Abstract
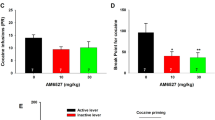
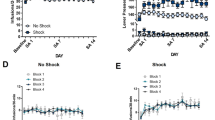
Cannabinoid CB1 receptors (CB1Rs) have been shown to be a promising target in medication development for the treatment of addiction. However, clinical trials with SR141716A (rimonabant, a selective CB1R antagonist/inverse agonist) for the treatment of obesity and smoking cessation failed due to unwanted side effects, such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal tendencies. Recent preclinical studies suggest that the neutral CB1R antagonist AM4113 may retain the therapeutic anti-addictive effects of SR141716A in nicotine self-administration models and possibly has fewer unwanted side effects. However, little is known about whether AM4113 is also effective for other drugs of abuse, such as opioids and psychostimulants, and whether it produces depressive side effects similar to SR141716A in experimental animals. In this study, we demonstrated that systemic administration of AM4113 (3 and 10 mg/kg) dose-dependently inhibited the self-administration of intravenous heroin but not cocaine or methamphetamine, whereas SR141716A (3 and 10 mg/kg) dose-dependently inhibited the self-administration of heroin and methamphetamine but not cocaine. In the electrical brain-stimulation reward (BSR) paradigm, SR141716A (3 and 10 mg/kg) dose-dependently increased the BSR stimulation threshold (i.e., decreased the stimulation reward), but AM4113 had no effect on BSR at the same doses, suggesting that SR141716A may produce aversive effects while AM4113 may not. Together, these findings show that neutral CB1R antagonists such as AM4113 deserve further research as a new class of CB1R-based medications for the treatment of opioid addiction without SR141716A-like aversive effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Brady JE, Li G. Prevalence of alcohol and other drugs in fatally injured drivers. Addiction. 2013;108:104–14.
Naim-Feil J, Zangen A. Addiction. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;116:613–30.
Jing L, Qiu Y, Zhang Y, Li JX. Effects of the cannabinoid CB(1) receptor allosteric modulator ORG 27569 on reinstatement of cocaine- and methamphetamine-seeking behavior in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;143:251–6.
Robson PJ. Therapeutic potential of cannabinoid medicines. Drug Test Anal. 2014;6:24–30.
Xi ZX, Peng XQ, Li X, Song R, Zhang HY, Liu QR, et al. Brain cannabinoid CB(2) receptors modulate cocaine’s actions in mice. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:1160–6.
Wiskerke J, Pattij T, Schoffelmeer AN, De Vries TJ. The role of CB1 receptors in psychostimulant addiction. Addict Biol. 2008;13:225–38.
Zhang HY, Gao M, Liu QR, Bi GH, Li X, Yang HJ, et al. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors modulate midbrain dopamine neuronal activity and dopamine-related behavior in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E5007–15.
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Little MD, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, et al. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87:1932–6.
Mailleux P, Vanderhaeghen JJ. Distribution of neuronal cannabinoid receptor in the adult rat brain: a comparative receptor binding radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience. 1992;48:655–68.
Chen J, Paredes W, Lowinson JH, Gardner EL. Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol enhances presynaptic dopamine efflux in medial prefrontal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;190:259–62.
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Di Chiara G. Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common mu1 opioid receptor mechanism. Science. 1997;276:2048–50.
Oleson EB, Cheer JF. A brain on cannabinoids: the role of dopamine release in reward seeking. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2: pii:a012229.
Lupica CR, Riegel AC. Endocannabinoid release from midbrain dopamine neurons: a potential substrate for cannabinoid receptor antagonist treatment of addiction. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48:1105–16.
Le Foll B, Gorelick DA, Goldberg SR. The future of endocannabinoid-oriented clinical research after CB1 antagonists. Psychopharmacology. 2009;205:171–4.
Gamaleddin IH, Trigo JM, Gueye AB, Zvonok A, Makriyannis A, Goldberg SR, et al. Role of the endogenous cannabinoid system in nicotine addiction: novel insights. Front Psychiatry. 2015;6:41.
