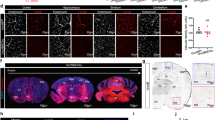
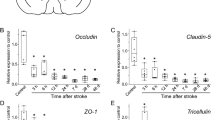
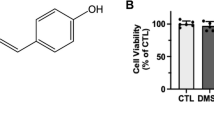
Abstract
Blood-brain barrier compromise represents a pivotal pathological mechanism in ischemic stroke, driving neurological deterioration. Netrin-5, an axon guidance protein family member, demonstrates regulatory potential for BBB integrity. Employing middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice and oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVECs), we found that Netrin-5 was significantly downregulated in the murine cortex post-MCAO and was also downregulated in HBMVECs upon OGD/R exposure. Adenoviral Netrin-5 delivery in MCAO mice attenuated cerebral infarction, improved functional outcomes, reduced edema, and preserved BBB integrity, evidenced by diminished Evans blue extravasation and albumin leakage. Furthermore, Netrin-5 restored tight junction protein ZO-1 expression and activated Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling. In HBMVECs, Netrin-5 overexpression counteracted OGD/R-induced endothelial permeability, elevated transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER), and increased ZO-1, Wnt3a, and β-catenin levels. Critically, Wnt3a knockdown abrogated these protective effects, establishing Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling as indispensable for Netrin-5-mediated BBB preservation. In contrast, knockdown of Netrin-5 exacerbated BBB disruption in MCAO mice and increased endothelial permeability in HBMVECs. These results position Netrin-5 as a potential therapeutic intervention for ischemic stroke.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Jin F, Jin L, Wei B, Li X, Li R, Liu W, et al. miR-96-5p alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by inhibiting pyroptosis via downregulating caspase 1. Exp Neurol. 2024;374:114676.
Ghori A, Prinz V, Nieminen-Kehlä M, Bayerl SH, Kremenetskaia I, Riecke J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor augments the tolerance towards cerebral stroke by enhancing neurovascular repair mechanism. Transl stroke Res. 2022;13:774–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-022-00991-z.
Li J, Liu Y, Zhang X, Chen R, Zhang L, Xue J, et al. Dl-3-N-Butylphthalide alleviates the blood-brain barrier permeability of focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion in mice. Neuroscience. 2019;413:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.06.020.
Sobral AF, Costa I, Teixeira V, Silva R, Barbosa DJ. Molecular motors in blood-brain barrier maintenance by astrocytes. Brain Sci. 2025;15:279. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030279.
Paraiso HC, Wang X, Kuo PC, Furnas D, Scofield BA, Chang FL, et al. Isolation of mouse cerebral microvasculature for molecular and single-cell analysis. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:84. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00084.
Alluri H, Peddaboina CS, Tharakan B. Evaluation of tight junction integrity in brain endothelial cells using confocal microscopy. Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2711:257–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3429-5_21.
Choi KH, Kim HS, Park MS, Kim JT, Kim JH, Cho KA, et al. Regulation of Caveolin-1 expression determines early brain edema after experimental focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2016;47:1336–43. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.116.013205.
Weber RZ, Grönnert L, Mulders G, Maurer MA, Tackenberg C, Schwab ME, et al. Characterization of the blood brain barrier disruption in the photothrombotic stroke model. Front Physiol. 2020;11:586226. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.586226.
Chen XY, Wan SF, Yao NN, Lin ZJ, Mao YG, Yu XH, et al. Inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 ameliorates ischemia/hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier injury through the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Military Med Res. 2021;8:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-021-00356-x.
Sebo DJ, Ali I, Fetsko AR, Trimbach AA, Taylor MR. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin in neural progenitor cells regulates blood-brain barrier development and promotes neuroinflammation. Sci Rep. 2025;15:3496. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-85784-8.
Cottarelli A, Corada M, Beznoussenko GV, Mironov AA, Globisch MA, Biswas S, et al. Fgfbp1 promotes blood-brain barrier development by regulating collagen IV deposition and maintaining Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Development. 2020;147:dev185140. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.185140.
Gu X, Dong M, Xia S, Li H, Bao X, Cao X, et al. γ-Glutamylcysteine ameliorates blood-brain barrier permeability and neutrophil extracellular traps formation after ischemic stroke by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signalling in mice. Eur J pharmacology. 2024;969:176409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176409.
Garrett AM, Jucius TJ, Sigaud LP, Tang FL, Xiong WC, Ackerman SL, et al. Analysis of expression pattern and genetic deletion of netrin5 in the developing mouse. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016;9:3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2016.00003.
Ziegon L, Schlegel M. Netrin-1: a modulator of macrophage driven acute and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23:275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010275.
Claro V, Ferro A. Netrin-1: Focus on its role in cardiovascular physiology and atherosclerosis. JRSM cardiovascular Dis. 2020;9:2048004020959574. https://doi.org/10.1177/2048004020959574.
Xia X, Hu Z, Wang S, Yin K. Netrin-1: an emerging player in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine growth factor Rev. 2022;64:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2022.01.003.
