Abstract
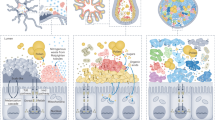
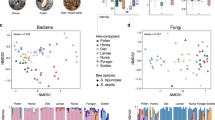
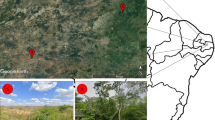
Animal-microbe symbioses are often stable for millions of years. An example is the clade consisting of social corbiculate bees—honeybees, bumblebees, and stingless bees—in which a shared ancestor acquired specialized gut bacteria that subsequently diversified with hosts. This model may be incomplete, however, as few microbiomes have been characterized for stingless bees, which are diverse and ecologically dominant pollinators in the tropics. We surveyed gut microbiomes of Brazilian stingless bees, focusing on the genus Melipona, for which we sampled multiple species and biomes. Strikingly, Melipona lacks Snodgrassella and Gilliamella, bacterial symbionts ubiquitous in other social corbiculate bees. Instead, Melipona species harbor more environmental bacteria and bee-specific Starmerella yeasts. Loss of Snodgrassella and Gilliamella may stem from ecological shifts in Melipona or the acquisition of new symbionts as functional replacements. Our findings demonstrate the value of broadly sampling microbiome biodiversity and show that even ancient symbioses can be lost.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Moran NA, McCutcheon JP, Nakabachi A. Genomics and evolution of heritable bacterial symbionts. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:165–90.
Bourguignon T, Lo N, Dietrich C, Roisin Y, Brune A, Evans TA, et al. Rampant host switching shaped the termite gut microbiome. Curr Biol. 2018;28:649–54.
Matsuura Y, Moriyama M, Łukasik P, Vanderpool D, Tanahashi M, Meng X. Recurrent symbiont recruitment from fungal parasites in cicadas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E5970–9.
Chong RA, Moran NA. Evolutionary loss and replacement of Buchnera, the obligate endosymbiont of aphids. ISME J. 2018;12:898–908.
Bennett GM, Moran NA. Heritable symbiosis: the advantages and perils of an evolutionary rabbit hole. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:10169–76.
Sudakaran S, Kost C, Kaltenpoth M. Symbiont acquisition and replacement as a source of ecological innovation. Trends Microbiol. 2017;25:1–16.
Martinson VG, Danforth BN, Minckley RL, Rueppell O, Tingek S, Moran NA. A simple and distinctive microbiota associated with honey bees and bumble bees. Mol Ecol. 2011;20:619–28.
Kwong WK, Medina LA, Koch H, Sing KW, Soh EJY, Ascher JS, et al. Dynamic microbiome evolution in social bees. Sci Adv. 2017;3:1–17.
Kwong WK, Moran NA. Gut microbial communities of social bees. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14:374–84.
Rothman JA, Leger L, Graystock P, Russell K, McFrederick QS. The bumble bee microbiome increases survival of bees exposed to selenate toxicity. Environ Microbiol. 2019;21:3417–29.
Koch H, Schmid-Hempel P. Socially transmitted gut microbiota protect bumble bees against an intestinal parasite. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:19288–92.
Zheng H, Powell JE, Steele MI, Dietrich C, Moran NA. Honeybee gut microbiota promotes host weight gain via bacterial metabolism and hormonal signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:4775–80.
Mockler BK, Kwong WK, Moran NA, Koch H. Microbiome structure influences infection by the parasite Crithidia bombi in bumble bees. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018;84:1–11.
Giannini TCG, Boff S, Cordeiro GD, Cartonalo EA Jr, Veiga AK, Imperatriz-Fonseca VL, et al. Crop pollinators in Brazil: a review of reported interactions. Apidologie. 2015;46:209–23.
Koch H, Abrol DP, Li J, Schmid-Hempel P. Diversity and evolutionary patterns of bacterial gut associates of corbiculate bees. Mol Ecol. 2013;22:2028–44.
Leonhardt SD, Kaltenpoth M. Microbial communities of three sympatric Australian stingless bee species. PLoS One. 2014;9:1–6.
Díaz S, de Souza Urbano S, Caesar L, Blochtein B, Sattler A, Zuge V, et al. Report on the microbiota of Melipona quadrifasciata affected by a recurrent disease. J Invertebr Pathol. 2017;143:35–39.
Teixeira ACP, Marini MM, Nicoli JR, Antonini Y, Martins RP, Lachance M-A, et al. Starmerella meliponinorum sp. nov., a novel ascomycetous yeast species associated with stingless bees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003;53:339–43.
Paludo CR, Menezes C, Silva-Junior EA, Vollet-Neto A, Andrade-Dominguez A, Pishchany G, et al. Stingless bee larvae require fungal steroid to pupate. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1–10.
Ramírez SR, Nieh JC, Quental TB, Roubik DW, Imperatriz-Fonseca VL, Pierce NE. A molecular phylogeny of the stingless bee genus Melipona (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2010;56:519–25.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the UFV, the financial support from CNPq, CAPES – Finance Code 001 and FAPEMIG, a USDA NIFA postdoctoral fellowship (2018-08156) to TJH, and NIH award R35GM131738 to NAM. We thank Marina Cunha, Gil Viana, José Souza, Eduardo Ferreira, Leandro Campos, Marcelo Silva, Antônio Alves, Sidcley de Lucena, Flávio Yamamoto, Hilton Gomes, Kalhil França, Gilvan Santos and Helder Resende for providing bees, and Fernando da Silveira for Amazonian bees identification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cerqueira, A.E.S., Hammer, T.J., Moran, N.A. et al. Extinction of anciently associated gut bacterial symbionts in a clade of stingless bees. ISME J 15, 2813–2816 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01000-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01000-1
This article is cited by
-
Spatial segregation and cross-kingdom interactions drive stingless bee hive microbiome assembly
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Evolution of gut microbiota across honeybee species revealed by comparative metagenomics
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Effects of live yeasts and their metabolic products on bumble bee microcolony development
Apidologie (2025)
-
The honeybee microbiota and its impact on health and disease
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2024)
-
Neotropical bee microbiomes point to a fragmented social core and strong species-level effects
Microbiome (2023)