Le Foll B, Goldberg SR. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists as promising new medications for drug dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;312:875–83.
Xi ZX, Spiller K, Pak AC, Gilbert J, Dillon C, Li X, et al. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists attenuate cocaine’s rewarding effects: experiments with self-administration and brain-stimulation reward in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:1735–45.
Navarro M, Carrera MR, Fratta W, Valverde O, Cossu G, Fattore L, et al. Functional interaction between opioid and cannabinoid receptors in drug self-administration. J Neurosci. 2001;21:5344–50.
Caille S, Parsons LH. Cannabinoid modulation of opiate reinforcement through the ventral striatopallidal pathway. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:804–13.
Caille S, Parsons LH. SR141716A reduces the reinforcing properties of heroin but not heroin-induced increases in nucleus accumbens dopamine in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:3145–9.
Navarro M, Carrera MR, Del Arco I, Trigo JM, Koob GF, Rodríguez de Fonseca F. Cannabinoid receptor antagonist reduces heroin self-administration only in dependent rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;501:235–7.
Schindler CW, Panlilio LV, Gilman JP, Justinova Z, Vemuri VK, Makriyannis A, et al. Effects of cannabinoid receptor antagonists on maintenance and reinstatement of methamphetamine self-administration in rhesus monkeys. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;633:44–9.
Cahill K, Ussher MH. Cannabinoid type 1 receptor antagonists for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;16:CD005353.
De Vries TJ, Homberg JR, Binnekade R, Raaso H, Schoffelmeer AN. Cannabinoid modulation of the reinforcing and motivational properties of heroin and heroin-associated cues in rats. Psychopharmacology. 2003;168:164–9.
Chaperon F, Soubrie P, Puech AJ, Thiebot MH. Involvement of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors in the establishment of place conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology. 1998;135:324–32.
De Vries TJ, Shaham Y, Homberg JR, Crombag H, Schuurman K, Dieben J, et al. A cannabinoid mechanism in relapse to cocaine seeking. Nat Med. 2001;7:1151–4.
Ward SJ, Rosenberg M, Dykstra LA, Walker EA. The CB1 antagonist rimonabant (SR141716) blocks cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking and other context and extinction phenomena predictive of relapse. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009;105:248–55.
Carai MA, Colombo G, Gessa GL. Rimonabant: the first therapeutically relevant cannabinoid antagonist. Life Sci. 2005;77:2339–50.
Pacher P, Bátkai S, Osei-Hyiaman D, Offertáler L, Liu J, Harvey-White J, et al. Hemodynamic profile, responsiveness to anandamide, and baroreflex sensitivity of mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289:H533–41.
Rigotti NA, Gonzales D, Dale LC, Lawrence D, Chang Y. A randomized controlled trial of adding the nicotine patch to rimonabant for smoking cessation: efficacy, safety and weight gain. Addiction. 2009;104:266–76.
Padwal RS, Majumdar SR. Drug treatments for obesity: orlistat, sibutramine, and rimonabant. Lancet. 2007;369:71–7.
Leite CE, Mocelin CA, Petersen GO, Leal MB, Thiesen FV. Rimonabant: an antagonist drug of the endocannabinoid system for the treatment of obesity. Pharmacol Rep. 2009;61:217–24.
Van Gaal LF, Rissanen AM, Scheen AJ, Ziegler O, Rössner S. Effects of the cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker rimonabant on weight reduction and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight patients: 1-year experience from the RIO-Europe study. Lancet. 2005;365:1389–97.
Pi-Sunyer FX, Aronne LJ, Heshmati HM, Devin J, Rosenstock J. Effect of rimonabant, a cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker, on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight or obese patients: RIO-North America: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:761–75.
Chambers AP, Vemuri VK, Peng Y, Wood JT, Olszewska T, Pittman QJ, et al. A neutral CB1 receptor antagonist reduces weight gain in rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;293:R2185–93.
Proietto J, Rissanen A, Harp JB, Erondu N, Yu Q, Suryawanshi S, et al. A clinical trial assessing the safety and efficacy of the CB1R inverse agonist taranabant in obese and overweight patients: low-dose study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010;34:1243–54.