Li Y, Liu C, Chen Z, Lin H, Li X. Netrin-1 protects blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion by activating the Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2)/occludin pathway. J biochemical Mol Toxicol. 2024;38:e23623. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.23623.
Fan Y, Shen F, Chen Y, Hao Q, Liu W, Su H, et al. Overexpression of netrin-1 induces neovascularization in the adult mouse brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008;28:1543–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2008.39.
Larrieu-Lahargue F, Welm AL, Thomas KR, Li DY. Netrin-4 induces lymphangiogenesis in vivo. Blood. 2010;115:5418–26. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-11-252338.
Chen YC, Zhu GY, Wang X, Shi L, Du TT, Liu DF, et al. Anterior thalamic nuclei deep brain stimulation reduces disruption of the blood-brain barrier, albumin extravasation, inflammation and apoptosis in kainic acid-induced epileptic rats. Neurological Res. 2017;39:1103–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2017.1379241.
Li C, Zhang S, Jiang X, Li Z, Zhang Y, Li X, et al. Human albumin aggravates cerebral edema by disrupting the blood‑brain barrier in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Acta neurobiologiae experimentalis. 2022;82:284–94. https://doi.org/10.55782/ane-2022-027.
Eiselein L, Wilson DW, Lamé MW, Rutledge JC. Lipolysis products from triglyceride-rich lipoproteins increase endothelial permeability, perturb zonula occludens-1 and F-actin, and induce apoptosis. Am J Physiol Heart circulatory Physiol. 2007;292:H2745–53. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00686.2006.
Guo Q, Wang J. Telmisartan ameliorates hypertension-induced kidney damage by restoring glomerular endothelial barrier function. J biochemical Mol Toxicol. 2025;39:e70377. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.70377.
Southgate TD, Kingston PA, Castro MG. Gene transfer into neural cells in vitro using adenoviral vectors. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2001;Chapter 4:Unit 4.23. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142301.ns0423s13.
Luo Y, Liao S, Yu J. Netrin-1 in post-stroke neuroprotection: beyond axon guidance cue. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20:1879–87. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159x20666220302150723.
Tu T, Zhang C, Yan H, Luo Y, Kong R, Wen P, et al. CD146 acts as a novel receptor for netrin-1 in promoting angiogenesis and vascular development. Cell Res. 2015;25:275–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.15.
Zhang H, Du D, Gao X, Tian X, Xu Y, Wang B, et al. PFT-α protects the blood-brain barrier through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway after acute ischemic stroke. Funct Integr genomics. 2023;23:314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01237-3.
Basu S, Ellinger B, Rizzo S, Deraeve C, Schürmann M, Preut H, et al. Biology-oriented synthesis of a natural-product inspired oxepane collection yields a small-molecule activator of the Wnt-pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:6805–10. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1015269108.
Blagodatski A, Klimenko A, Jia L, Katanaev VL. Small molecule wnt pathway modulators from natural sources: history, state of the art and perspectives. Cells. 2020;9:589. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030589.
Chen SD, Lee JM, Yang DI, Nassief A, Hsu CY. Combination therapy for ischemic stroke: potential of neuroprotectants plus thrombolytics. Am J cardiovascular drugs. 2002;2:303–13. https://doi.org/10.2165/00129784-200202050-00003.
Mittmann N, Seung SJ, Hill MD, Phillips SJ, Hachinski V, Coté R, et al. Impact of disability status on ischemic stroke costs in Canada in the first year. Can J neurological Sci Le J canadien des Sci neurologiques. 2012;39:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0317167100015638.
Sieminski M, Reimus M, Kałas M, Stępniewska E. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of melatonin in secondary traumatic brain injury. Antioxidants. 2024;14:25. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010025.
Keleman K, Dickson BJ. Short- and long-range repulsion by the drosophila Unc5 netrin receptor. Neuron. 2001;32:605–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00505-0.
Gopal AA, Rappaz B, Rouger V, Martyn IB, Dahlberg PD, Meland RJ, et al. Netrin-1-Regulated Distribution of UNC5B and DCC in Live Cells Revealed by TICCS. Biophysical J. 2016;110:623–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2015.12.022.
Krolak T, Chan KY, Kaplan L, Huang Q, Wu J, Zheng Q, et al. A high-efficiency AAV for endothelial cell transduction throughout the central nervous system. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022;1:389–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44161-022-00046-4.
Zheng T, Shi Y, Zhang J, Peng J, Zhang X, Chen K, et al. MiR-130a exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemic stroke through PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy. 2019;117:109117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109117.
Fluri F, Schuhmann MK, Kleinschnitz C. Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:3445–54. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S56071.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by “National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program) (82372825)”.
Funding
This study was supported by “National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program) (82372825)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. C. and L.G.C. conceived and designed the study. Y.C., L.L., Y.M., and L.P. performed the investigation. Y.C. and L.G.C. wrote the manuscript. All authors critically reviewed and approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declair no competing intrests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Liu, L., Ming, Y. et al. Netrin-5 Preserves Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity via Wnt3a/β-Catenin Pathway Activation in Murine Cerebral Ischemia. Transl Psychiatry (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-026-03903-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-026-03903-z