Abstract
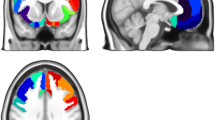
Previous work suggests people with anorexia nervosa (AN) display reduced facial expression of emotion. This may influence illness progression as blunted emotional reactions can negatively impact social relationships and increase isolation. The present study aimed to replicate and further build on previous findings by examining facial and brain responses to naturalistic, emotional films. In total, 141 women (71 AN/weight restored AN, 70 healthy comparison) completed two tasks in a fixed order: 1.) facial affect task and 2.) functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) task. In both tasks, participants reacted to positive, neutral, and negative films, and rated their mood after each one. The effects of group and film category on facial expressions, brain responses, and mood ratings were examined. The AN group displayed reduced positive facial affect over time and lower self-reported mood in response to positive but not negative or neutral films. The fMRI task revealed no significant group differences in response to positive, neutral, or negative films. However, there was widespread activation of occipital, parietal, temporal, and frontal regions in response to the emotional films across groups. The behavioural findings replicate previously reported altered reactivity to positive films in AN. Additionally, task-related brain activation was observed in regions typically associated with the processing of naturalistic emotional stimuli, suggesting the task was valid. However, the lack of group differences during the fMRI task raises questions about whether the behavioural differences could be related to slower warming up to the task among those with AN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. 2013.
Fairburn CG, Cooper Z, Shafran R. Cognitive behaviour therapy for eating disorders: a “transdiagnostic” theory and treatment. Behav Res Ther. 2003;41:509–28.
Rieger E, Van Buren DJ, Bishop M, Tanofsky-Kraff M, Welch R, Wilfley DE. An eating disorder-specific model of interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT-ED): Causal pathways and treatment implications. Clin Psychol Rev. 2010;30:400–10.
Treasure J, Schmidt U. The cognitive-interpersonal maintenance model of anorexia nervosa revisited: a summary of the evidence for cognitive, socio-emotional and interpersonal predisposing and perpetuating factors. J Eat Disord. 2013;1:13.
Davies H, Wolz I, Leppanen J, Fernandez-Aranda F, Schmidt U, Tchanturia K. Facial expression to emotional stimuli in non-psychotic disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;64:252–71.
Leppanen J, Dapelo MM, Davies H, Lang K, Treasure J, Tchanturia K. Computerised analysis of facial emotion expression in eating disorders. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0178972.
Brockmeyer T, Pellegrino J, Maier C, Münch HM, Harmer CJ, Walther S, et al. Blunted emotion-modulated startle reflex in anorexia nervosa. International Journal of Eating Disorders. 2019;52:270–7.
Lang K, Larsson EEC, Mavromara L, Simic M, Treasure J, Tchanturia K. Diminished facial emotion expression and associated clinical characteristics in Anorexia Nervosa. Psychiatry Res. 2016;236:165–72.
Dapelo MM, Hart S, Hale C, Morris R, Tchanturia K. Expression of positive emotions differs in illness and recovery in anorexia nervosa. Psychiatry Res. 2016;246:48–51.
Schneider KG, Hempel RJ, Lynch TR. That “poker face” just might lose you the game! The impact of expressive suppression and mimicry on sensitivity to facial expressions of emotion. Emotion. 2013;13:852–66.
McAdams CJ, Efseroff B, McCoy J, Ford L, Timko CA. Social processing in eating disorders: neuroimaging paradigms and research domain organizational constructs. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022;24:777–88.
Zhong S, Su T, Gong J, Huang L, Wang Y. Brain functional alterations in patients with anorexia nervosa: A meta-analysis of task-based functional MRI studies. Psychiatry Res. 2023;327:115358.
Saarimäki H. Naturalistic stimuli in affective neuroimaging: a review. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021;15:675068.
Zaki J, Ochsner K. The need for a cognitive neuroscience of naturalistic social cognition. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1167:16–30.
Saarimäki H, Nummenmaa L, Volynets S, Santavirta S, Aksiuto A, Sams M, et al. Cerebral topographies of perceived and felt emotions. Imaging Neuroscience. 2025;3:imag_a_00517.
Redcay E, Moraczewski D. Social cognition in context: A naturalistic imaging approach. Neuroimage. 2020;216:116392.
Leppanen J, Tosunlar L, Blackburn R, Williams S, Tchanturia K, Sedgewick F. Critical incidents in anorexia nervosa: perspectives of those with a lived experience. J Eat Disord. 2021;9:53.
Leppanen J, Patsalos O, Surguladze S, Kerr-Gaffney J, Williams S, Tchanturia K. Evaluation of film stimuli for the assessment of social-emotional processing: a pilot study. PeerJ. 2022;10:e14160.