Sink KS, McLaughlin PJ, Wood JA, Brown C, Fan P, Vemuri VK, et al. The novel cannabinoid CB1 receptor neutral antagonist AM4113 suppresses food intake and food-reinforced behavior but does not induce signs of nausea in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:946–55.
Sink KS, Vemuri VK, Wood J, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD. Oral bioavailability of the novel cannabinoid CB1 antagonist AM6527: effects on food-reinforced behavior and comparisons with AM4113. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009;91:303–6.
Ruiu S, Pinna GA, Marchese G, Mussinu JM, Saba P, Tambaro S, et al. Synthesis and characterization of NESS 0327: a novel putative antagonist of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;306:363–70.
Seltzman HH, Maitra R, Bortoff K, Henson J, Reggio PH, Wesley D, et al. Metabolic profiling of CB1 neutral antagonists. Methods Enzymol. 2017;593:199–215.
Pavon FJ, Bilbao A, Hernández-Folgado L, Cippitelli A, Jagerovic N, Abellán G, et al. Antiobesity effects of the novel in vivo neutral cannabinoid receptor antagonist 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-hexyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole--LH 21. Neuropharmacology. 2006;51:358–66.
Järbe TU, LeMay BJ, Olszewska T, Vemuri VK, Wood JT, Makriyannis A. Intrinsic effects of AM4113, a putative neutral CB1 receptor selective antagonist, on open-field behaviors in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008;91:84–90.
Kangas BD, Delatte MS, Vemuri VK, Thakur GA, Nikas SP, Subramanian KV, et al. Cannabinoid discrimination and antagonism by CB(1) neutral and inverse agonist antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013;344:561–7.
Wills KL, Vemuri K, Kalmar A, Lee A, Limebeer CL, Makriyannis A, et al. CB1 antagonism: interference with affective properties of acute naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal in rats. Psychopharmacology. 2014;231:4291–300.
Balla A, Dong B, Shilpa BM, Vemuri K, Makriyannis A, Pandey SC, et al. Cannabinoid-1 receptor neutral antagonist reduces binge-like alcohol consumption and alcohol-induced accumbal dopaminergic signaling. Neuropharmacology. 2017;131:200–8.
Gueye AB, Pryslawsky Y, Trigo JM, Poulia N, Delis F, Antoniou K, et al. The CB1 neutral antagonist AM4113 retains the therapeutic efficacy of the inverse agonist rimonabant for nicotine dependence and weight loss with better psychiatric tolerability. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;19:pii:pyw068.
Schindler CW, Redhi GH, Vemuri K, Makriyannis A, Le Foll B, Bergman J, et al. Blockade of nicotine and cannabinoid reinforcement and relapse by a cannabinoid CB1-receptor neutral antagonist AM4113 and inverse agonist rimonabant in squirrel monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016;41:2283–93.
Kolodny A, Courtwright DT, Hwang CS, Kreiner P, Eadie JL, Clark TW, et al. The prescription opioid and heroin crisis: a public health approach to an epidemic of addiction. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:559–74.
Kalivas PW, Volkow ND. New medications for drug addiction hiding in glutamatergic neuroplasticity. Mol Psychiatry. 2011;16:974–86.
Storr MA, Bashashati M, Hirota C, Vemuri VK, Keenan CM, Duncan M, et al. Differential effects of CB(1) neutral antagonists and inverse agonists on gastrointestinal motility in mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;22:787–96, e223.
Gardner EL. Endocannabinoid signaling system and brain reward: emphasis on dopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005;81:263–84.
Xi ZX, Gilbert JG, Peng XQ, Pak AC, Li X, Gardner EL. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 inhibits cocaine-primed relapse in rats: role of glutamate in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci. 2006;26:8531–6.
O’Brien CP, Gardner EL. Critical assessment of how to study addiction and its treatment: human and non-human animal models. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;108:18–58.
