Abstract
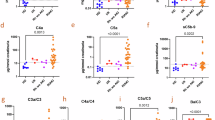
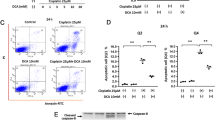
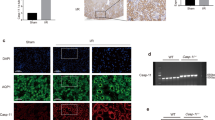
c-Myc plays an important role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and cell apoptosis. FasL/Fas pathway is a key regulator of cell apoptosis. This study was aimed to investigate the effects of c-Myc on the FasL/Fas pathway in ischemia-reperfusion (I/R)-induced renal injury. Rats were objected to bilateral renal ischemia for 60 min and reperfused for 24 or 48 h. NRK-52E cells were treated with hypoxia-reoxygenation (H/R) or FasL. Immunohistochemistry was used to identify the distribution of c-Myc. Cell apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL staining. Ad-c-Myc and recombinant pcDAN 3.0 were used to overexpress c-Myc and c-FLIP, respectively. ChIP assay and luciferase assay were used to detect the binding of c-Myc to c-FLIP promoter. In I/R rats, c-Myc was increased significantly and mainly located in renal tubular epithelial cells; meanwhile, c-FLIP was decreased, cleaved caspase-8, cleaved caspase-3 and TUNEL-positive staining cells were increased. Treatment of I/R rats with c-Myc inhibitor 10058-F4 significantly attenuated the decrease in c-FLIP, the increase in cleaved caspase-8, cleaved caspase-3, TUNEL-positive cells, Scr and BUN in I/R rats. In NRK-52E cells, hypoxia and reoxygen induced the increase in c-Myc and decrease in c-FLIP. ChIP and luciferase assay results indicated that c-Myc binds to the promoter region of c-FLIP gene. Overexpression of c-Myc markedly decreased c-FLIP. Overexpression of c-FLIP inhibited the increase in cleaved caspase-8 and caspase-3 induced by FasL. Data indicated that c-Myc is increased in kidneys of I/R rats and negatively regulates the expression of c-FLIP, then enhanced FasL-induced cell apoptosis in I/R stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Negi S, Koreeda D, Kobayashi S, Yano T, Tatsuta K, Mima T, et al. Acute kidney injury: epidemiology, outcomes, complications, and therapeutic strategies. Semin Dial. 2018;31:519–27.
Kanagasundaram NS. Pathophysiology of ischaemic acute kidney injury. Ann Clin Biochem. 2015;52:193–205.
Hoste EA, Clermont G, Kersten A, Venkataraman R, Angus DC, De Bacquer D, et al. RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury are associated with hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a cohort analysis. Crit Care. 2006;10:R73.
Requiao-Moura LR, Durao JMS, Matos AC, Pacheco-Silva A. Ischemia and reperfusion injury in renal transplantation: hemodynamic and immunological paradigms. Einst (Sao Paulo). 2015;13:129–35.
Zhang YL, Qiao SK, Wang RY, Guo XN. NGAL attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury through autophagy activation and apoptosis inhibition in rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;289:40–46.
Date T, Mochizuki S, Belanger AJ, Yamakawa M, Luo Z, Vincent KA, et al. Differential effects of membrane and soluble Fas ligand on cardiomyocytes: role in ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35:811–21.
Zheng M, Song D, Luo Z, Lu Z, Wu Y, Wang W. Effect of puerarin on expression of Fas/FasL mRNA in pulmonary injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rabbits. Nat Prod Commun. 2015;10:253–56.
Liu XM, Yang ZM, Liu XK. Fas/FasL induces myocardial cell apoptosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion rat model. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:2913–18.
Yin XH, Han YL, Zhuang Y, Yan JZ, Li C. Geldanamycin inhibits Fas signaling pathway and protects neurons against ischemia. Neurosci Res. 2017;124:33–39.
Filep JG. Attenuation of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury: silencing the Fas gene. Crit Care Med. 2016;44:1619–20.
Ko GJ, Jang HR, Huang Y, Womer KL, Liu M, Higbee E, et al. Blocking Fas ligand on leukocytes attenuates kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:732–42.
Nogae S, Miyazaki M, Kobayashi N, Saito T, Abe K, Saito H, et al. Induction of apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion model of mouse kidney: possible involvement of Fas. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:620–31.
Wang Y, Mu Y, Zhou X, Ji H, Gao X, Cai WW, et al. SIRT2-mediated FOXO3a deacetylation drives its nuclear translocation triggering FasL-induced cell apoptosis during renal ischemia reperfusion. Apoptosis. 2017;22:519–30.
Hamar P, Song E, Kokeny G, Chen A, Ouyang N, Lieberman J. Small interfering RNA targeting Fas protects mice against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:14883–88.
Del RM, Imam A, DeLeon M, Gomez G, Mishra J, Ma Q, et al. The death domain of kidney ankyrin interacts with Fas and promotes Fas-mediated cell death in renal epithelia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:41–51.
Safa AR. c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic regulator. Exp Oncol. 2012;34:176–84.
Bagnoli M, Canevari S, Mezzanzanica D. Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) signalling: a key regulator of receptor-mediated apoptosis in physiologic context and in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:210–13.
Du C, Guan Q, Yin Z, Zhong R, Jevnikar AM. IL-2-mediated apoptosis of kidney tubular epithelial cells is regulated by the caspase-8 inhibitor c-FLIP. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1397–409.