First MB, Williams JBW, Karg RS, Spitzer RL Structured clinical Interview for DSM-5—research version. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2015.
Fairburn CG, Beglin SJ. Assessment of eating disorders: interview or self-report questionnaire?. Int J Eat Disord. 1994;16:363–70.
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983;67:361–70.
Betella A, Verschure PFMJ. The affective slider: a digital self-assessment scale for the measurement of human emotions. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0148037.
Baltrusaitis T, Zadeh A, Lim YC, Morency L-P. OpenFace 2.0: facial behavior analysis toolkit. 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), 2018. p. 59–66.
Wood E, Baltruaitis T, Zhang X, Sugano Y, Robinson P, Bulling A. Rendering of eyes for eye-shape registration and gaze estimation. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015. p. 3756–64.
Barrett LF, Adolphs R, Marsella S, Martinez AM, Pollak SD. Emotional expressions reconsidered: challenges to inferring emotion from human facial movements. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2019;20:1–68.
Küntzler T, Höfling TTA, Alpers GW. Automatic facial expression recognition in standardized and non-standardized emotional expressions. Front Psychol. 2021;12:627561.
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. 2021.
Wood SN. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. 2011;73:3–36.
Wood SN, Pya N, Säfken B. Smoothing parameter and model selection for general smooth models. J Am Stat Assoc. 2016;111:1548–63.
Wood SN. Thin plate regression splines. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. 2003;65:95–114.
Brooks ME, Kristensen K, Benthem KJvan, Magnusson A, Berg CW, Nielsen A, et al. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. The R Journal. 2017;9:378–400.
McGillycuddy M, Popovic G, Bolker BM, Warton DI. Parsimoniously fitting large multivariate random effects in glmmTMB. J Stat Softw. 2025;112:1–19.
Esteban O, Birman D, Schaer M, Koyejo OO, Poldrack RA, Gorgolewski KJ. MRIQC: Advancing the automatic prediction of image quality in MRI from unseen sites. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0184661.
Esteban O, Markiewicz CJ, Blair RW, Moodie CA, Isik AI, Erramuzpe A, et al. fMRIPrep: a robust preprocessing pipeline for functional MRI. Nat Methods. 2019;16:111–6.
Esteban O, Ciric R, Finc K, Blair RW, Markiewicz CJ, Moodie CA, et al. Analysis of task-based functional MRI data preprocessed with fMRIPrep. Nat Protoc. 2020;15:2186–202.
Nilearn contributors. Nilearn. 2024.
Lindquist MA, Wager TD. Validity and power in hemodynamic response modeling: a comparison study and a new approach. Hum Brain Mapp. 2007;28:764–84.
Mackes NK, Golm D, O’Daly OG, Sarkar S, Sonuga-Barke EJS, Fairchild G, et al. Tracking emotions in the brain – revisiting the empathic accuracy task. Neuroimage. 2018;178:677–86.
Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Pedregosa F, Michel V, Thirion B. Multi-subject dictionary learning to segment an atlas of brain spontaneous activity. In: Székely G, Hahn HK, editors. Information Processing in Medical Imaging, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2011. p. 562-73.
Lyons T. Rough paths, Signatures and the modelling of functions on streams. 2014.
Morrill J, Fermanian A, Kidger P, Lyons T. A Generalised Signature Method for Multivariate Time Series Feature Extraction. 2021.
Moore PJ, Lyons TJ, Gallacher J. Initiative for the ADN. Using path signatures to predict a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0222212.
Cheng J, Zhang X, Ni H, Li C, Xu X, Wu Z, et al. Path signature neural network of cortical features for prediction of infant cognitive scores. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2022;41:1665–76.
Baryshnikov Y, Schlafly E. Cyclicity in multivariate time series and applications to functional MRI data. 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), 2016. p. 1625-30.
Winkler AM, Ridgway GR, Webster MA, Smith SM, Nichols TE. Permutation inference for the general linear model. Neuroimage. 2014;92:381–97.
Davies H, Schmidt U, Stahl D, Tchanturia K. Evoked facial emotional expression and emotional experience in people with anorexia nervosa. International Journal of Eating Disorders. 2011;44:531–9.
Davies H, Schmidt U, Tchanturia K. Emotional facial expression in women recovered from anorexia nervosa. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:291.
Arioli M, Cattaneo Z, Parimbelli S, Canessa N. Relational vs representational social cognitive processing: a coordinate-based meta-analysis of neuroimaging data. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2023;18:nsad003.
Diveica V, Koldewyn K, Binney RJ. Establishing a role of the semantic control network in social cognitive processing: A meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage. 2021;245:118702.
