comput Biol J Comput Mol Cell Biol. 2000;7:429–47.
Boratyński Z, Brito JC, Campos JC, Cunha JL, Granjon L, Mappes T, et al. Repeated evolution of camouflage in speciose desert rodents. Sci Rep. 2017;7:3522.
Bennet M, McCarthy A, Fix D, Edwards MR, Repp F, Vach P, et al. Influence of magnetic fields on magneto-aerotaxis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e101150.
Wang K, Ge X, Bo T, Chen Q, Chen G, Liu W. Interruption of the denitrification pathway influences cell growth and magnetosome formation in Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2011;53:55–62.
Li Y, Katzmann E, Borg S, Schüler D. The periplasmic nitrate reductase Nap is required for anaerobic growth and involved in redox control of magnetite biomineralization in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:4847–56.
Li Y, Raschdorf O, Silva KT, Schüler D. The terminal oxidase cbb3 functions in redox control of magnetite biomineralization in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. J Bacteriol. 2014;196:2552–62.
Li Y, Sabaty M, Borg S, Silva KT, Pignol D, Schüler D. The oxygen sensor MgFnr controls magnetite biomineralization by regulation of denitrification in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. BMC Microbiol. 2014;14:153.
Cohan FM, Koeppel AF. The origins of ecological diversity in prokaryotes. Curr Biol. 2008;18:R1024–34.
Kolinko I, Lohße A, Borg S, Raschdorf O, Jogler C, Tu Q, et al. Biosynthesis of magnetic nanostructures in a foreign organism by transfer of bacterial magnetosome gene clusters. Nat Nanotechnol. 2014;9:193–7.
Schübbe S, Kube M, Scheffel A, Wawer C, Heyen U, Meyerdierks A, et al. Characterization of a spontaneous nonmagnetic mutant of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense reveals a large deletion comprising a putative magnetosome island. J Bacteriol. 2003;185:5779–90.
Rioux J-B, Philippe N, Pereira S, Pignol D, Wu L-F, Ginet N. A second actin-like MamK protein in Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1 encoded outside the genomic magnetosome island. PloS One. 2010;5:e9151.
Abreu N, Mannoubi S, Ozyamak E, Pignol D, Ginet N, Komeili A. Interplay between two bacterial actin homologs, MamK and MamK-Like, is required for the alignment of magnetosome organelles in Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1. J Bacteriol. 2014;196:3111–21.
Brune A, Frenzel P, Cypionka H. Life at the oxic-anoxic interface: microbial activities and adaptations. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2000;24:691–710.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by projects from the French National Research Agency (ANR Tremplin-ERC: ANR-16-TERC-0025-01 and ANR PRC: ANR-18-CE31-0003). Genome sequencing was funded thanks to the Appel à Projets en Génomique Environnementale—CNRS (DJ/ST/IP/2013/D-112). We are grateful to the INRA MIGALE bioinformatics platform (http://migale.jouy.inra.fr) for providing computational resources. We acknowledge the Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN) at CEA Cadarache for the access of the transmission electron microscope Tecnai G2 BioTWIN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteil, C.L., Grouzdev, D.S., Perrière, G. et al. Repeated horizontal gene transfers triggered parallel evolution of magnetotaxis in two evolutionary divergent lineages of magnetotactic bacteria. ISME J 14, 1783–1794 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0647-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0647-x
This article is cited by
-
Biosynthesis and function of magnetic organelles in magnetotactic bacteria
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2025)
-
Silent gene clusters encode magnetic organelle biosynthesis in a non-magnetotactic phototrophic bacterium
The ISME Journal (2023)
-
McaA and McaB control the dynamic positioning of a bacterial magnetic organelle
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Magnetotactic bacteria and magnetofossils: ecology, evolution and environmental implications
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes (2022)