Solinas M, Panlilio LV, Antoniou K, Pappas LA, Goldberg SR. The cannabinoid CB1 antagonist N-piperidinyl-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl) -4-methylpyrazole-3-carboxamide (SR-141716A) differentially alters the reinforcing effects of heroin under continuous reinforcement, fixed ratio, and progressive ratio schedules of drug self-administration in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;306:93–102.
Fattore L, Spano S, Cossu G, Deiana S, Fadda P, Fratta W. Cannabinoid CB(1) antagonist SR 141716A attenuates reinstatement of heroin self-administration in heroin-abstinent rats. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48:1097–104.
Alvarez-Jaimes L, Polis I, Parsons LH. Attenuation of cue-induced heroin-seeking behavior by cannabinoid CB1 antagonist infusions into the nucleus accumbens core and prefrontal cortex, but not basolateral amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:2483–93.
Cohen C, Kodas E, Griebel G. CB1 receptor antagonists for the treatment of nicotine addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005;81:387–95.
Shoaib M. The cannabinoid antagonist AM251 attenuates nicotine self-administration and nicotine-seeking behaviour in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2008;54:438–44.
Budzynska B, Kruk M, Biala G. Effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM 251 on the reinstatement of nicotine-conditioned place preference by drug priming in rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2009;61:304–10.
Simonnet A, Cador M, Caille S. Nicotine reinforcement is reduced by cannabinoid CB1 receptor blockade in the ventral tegmental area. Addict Biol. 2013;18:930–6.
Filip M, Gołda A, Zaniewska M, McCreary AC, Nowak E, Kolasiewicz W, et al. Involvement of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in drug addiction: effects of rimonabant on behavioral responses induced by cocaine. Pharmacol Rep. 2006;58:806–19.
Lesscher HM, Hoogveld E, Burbach JP, van Ree JM, Gerrits MA. Endogenous cannabinoids are not involved in cocaine reinforcement and development of cocaine-induced behavioural sensitization. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005;15:31–7.
Vinklerova J, Novakova J, Sulcova A. Inhibition of methamphetamine self-administration in rats by cannabinoid receptor antagonist AM 251. J Psychopharmacol. 2002;16:139–43.
Anggadiredja K, akamichi M, Hiranita T, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y, Watanabe S, et al. Endocannabinoid system modulates relapse to methamphetamine seeking: possible mediation by the arachidonic acid cascade. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:1470–8.
Hiranita T, Nawata Y, Sakimura K, Yamamoto T. Methamphetamine-seeking behavior is due to inhibition of nicotinic cholinergic transmission by activation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2008;55:1300–6.
Boctor SY, Martinez JL Jr., Koek W, France CP. The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 does not modify methamphetamine reinstatement of responding. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;571:39–43.
Wise RA. Addictive drugs and brain stimulation reward. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1996;19:319–40.
Fish EW, Riday TT, McGuigan MM, Faccidomo S, Hodge CW, Malanga CJ. Alcohol, cocaine, and brain stimulation-reward in C57Bl6/J and DBA2/J mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010;34:81–9.
Paxinos G & Watson C (1998) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program (IRP) of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) (Z1A DA000389), National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Author contributions
ELG, AM, Y-lW, and Z-xX designed the experiments. X-hH, KV, G-hB, and JZ performed the experiments. X-hH, CJJ, and Z-xX analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript with help from all other co-authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Xh., Jordan, C.J., Vemuri, K. et al. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor neutral antagonist AM4113 inhibits heroin self-administration without depressive side effects in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40, 365–373 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0059-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0059-x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cannabinoid CB1 receptor and mu-opioid receptor interaction: new insights from conditional knockout mice
Neuropsychopharmacology (2025)
-
AM6527, a neutral CB1 receptor antagonist, suppresses opioid taking and seeking, as well as cocaine seeking in rodents without aversive effects
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Therapeutic potential of PIMSR, a novel CB1 receptor neutral antagonist, for cocaine use disorder: evidence from preclinical research
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Endocannabinoid signaling regulates the reinforcing and psychostimulant effects of ketamine in mice
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Non-Opioid Treatments for Opioid Use Disorder: Rationales and Data to Date
Drugs (2020)