Carfagno M, Barone E, Arsenio E, Bello R, Marone L, Volpicelli A, et al. Mediation role of interpersonal problems between insecure attachment and eating disorder psychopathology. Eat Weight Disord. 2024;29:43.
Sternheim LC, Bijsterbosch JM, Wever MCM, van Elburg AA, Frank GKW. Examining anxious temperament in anorexia nervosa: Behavioural inhibition and intolerance of uncertainty and their contribution to trait anxiety in adolescents with anorexia nervosa. J Affect Disord. 2024;348:116–23.
Winecoff AA, Ngo L, Moskovich A, Merwin R, Zucker N. The functional significance of shyness in anorexia nervosa. European Eating Disorders Review. 2015;23:327–32.
Harrison A. Experimental investigation of non-verbal communication in eating disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2021;297:113732.
D’Agata F, Caroppo P, Spalatro A, Lavagnino L, Daga GA, Boghi A, et al. Emotional imagination of negative situations: Functional neuroimaging in anorexia and bulimia. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0231684.
Halls D, Leslie M, Leppanen J, Sedgewick F, Surguladze S, Fonville L, et al. The emotional face of anorexia nervosa: the neural correlates of emotional processing. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021;42:3077–87.
Leslie M, Halls D, Leppanen J, Sedgewick F, Smith K, Hayward H, et al. Neural correlates of theory of mind are preserved in young women with anorexia nervosa. Front Psychol. 2020;11:568073.
Stanetzky L, Hartz A, Buettgen K, Dahmen B, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Konrad K, et al. Longitudinal changes in neural responses to fearful faces in adolescents with anorexia nervosa – A fMRI study. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging. 2024;345:111904.
Cardi V, Corfield F, Leppanen J, Rhind C, Deriziotis S, Hadjimichalis A, et al. Emotional processing of infants displays in eating disorders. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e113191.
Rhind C, Mandy W, Treasure J, Tchanturia K. An exploratory study of evoked facial affect in adolescent females with anorexia nervosa. Psychiatry Res. 2014;220:711–5.
Russell JA. Core affect and the psychological construction of emotion. Psychol Rev. 2003;110:145–72.
Rowlands K, Beaty T, Simic M, Grafton B, Hirsch C, Treasure J, et al. Cognitive bias modification training of attention and interpretation to reduce expectations of social rejection in adolescents with eating disorders: A small efficacy randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Eating Disorders. 2022;55:1506–20.
Korn J, Dietel FA, Hartmann AS. Testing the specificity of interpretation biases in women with eating disorder symptoms: An online experimental assessment. International Journal of Eating Disorders. 2020;53:372–82.
Lukas L, Nuding L, Schulte-Körne G, Platt B, Sfärlea A. Seeing oneself as an unattractive loser: Similar interpretation and memory biases in adolescents with anorexia nervosa and adolescents with depression or anxiety. European Eating Disorders Review. 2024;32:855–68.
Treasure J, Willmott D, Ambwani S, Cardi V, Clark Bryan D, Rowlands K, et al. Cognitive interpersonal model for anorexia nervosa revisited: the perpetuating factors that contribute to the development of the severe and enduring illness. J Clin Med. 2020;9:630.
Baker DH, Vilidaite G, Lygo FA, Smith AK, Flack TR, Gouws AD, et al. Power contours: optimising sample size and precision in experimental psychology and human neuroscience. Psychol Methods. 2021;26:295–314.
Bailey LM, McMillan LE, Newman AJ. A sinister subject: Quantifying handedness-based recruitment biases in current neuroimaging research. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2020;51:1642–56.
Brown TA, Keel PK. Eating disorders in boys and men. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2023;19:177–205.
Heiden-Rootes K, Linsenmeyer W, Levine S, Oliveras M, Joseph M. A scoping review of the research literature on eating and body image for transgender and nonbinary adults. J Eat Disord. 2023;11:111.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded in part by the Wellcome Trust [213578/Z/18/Z]. This research was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre (BRC). KA is supported by the Medical Research Council grant no. MR/X030539/1 and the Medical Research Council/Arts and Humanities Research Council/Economic and Social Research Council Adolescence, Mental Health and the Developing Mind initiative as part of the EDIFY programme (grant no. MR/W002418/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL, KT, and SW contributed to Conceptualization. JL, KT, and KA contributed to Funding acquisition. OB, DH, KA, KT, and SW provided Resources. KT and SW provided Supervision. JL contributed to Investigation. JL and DH contributed to Formal analysis. JL Wrote the original draft. JL, OB, DH, KA, KT, and SW contributed to Writing – reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Leppanen, J., Bailey, O., Halls, D. et al. Evoked emotions in anorexia nervosa: neural and behavioural correlates of social-emotional processing. Transl Psychiatry (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-026-03819-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-026-03819-8