Dang CV. c-Myc target genes involved in cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:1–11.
Shen Y, Miao N, Wang B, Xu J, Gan X, Xu D, et al. c-Myc promotes renal fibrosis by inducing integrin alphav-mediated transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Kidney Int. 2017;92:888–99.
Rogers NM, Zhang ZJ, Wang JJ, Thomson AW, Isenberg JS. CD47 regulates renal tubular epithelial cell self-renewal and proliferation following renal ischemia reperfusion. Kidney Int. 2016;90:334–47.
Yilmaz S, Paavonen T, Hayry P. Chronic rejection of rat renal allografts. II. The impact of prolonged ischemia time on transplant histology. Transplantation. 1992;53:823–27.
Miao N, Wang B, Xu D, Wang Y, Gan X, Zhou L, et al. Caspase-11 promotes cisplatin-induced renal tubular apoptosis through a caspase-3-dependent pathway. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2018;314:F269–79.
Sun Z, Shen L, Sun X, Tong G, Sun D, Han T, et al. Variation of NDRG2 and c-Myc expression in rat heart during the acute stage of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Histochem Cell Biol. 2011;135:27–35.
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH, Peter ME. The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:1541–48.
Zhang JF, Shi LL, Zhang L, Zhao ZH, Liang F, Xu X, et al. MicroRNA-25 negatively regulates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced cell apoptosis through Fas/FasL pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 2016;58:507–16.
Patel JH, McMahon SB. BCL2 is a downstream effector of MIZ-1 essential for blocking c-MYC-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:5–13.
Järvinen K, Hotti A, Santos L, Nummela P, Hölttä E. Caspase-8, c-FLIP, and caspase-9 in c-Myc-induced apoptosis of fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317:2602–15.
Morrish F, Giedt C, Hockenbery D. c-MYC apoptotic function is mediated by NRF-1 target genes. Genes Dev. 2003;17:240–55.
Maclean KH, Keller UB, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Nilsson JA, Cleveland JL. c-Myc augments gamma irradiation-induced apoptosis by suppressing Bcl-XL. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:7256–70.
Nieminen AI, Partanen JI, Klefstrom J. c-Myc blazing a trail of death: coupling of the mitochondrial and death receptor apoptosis pathways by c-Myc. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:2464–72.
Juin P, Hunt A, Littlewood T, Griffiths B, Swigart LB, Korsmeyer S, et al. c-Myc functionally cooperates with Bax to induce apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:6158–69.
Dai MS, Jin Y, Gallegos JR, Lu H. Balance of Yin and Yang: ubiquitylation-mediated regulation of p53 and c-Myc. Neoplasia. 2006;8:630–44.
Eischen CM, Weber JD, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Cleveland JL. Disruption of the ARF-Mdm2-p53 tumor suppressor pathway in Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2658–69.
Boone DN, Qi Y, Li Z, Hann SR. Egr1 mediates p53-independent c-Myc-induced apoptosis via a noncanonical ARF-dependent transcriptional mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:632–37.
Tong X, O’Kelly J, Xie D, Mori A, Lemp N, McKenna R, et al. Cyr61 suppresses the growth of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via the beta-catenin-c-myc-p53 pathway. Oncogene. 2004;23:4847–55.
Kelly KJ, Plotkin Z, Vulgamott SL, Dagher PC. P53 mediates the apoptotic response to GTP depletion after renal ischemia-reperfusion: protective role of a p53 inhibitor. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:128–38.
Ying Y, Kim J, Westphal SN, Long KE, Padanilam BJ. Targeted deletion of p53 in the proximal tubule prevents ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:2707–16.
Gartel AL, Ye X, Goufman E, Shianov P, Hay N, Najmabadi F, et al. Myc represses thep21(WAF1/CIP1) promoter and interacts with Sp1/Sp3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:4510–15.
Madapura HS, Salamon D, Wiman KG, Lain S, Klein E, Nagy N. cMyc-p53 feedback mechanism regulates the dynamics of T lymphocytes in the immune response. Cell Cycle. 2016;15:1267–75.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos. 81670664, 81470591 to Li-min Lu, No. 81100531 to Wei Zhang and No. 81770718 to Xiao-xia Wang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L-m L, J L, H X, X-x W, W Z, D X, and B W designed the research project; D X, B W, P-p C, and F Y performed the experiments; Y-z W, N-j M, Z-l Z, L Z, Q C, and H-y X analyzed the data; L-m L, D X, and B W wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Wang, B., Chen, Pp. et al. c-Myc promotes tubular cell apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal injury by negatively regulating c-FLIP and enhancing FasL/Fas-mediated apoptosis pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40, 1058–1066 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0201-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0201-9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nuclear respiratory factor-1 promotes CFLAR transcription in H9C2 cardiomyocytes, protecting them against hypoxia-induced apoptosis
Molecular Biology Reports (2025)
-
STAT3 blockade ameliorates LPS-induced kidney injury through macrophage-driven inflammation
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Dichloroacetate reduces cisplatin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the JNK/14-3-3/Bax/caspase-9 pathway and suppressing caspase-8 activation via cFLIP in murine tubular cells
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Hexarelin alleviates apoptosis on ischemic acute kidney injury via MDM2/p53 pathway
European Journal of Medical Research (2023)
-
KLF4 initiates sustained YAP activation to promote renal fibrosis in mice after ischemia-reperfusion kidney injury
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2021)